C2 Topic 1 Can Do Sheet
... a arranged the elements, known at that time, in a periodic table by using properties of these elements and their compounds b used his table to predict the existence and properties of some elements not then discovered 1.2 Classify elements as metals or non-metals according to their position in the pe ...
... a arranged the elements, known at that time, in a periodic table by using properties of these elements and their compounds b used his table to predict the existence and properties of some elements not then discovered 1.2 Classify elements as metals or non-metals according to their position in the pe ...
200
... • Q Dalton said all atoms are identical. Right or wrong… explain. • A Wrong, isotopes are the same atom with different numbers of neutrons. ...
... • Q Dalton said all atoms are identical. Right or wrong… explain. • A Wrong, isotopes are the same atom with different numbers of neutrons. ...
Salesian High School Elements and atoms Chemistry quiz The
... 7) Which of the following is one of the statements that make up Dalton’s atomic theory? a) All atoms contain electrons. b) All atoms of a given element are identical. c) Atoms are divisible. d) Atoms gain and lose electrons in chemical reactions ...
... 7) Which of the following is one of the statements that make up Dalton’s atomic theory? a) All atoms contain electrons. b) All atoms of a given element are identical. c) Atoms are divisible. d) Atoms gain and lose electrons in chemical reactions ...
In a mass spectrometer, charged particles are injected into a
... region of uniform magnetic field (all with the same speed), where they travel along circular trajectories and, in this example, are collected after completing one-half of a complete circular orbit. If different mass isotopes are injected, they will trace different paths and be collected at different ...
... region of uniform magnetic field (all with the same speed), where they travel along circular trajectories and, in this example, are collected after completing one-half of a complete circular orbit. If different mass isotopes are injected, they will trace different paths and be collected at different ...
Document
... An industrially important element contains 26 electrons and rusts in the presence of air and moisture. Identify the element. ...
... An industrially important element contains 26 electrons and rusts in the presence of air and moisture. Identify the element. ...
nuclear chemistry notes 1
... Elements 93-110 are man-made radioactive elements. Since these man-made atoms are so big, they can be created by combining two smaller atoms together. The protons and neutrons combine into one large nucleus. ...
... Elements 93-110 are man-made radioactive elements. Since these man-made atoms are so big, they can be created by combining two smaller atoms together. The protons and neutrons combine into one large nucleus. ...
radioactive decay - Aurora City Schools
... – Always the same for an element; change the atomic number and you change the element ...
... – Always the same for an element; change the atomic number and you change the element ...
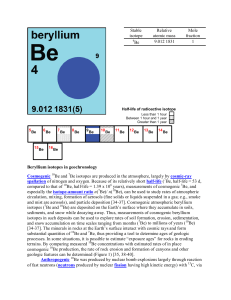
Rhenium isotopes in geochronology Stable isotope Relative atomic
... normal material – a reasonably possible source for an element or its compounds in commerce, for industry or science; the material is not itself studied for some extraordinary anomaly and its mole fractions (isotopic abundances) have not been modified significantly in a geologically brief period [4]. ...
... normal material – a reasonably possible source for an element or its compounds in commerce, for industry or science; the material is not itself studied for some extraordinary anomaly and its mole fractions (isotopic abundances) have not been modified significantly in a geologically brief period [4]. ...
Unit 2 Notes - School City of Hobart
... Nuclear reactions involve changes in atomic nuclei to generate energy. Nuclear Chemistry is the study of those reactions, with an emphasis on their uses in chemistry and their effects on biological systems 21.1 Radioactivity • Nucleon is simply another name for particles in the nucleus (proton/neutr ...
... Nuclear reactions involve changes in atomic nuclei to generate energy. Nuclear Chemistry is the study of those reactions, with an emphasis on their uses in chemistry and their effects on biological systems 21.1 Radioactivity • Nucleon is simply another name for particles in the nucleus (proton/neutr ...
Ch. 14.2 Notes
... 5. They are all carbon atoms because they all have six protons. These three kinds of carbon atoms are called _____________. 6. The isotopes of carbon are called _________________, ______________ and ________________. 7. The numbers tell _____________________________________________________________ _ ...
... 5. They are all carbon atoms because they all have six protons. These three kinds of carbon atoms are called _____________. 6. The isotopes of carbon are called _________________, ______________ and ________________. 7. The numbers tell _____________________________________________________________ _ ...
Worksheet
... 15. __________ He used the term “atomos” to describe an indivisible part at the base of all matter. 16. __________ He is the Father of the Atomic Theory. 17. __________ He designed a mathematical equation for the model of the atom. 18. __________ He determined the charge of the electron. 19. _______ ...
... 15. __________ He used the term “atomos” to describe an indivisible part at the base of all matter. 16. __________ He is the Father of the Atomic Theory. 17. __________ He designed a mathematical equation for the model of the atom. 18. __________ He determined the charge of the electron. 19. _______ ...
isotope - Aurora City Schools
... – Always the same for an element; change the atomic number and you change the element ...
... – Always the same for an element; change the atomic number and you change the element ...
Chapter 6 Review“The Periodic Table”
... Review“The Periodic Table” 1. How is the number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom calculated? 2. All atoms are neutral, with the number of protons equaling the ___. 3. Isotopes of the same element have different _____. 4. Using the periodic table, determine the number of neutrons in 16O. 5. What ...
... Review“The Periodic Table” 1. How is the number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom calculated? 2. All atoms are neutral, with the number of protons equaling the ___. 3. Isotopes of the same element have different _____. 4. Using the periodic table, determine the number of neutrons in 16O. 5. What ...
Atomic Structure
... Early Atomic Theory “Cosmic substance is made up of an infinite number of elements or particles ...
... Early Atomic Theory “Cosmic substance is made up of an infinite number of elements or particles ...
Isotope

Isotopes are variants of a particular chemical element which differ in neutron number, although all isotopes of a given element have the same number of protons in each atom. The term isotope is formed from the Greek roots isos (ἴσος ""equal"") and topos (τόπος ""place""), meaning ""the same place""; thus, the meaning behind the name it is that different isotopes of a single element occupy the same position on the periodic table. The number of protons within the atom's nucleus is called atomic number and is equal to the number of electrons in the neutral (non-ionized) atom. Each atomic number identifies a specific element, but not the isotope; an atom of a given element may have a wide range in its number of neutrons. The number of nucleons (both protons and neutrons) in the nucleus is the atom's mass number, and each isotope of a given element has a different mass number.For example, carbon-12, carbon-13 and carbon-14 are three isotopes of the element carbon with mass numbers 12, 13 and 14 respectively. The atomic number of carbon is 6, which means that every carbon atom has 6 protons, so that the neutron numbers of these isotopes are 6, 7 and 8 respectively.