Introduction to Radiation and Radioactivity
... Atomic nomenclature Atomic number = Z the number of protons in the atom. Determines which element it is. Atomic mass (or Mass number) = A the total number of protons and neutrons. A = Z + N (# of neutrons) ...
... Atomic nomenclature Atomic number = Z the number of protons in the atom. Determines which element it is. Atomic mass (or Mass number) = A the total number of protons and neutrons. A = Z + N (# of neutrons) ...
Nuclear Notes Introduction
... was originally formed. 4. nuclear binding energy- the energy that was released when a nucleus is formed from nucleons (E = mc2 ). It can also be thought of as the amount of energy required to break apart the nucleus; therefore, the nuclear binding energy is also a measure of the stability of a nucle ...
... was originally formed. 4. nuclear binding energy- the energy that was released when a nucleus is formed from nucleons (E = mc2 ). It can also be thought of as the amount of energy required to break apart the nucleus; therefore, the nuclear binding energy is also a measure of the stability of a nucle ...
The discovery of the natural radioactive decay of uranium in 1896 by
... leading to the development of nuclear fission and fusion as energy sources. A byproduct of this atomic research has been the development and continuing refinement of the various methods and techniques used to measure the age of Earth materials. Precise dating has been accomplished since 1950. A chem ...
... leading to the development of nuclear fission and fusion as energy sources. A byproduct of this atomic research has been the development and continuing refinement of the various methods and techniques used to measure the age of Earth materials. Precise dating has been accomplished since 1950. A chem ...
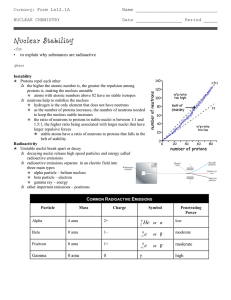
Nuclear Stability
... q the higher the atomic number is, the greater the repulsion among protons is, making the nucleus unstable p atoms with atomic numbers above 82 have no stable isotopes q neutrons help to stabilize the nucleus p hydrogen is the only element that does not have neutrons p as the number of protons incre ...
... q the higher the atomic number is, the greater the repulsion among protons is, making the nucleus unstable p atoms with atomic numbers above 82 have no stable isotopes q neutrons help to stabilize the nucleus p hydrogen is the only element that does not have neutrons p as the number of protons incre ...
Chapter 3 – Atomic Structure - Mercer Island School District
... – Law of Constant Composition – compounds contain the same elements always in the same proportions. ...
... – Law of Constant Composition – compounds contain the same elements always in the same proportions. ...
Chemistry Review: Antoine Lavoisier (1743
... the same number of electrons, their chemical properties will be exactly the same. However, they have different masses due to the different number of neutrons; therefore, they will have slightly different properties that relate to mass. (Ex. Density , melting and boiling point). Also. Since the neutr ...
... the same number of electrons, their chemical properties will be exactly the same. However, they have different masses due to the different number of neutrons; therefore, they will have slightly different properties that relate to mass. (Ex. Density , melting and boiling point). Also. Since the neutr ...
Name
... 9. The conversion of an atomic nucleus of one element into an atomic nucleus of another element through a loss or gain in the number of protons. 10. High-energy radiation emitted by the nuclei of radioactive atoms. 11. Nuclear fusion produced by high temperature. Down 2. The force of interaction bet ...
... 9. The conversion of an atomic nucleus of one element into an atomic nucleus of another element through a loss or gain in the number of protons. 10. High-energy radiation emitted by the nuclei of radioactive atoms. 11. Nuclear fusion produced by high temperature. Down 2. The force of interaction bet ...
Chapter 4 Study Guide Physical Science 1. The word atom comes
... 2. Halogens are very reactive elements located in Group _______of the periodic table. 3. The nucleus of an atom has a(n) ____________________ electric charge. 4. Carbon is found in group ______ of the periodic table. 5. Bohr’s model of the atom compares electrons to ____________________. 6. Elements ...
... 2. Halogens are very reactive elements located in Group _______of the periodic table. 3. The nucleus of an atom has a(n) ____________________ electric charge. 4. Carbon is found in group ______ of the periodic table. 5. Bohr’s model of the atom compares electrons to ____________________. 6. Elements ...
Abstract
... Our solar system is made up with a variety of elements having atomic weight from 1 to over 300 u. In the Sun, only He is produced from H through the nuclear fusion reactions. Therefore, most elements heavier than He were already present in the beginning of solar system and had been produced in stars ...
... Our solar system is made up with a variety of elements having atomic weight from 1 to over 300 u. In the Sun, only He is produced from H through the nuclear fusion reactions. Therefore, most elements heavier than He were already present in the beginning of solar system and had been produced in stars ...
Atomic Structure
... Electrons in the atom are to be found 90% of the time in 3D regions called orbitals THE BOHR ATOM When an electron transitions from the excited to the ground state, the atom loses energy When an electron transitions from the ground to the excited state, the atom absorbs energy Ground State Electron ...
... Electrons in the atom are to be found 90% of the time in 3D regions called orbitals THE BOHR ATOM When an electron transitions from the excited to the ground state, the atom loses energy When an electron transitions from the ground to the excited state, the atom absorbs energy Ground State Electron ...
3-2 Radioactivity and the nucleus
... He concluded that most of the atom is made of ‘empty space’, and that the core of the atom carried a positive charge (he called the core nucleus and the positive charges the protons). ...
... He concluded that most of the atom is made of ‘empty space’, and that the core of the atom carried a positive charge (he called the core nucleus and the positive charges the protons). ...
10.2
... ‘empty space’, and that the core of the atom carried a positive charge (he called the core nucleus and the positive charges the protons). • He also suggested that electrons orbit the nucleus like planets orbit the Sun (Fig.3 p.281). ...
... ‘empty space’, and that the core of the atom carried a positive charge (he called the core nucleus and the positive charges the protons). • He also suggested that electrons orbit the nucleus like planets orbit the Sun (Fig.3 p.281). ...
atomic number - Thomas C. Cario Middle School
... The periodic table is a chart containing information about the atoms that make up all matter. An element is a substance made up of only one type of atom. The atomic number of an atom is equal to the number of protons in its nucleus. The number of electrons surrounding the nucleus of an atom is equal ...
... The periodic table is a chart containing information about the atoms that make up all matter. An element is a substance made up of only one type of atom. The atomic number of an atom is equal to the number of protons in its nucleus. The number of electrons surrounding the nucleus of an atom is equal ...
Atoms and Isotopes Worksheet
... 3. The atomic masses of two isotopes of Cobalt are 59 and 60. If Cobalt has 27 electrons, what is the number of protons and neutrons in each isotope? ...
... 3. The atomic masses of two isotopes of Cobalt are 59 and 60. If Cobalt has 27 electrons, what is the number of protons and neutrons in each isotope? ...
Isotopes and Ions - Wando High School
... Two isotopes of an element will have the same atomic number, but different mass numbers (and atomic masses) CARBON (above right) 1. What is the mass number to the left? 2. What is the mass number to the right? 3. What is the atomic number to the left? 4. What is the atomic number to the right? ...
... Two isotopes of an element will have the same atomic number, but different mass numbers (and atomic masses) CARBON (above right) 1. What is the mass number to the left? 2. What is the mass number to the right? 3. What is the atomic number to the left? 4. What is the atomic number to the right? ...
Isotope

Isotopes are variants of a particular chemical element which differ in neutron number, although all isotopes of a given element have the same number of protons in each atom. The term isotope is formed from the Greek roots isos (ἴσος ""equal"") and topos (τόπος ""place""), meaning ""the same place""; thus, the meaning behind the name it is that different isotopes of a single element occupy the same position on the periodic table. The number of protons within the atom's nucleus is called atomic number and is equal to the number of electrons in the neutral (non-ionized) atom. Each atomic number identifies a specific element, but not the isotope; an atom of a given element may have a wide range in its number of neutrons. The number of nucleons (both protons and neutrons) in the nucleus is the atom's mass number, and each isotope of a given element has a different mass number.For example, carbon-12, carbon-13 and carbon-14 are three isotopes of the element carbon with mass numbers 12, 13 and 14 respectively. The atomic number of carbon is 6, which means that every carbon atom has 6 protons, so that the neutron numbers of these isotopes are 6, 7 and 8 respectively.