Document
... a) The mass of a proton is greater than the mass of an electron. b) A proton is positively charged and an electron is negatively charged. c) Most of the atom’s volume is the sphere-shaped cloud of electrons d) One or more neutrons in the nucleus add mass to the atom. ...
... a) The mass of a proton is greater than the mass of an electron. b) A proton is positively charged and an electron is negatively charged. c) Most of the atom’s volume is the sphere-shaped cloud of electrons d) One or more neutrons in the nucleus add mass to the atom. ...
Atoms, compounds and elements - Mrs. Tes de Luna`s Science Class
... ◦ The first part of his theory states that all matter is made of atoms, which are indivisible. ◦ The second part of the theory says all atoms of a given element are identical in mass and properties. ◦ The third part says compounds are combinations of two or more different types of atoms. ◦ The fourt ...
... ◦ The first part of his theory states that all matter is made of atoms, which are indivisible. ◦ The second part of the theory says all atoms of a given element are identical in mass and properties. ◦ The third part says compounds are combinations of two or more different types of atoms. ◦ The fourt ...
Joseph John Thomson 1856-1940
... Rutherford and he was the first to elucidate the related concepts of the half-life and decay constant. With Frederick Soddy at McGill University, Rutherford showed that elements such as uranium and thorium became different elements (i.e., transmuted) through the process of radioactive decay. At the ...
... Rutherford and he was the first to elucidate the related concepts of the half-life and decay constant. With Frederick Soddy at McGill University, Rutherford showed that elements such as uranium and thorium became different elements (i.e., transmuted) through the process of radioactive decay. At the ...
File
... 11. What are the rows in the periodic table called and what do they show? periods 12. Using the periodic table, find the element that is found in group 2 period 3. ...
... 11. What are the rows in the periodic table called and what do they show? periods 12. Using the periodic table, find the element that is found in group 2 period 3. ...
SCIENCE 9
... ELECTROLYSIS- the process of decomposing a chemical compound by passing an electric current through it ELEMENT- is a pure substance made up of one type of particle, or atom. Eache element has its own distinct properties and cannot be broken down into simpler substances by means of a chemical change ...
... ELECTROLYSIS- the process of decomposing a chemical compound by passing an electric current through it ELEMENT- is a pure substance made up of one type of particle, or atom. Eache element has its own distinct properties and cannot be broken down into simpler substances by means of a chemical change ...
Hpsxray - Nucleonica
... and he was the first to elucidate the related concepts of the half-life and decay constant. With Frederick Soddy at McGill University, Rutherford showed that elements such as uranium and thorium became different elements (i.e., transmuted) through the process of radioactive decay. At the time, such ...
... and he was the first to elucidate the related concepts of the half-life and decay constant. With Frederick Soddy at McGill University, Rutherford showed that elements such as uranium and thorium became different elements (i.e., transmuted) through the process of radioactive decay. At the time, such ...
Notes matter energy
... Chemical properties describe the chemical reactions that a substance could undergo (or not undergo), meaning that the composition of elements changes. Physical change means to change the physical state or shape of a substance without changing its chemical composition. Chemical change means that a ch ...
... Chemical properties describe the chemical reactions that a substance could undergo (or not undergo), meaning that the composition of elements changes. Physical change means to change the physical state or shape of a substance without changing its chemical composition. Chemical change means that a ch ...
Document
... This claim is false because it — F violates the principle of constant composition G contradicts the law of conservation of matter H ignores the strength of the theory of strings J violates the rules of gravitational attraction ...
... This claim is false because it — F violates the principle of constant composition G contradicts the law of conservation of matter H ignores the strength of the theory of strings J violates the rules of gravitational attraction ...
Nuclear Chemistry
... Nuclear energy An ion is a “charged atom” or group of atoms. Ionization occurs when electrons are removed from atoms by a, b or g radiation. This can result in damage to your body. ...
... Nuclear energy An ion is a “charged atom” or group of atoms. Ionization occurs when electrons are removed from atoms by a, b or g radiation. This can result in damage to your body. ...
Fundamentals of Chemistry
... Figure 2.13 (Zumdahl) (a) Expected Results of the Metal Foil Experiment if Thomson's Model Were Correct (b) Actual Results ...
... Figure 2.13 (Zumdahl) (a) Expected Results of the Metal Foil Experiment if Thomson's Model Were Correct (b) Actual Results ...
6.1 ATOMS, ELEMENTS, and COMPOUNDS
... by covalent bonds. • Can be a single, double, or triple bond depending on number of pairs of electrons shared. 2_____________________—forms when atom gives up electrons and another receives electrons in order to become stable • Electrical attraction between two oppositely charged atoms or groups of ...
... by covalent bonds. • Can be a single, double, or triple bond depending on number of pairs of electrons shared. 2_____________________—forms when atom gives up electrons and another receives electrons in order to become stable • Electrical attraction between two oppositely charged atoms or groups of ...
Atomic Structure
... • Cations – positively charged due to loss of electrons. • Anions – negatively charged due to gain of electrons. ...
... • Cations – positively charged due to loss of electrons. • Anions – negatively charged due to gain of electrons. ...
Atoms and Elements: Are they Related?
... means they are in nature and not made in a laboratory by scientists. • As of this year (2011) there are 118 confirmed elements. There are 4 more under investigation and ...
... means they are in nature and not made in a laboratory by scientists. • As of this year (2011) there are 118 confirmed elements. There are 4 more under investigation and ...
matter and its reactivity. Objects in the universe are composed of
... reaction matter cannot be created or destroyed. The total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products Develop models to explain common chemical reactions and changes in states of matter. ...
... reaction matter cannot be created or destroyed. The total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products Develop models to explain common chemical reactions and changes in states of matter. ...
Name Date: __ ______ Chemistry Semester I Final Exam Review
... 48. The half-life of phosphorous-30 is 2.5 min. If you start with 35 g of phosphorus-30, how many grams would remain after 20.0 min? ...
... 48. The half-life of phosphorous-30 is 2.5 min. If you start with 35 g of phosphorus-30, how many grams would remain after 20.0 min? ...
Unit 3 Notes
... Radioactivity is the process of nuclear decay, in which an unstable nucleus gives off matter and energy. Nuclei with too many or too few neutrons compared to the number of protons are radioactive. The three types of nuclear radiation are alpha, beta, and ...
... Radioactivity is the process of nuclear decay, in which an unstable nucleus gives off matter and energy. Nuclei with too many or too few neutrons compared to the number of protons are radioactive. The three types of nuclear radiation are alpha, beta, and ...
nuclear physics - The Physics Cafe
... Energy will be released if a nucleus with a mass number less than about 80 undergoes fission as a result of particle bombardment. ...
... Energy will be released if a nucleus with a mass number less than about 80 undergoes fission as a result of particle bombardment. ...
nature of Matter
... atomic number. Example: H has an atomic number of 1 so, it has only 1 proton in its nucleus and consequently, 1 electron. The mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus. Examples: Potassium-39 (19 protons & 20 neutrons) Uranium-235 (92 protons & 143 neutrons) ...
... atomic number. Example: H has an atomic number of 1 so, it has only 1 proton in its nucleus and consequently, 1 electron. The mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus. Examples: Potassium-39 (19 protons & 20 neutrons) Uranium-235 (92 protons & 143 neutrons) ...
Lecture 1 – Matter, Atomic Structure
... A mixture is a combination of two or more substances in which the substances retain their distinct identities. 1. Homogenous mixture – composition of the mixture is the same throughout soft drink, milk, solder 2. Heterogeneous mixture – composition is not uniform throughout cement, iron filings in ...
... A mixture is a combination of two or more substances in which the substances retain their distinct identities. 1. Homogenous mixture – composition of the mixture is the same throughout soft drink, milk, solder 2. Heterogeneous mixture – composition is not uniform throughout cement, iron filings in ...
Chemistry Test Review - Greenslime Home Page
... a. Atom – the smallest part of an element that still acts like that element; can’t be broken down; basic part of matter b. Element – a substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances containing only 1 type of atom c. Compound – two or more different elements chemically combined d. Molec ...
... a. Atom – the smallest part of an element that still acts like that element; can’t be broken down; basic part of matter b. Element – a substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances containing only 1 type of atom c. Compound – two or more different elements chemically combined d. Molec ...
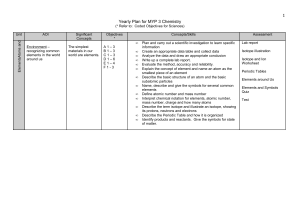
Yearly Plan for MYP 1 Science
... elements Define atomic number and mass number Interpret chemical notation for elements, atomic number, mass number, charge and how many atoms Describe the term isotope and illustrate an isotope, showing its protons, neutrons and electrons Describe the Periodic Table and how it is organized Identify ...
... elements Define atomic number and mass number Interpret chemical notation for elements, atomic number, mass number, charge and how many atoms Describe the term isotope and illustrate an isotope, showing its protons, neutrons and electrons Describe the Periodic Table and how it is organized Identify ...
Module 6 Chemical Reactions
... the neutrons released by each fission can strike other nuclei; this is called a chain reaction. • As in a nuclear reactor or a nuclear bomb, there are many more millions of uranium nuclei, so more reactions that can be triggered. • In a nuclear reactor, the chain reaction is controlled. Devices call ...
... the neutrons released by each fission can strike other nuclei; this is called a chain reaction. • As in a nuclear reactor or a nuclear bomb, there are many more millions of uranium nuclei, so more reactions that can be triggered. • In a nuclear reactor, the chain reaction is controlled. Devices call ...
E = mc 2 - Gordon State College
... Dividing the mass of a nucleus by the number of nucleons in the nucleus gives the mass per nucleon. Graph of nuclear mass per nucleon inside each nucleus versus atomic number from hydrogen to uranium: • greatest mass per nucleon occurs for hydrogen, because it has no binding energy to pull its mass ...
... Dividing the mass of a nucleus by the number of nucleons in the nucleus gives the mass per nucleon. Graph of nuclear mass per nucleon inside each nucleus versus atomic number from hydrogen to uranium: • greatest mass per nucleon occurs for hydrogen, because it has no binding energy to pull its mass ...