Classification of Matter
... Also the original solid (HgO) and the product (Hg) are not the same colour. HgO is red and Hg is shiny and silvery. We have gas escaping (as suggested by the loss in solid mass: 432 vs. 400g) and a solid that is different from the original (difference in colour); the combination of these two observ ...
... Also the original solid (HgO) and the product (Hg) are not the same colour. HgO is red and Hg is shiny and silvery. We have gas escaping (as suggested by the loss in solid mass: 432 vs. 400g) and a solid that is different from the original (difference in colour); the combination of these two observ ...
Extra revision sheet quarter 2 Physical science Grade 9
... 1. When an object covers equal distances in equal amounts of time, it is moving at a(n) ____________________ speed. 2. Velocity describes both speed and ____________________. 3. Because the speed of an object can change from one instant to the next, dividing the total distance covered by the time of ...
... 1. When an object covers equal distances in equal amounts of time, it is moving at a(n) ____________________ speed. 2. Velocity describes both speed and ____________________. 3. Because the speed of an object can change from one instant to the next, dividing the total distance covered by the time of ...
Physics HW Chapters 383940 (Due May 23, Test May 28)
... a. changes, and so does its mass number. b. changes, but its mass number remains constant. c. remains constant, and so does its mass number. d. remains constant, but its mass number changes. e. none of the above. ____ 61. When uranium (92 protons) ejects an alpha particle, the nucleus left behind ha ...
... a. changes, and so does its mass number. b. changes, but its mass number remains constant. c. remains constant, and so does its mass number. d. remains constant, but its mass number changes. e. none of the above. ____ 61. When uranium (92 protons) ejects an alpha particle, the nucleus left behind ha ...
Atomic Origins: Chapter Problems Big Bang Class Work 1. How old
... This element has a radioactive isotope (X6) with a half-life of 80.4 milliseconds. How long will it take for 60 g of the substance to decay to 3.75 g? e. This element was generated through a fusion reaction. Where in the universe did this fusion reaction occur? 3. Hydrogen has two stable isotopes, h ...
... This element has a radioactive isotope (X6) with a half-life of 80.4 milliseconds. How long will it take for 60 g of the substance to decay to 3.75 g? e. This element was generated through a fusion reaction. Where in the universe did this fusion reaction occur? 3. Hydrogen has two stable isotopes, h ...
SOME BASIC CHEMICAL TERMS
... encounter. Matter, the material of which the universe is composed, may be defined as anything that occupies space and has mass. Most of the materials we encounter in our daily lives, such as air, milk, and steel, are mixtures. Mixtures contain two or more substances that can be physically separated ...
... encounter. Matter, the material of which the universe is composed, may be defined as anything that occupies space and has mass. Most of the materials we encounter in our daily lives, such as air, milk, and steel, are mixtures. Mixtures contain two or more substances that can be physically separated ...
THE ATOMIC NUCLEUS AND RADIOACTIVITY
... energy equivalence. Particles decay spontaneously only when their combined products have less mass after decay than before. The mass of a neutron is slightly greater than the total mass of a proton plus electron (and the antineutrino). So when a neutron decays, there is less mass after decay than be ...
... energy equivalence. Particles decay spontaneously only when their combined products have less mass after decay than before. The mass of a neutron is slightly greater than the total mass of a proton plus electron (and the antineutrino). So when a neutron decays, there is less mass after decay than be ...
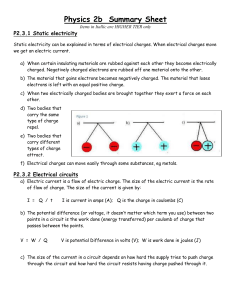
Static electricity
... a) Nuclear fusion is the joining of two atomic nuclei to form a larger one. The early universe only contained hydrogen but fusion has made more elements. b) Nuclear fusion is the process by which energy is released in stars. c) Stars form when enough dust and gas from space is pulled together by gra ...
... a) Nuclear fusion is the joining of two atomic nuclei to form a larger one. The early universe only contained hydrogen but fusion has made more elements. b) Nuclear fusion is the process by which energy is released in stars. c) Stars form when enough dust and gas from space is pulled together by gra ...
Chapter 4.1 and 4.2 - science-b
... Atoms are composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and neutrons are found in the tiny nucleus of the atom . The cloud that they form is the majority of the atom’s size. ...
... Atoms are composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and neutrons are found in the tiny nucleus of the atom . The cloud that they form is the majority of the atom’s size. ...
how did we find out about nuclear power? isaac asimov
... Rutherford began another kind of experiment. He let flying alpha particles from radioactive substances hit a thin sheet of gold foil. The alpha particles al- most always went through the foil without trouble. When they did, they hit a photographic plate on the other side of the foil and darkened it, ...
... Rutherford began another kind of experiment. He let flying alpha particles from radioactive substances hit a thin sheet of gold foil. The alpha particles al- most always went through the foil without trouble. When they did, they hit a photographic plate on the other side of the foil and darkened it, ...
Chapter 5 – Chemical Reactions
... Nuclear change – change in the nucleus of an atom (This will cause one element to change into another.) Examples: nuclear power plants, atomic bombs or radioactive decay ...
... Nuclear change – change in the nucleus of an atom (This will cause one element to change into another.) Examples: nuclear power plants, atomic bombs or radioactive decay ...
8.P.1.1Homework for Website
... A. The atomic size of the elements decreases from left to right and increases from top to bottom B. The atomic size of the elements increases from left to right and increases from top to bottom C. The atomic size of the elements decreases from left to right and decreases from top to bottom 16. Which ...
... A. The atomic size of the elements decreases from left to right and increases from top to bottom B. The atomic size of the elements increases from left to right and increases from top to bottom C. The atomic size of the elements decreases from left to right and decreases from top to bottom 16. Which ...
Physics 3 - Westmount High School
... WWII, the secret project that built the first atomic bombs. One of the uranium isotopes (Uranium235, which has a mass of 235 atomic mass units) is a useful chemical element to split into lighter elements. This split releases enough energy to trigger the chain reaction required for a nuclear bomb. Ho ...
... WWII, the secret project that built the first atomic bombs. One of the uranium isotopes (Uranium235, which has a mass of 235 atomic mass units) is a useful chemical element to split into lighter elements. This split releases enough energy to trigger the chain reaction required for a nuclear bomb. Ho ...
Atomic Energy for Military Purposes
... natural alpha particles from polonium fell on certain of the light elements, specifically beryllium, boron, or lithium, an unusually penetrating radiation was produced. At first this radiation was thought to be gamma radiation although it was more penetrating than any gamma rays known, and the detai ...
... natural alpha particles from polonium fell on certain of the light elements, specifically beryllium, boron, or lithium, an unusually penetrating radiation was produced. At first this radiation was thought to be gamma radiation although it was more penetrating than any gamma rays known, and the detai ...
Chapter 10
... beta particle, what new element results? a. The same element with the same mass b. One with both atomic number and atomic mass reduced by 1 c. One with atomic number increased by 1 and atomic mass reduced by 1 d. One with atomic mass increased by 1 and no change in atomic mass Explanation: Beta emis ...
... beta particle, what new element results? a. The same element with the same mass b. One with both atomic number and atomic mass reduced by 1 c. One with atomic number increased by 1 and atomic mass reduced by 1 d. One with atomic mass increased by 1 and no change in atomic mass Explanation: Beta emis ...
Teacher Materials - Scope, Sequence, and Coordination
... Radioactivity and its Applications. (a) Students should develop an understanding of average lifetime for a radioactive material expressed in terms of half-life (1.433T1/2). They should use results of such calculations for various radioactive materials to consider implications for radioactive wastes. ...
... Radioactivity and its Applications. (a) Students should develop an understanding of average lifetime for a radioactive material expressed in terms of half-life (1.433T1/2). They should use results of such calculations for various radioactive materials to consider implications for radioactive wastes. ...
A Thumbnail Review of Regents Chemistry
... Transmutation = Nuclear Change Natural Transmutation = Decay = Table N = 1 reactant: 19779Au 0-1e + 19780Hg Artificial Transmutation = 2 reactants: 147N +10n 146C + 11p Radioisotope = unstable nucleus Atomic # 84 and above = only radioactive isotopes 1 ½ ¼ 1/8 = 3 half live events Half-Lif ...
... Transmutation = Nuclear Change Natural Transmutation = Decay = Table N = 1 reactant: 19779Au 0-1e + 19780Hg Artificial Transmutation = 2 reactants: 147N +10n 146C + 11p Radioisotope = unstable nucleus Atomic # 84 and above = only radioactive isotopes 1 ½ ¼ 1/8 = 3 half live events Half-Lif ...
Preview Sample 1
... Refer to the periodic table and find where the elements are located. The farther they are to the left of the metal-nonmetal transition line (“zigzag” line), the more metallic they are. Elements to the right of this line are nonmetals. Another way of thinking of this is that the farther left in a per ...
... Refer to the periodic table and find where the elements are located. The farther they are to the left of the metal-nonmetal transition line (“zigzag” line), the more metallic they are. Elements to the right of this line are nonmetals. Another way of thinking of this is that the farther left in a per ...
catch some rays: alpha, beta, gamma (modified for adeed)
... 9. Pull apart an exploding pull-string popper. Discuss what made the sound and where that energy came from. Explain that in each example, energy was released, but that no matter was changed. These are chemical reactions, not nuclear. The difference is, in a nuclear reaction matter is actually chang ...
... 9. Pull apart an exploding pull-string popper. Discuss what made the sound and where that energy came from. Explain that in each example, energy was released, but that no matter was changed. These are chemical reactions, not nuclear. The difference is, in a nuclear reaction matter is actually chang ...
Gr 10 Review sheet chemistry
... 1. Change of________________ 2. Formation of a ________________ 3. Formation of _____________ 4. Release or absorption of_____________ ...
... 1. Change of________________ 2. Formation of a ________________ 3. Formation of _____________ 4. Release or absorption of_____________ ...
File
... 7. Heat of fusion (Hf)is the energy needed to convert one gram of a substance from solid to liquid. 8. Heat of vaporization (Hv) is the energy needed to convert one gram of a substance from liquid to gas. 9. Specific heat (C) is the energy required to raise one gram of a substance 1 degree (Celcius ...
... 7. Heat of fusion (Hf)is the energy needed to convert one gram of a substance from solid to liquid. 8. Heat of vaporization (Hv) is the energy needed to convert one gram of a substance from liquid to gas. 9. Specific heat (C) is the energy required to raise one gram of a substance 1 degree (Celcius ...
What You Need To Know for the Chemistry Regents
... 7. Heat of fusion (Hf)is the energy needed to convert one gram of a substance from solid to liquid. 8. Heat of vaporization (Hv) is the energy needed to convert one gram of a substance from liquid to gas. 9. Specific heat (C) is the energy required to raise one gram of a substance 1 degree (Celcius ...
... 7. Heat of fusion (Hf)is the energy needed to convert one gram of a substance from solid to liquid. 8. Heat of vaporization (Hv) is the energy needed to convert one gram of a substance from liquid to gas. 9. Specific heat (C) is the energy required to raise one gram of a substance 1 degree (Celcius ...
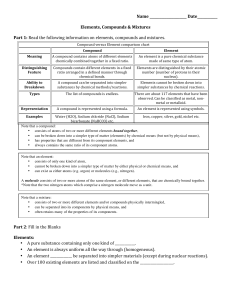
Compound vs Element chart
... • Mixtures can be uniform (called ________________________) and are known as solutions. • Mixtures can also be non-uniform (called ________________________). • Mixtures can be separated into their components by chemical or physical means. • The properties of a mixture are similar to the properti ...
... • Mixtures can be uniform (called ________________________) and are known as solutions. • Mixtures can also be non-uniform (called ________________________). • Mixtures can be separated into their components by chemical or physical means. • The properties of a mixture are similar to the properti ...
Intro to Atoms - Freehold Borough Schools
... change into another substance. Reactivity: The speed in which an element combines or reacts with other elements Corrosion: the wearing away of metal due to a chemical reaction Metals can be considered an alloy which is a mixture of a metal with one other element (usually found together in nature) ...
... change into another substance. Reactivity: The speed in which an element combines or reacts with other elements Corrosion: the wearing away of metal due to a chemical reaction Metals can be considered an alloy which is a mixture of a metal with one other element (usually found together in nature) ...
ATOMS, MOLECULES and IONS
... In a simple ion, one nucleus is present, but the species carries a charge because the number of electrons does not equal the +ve charge on the nucleus. This means that the atom has either lost or gained one or more electrons........ A gain of electrons results in a negatively charged ion; known as a ...
... In a simple ion, one nucleus is present, but the species carries a charge because the number of electrons does not equal the +ve charge on the nucleus. This means that the atom has either lost or gained one or more electrons........ A gain of electrons results in a negatively charged ion; known as a ...