An Overview of Organic Reactions
... organic solvent Biological reactions in aqueous medium inside cells They are promoted by catalysts that lower the activation barrier The catalysts are usually proteins, called enzymes Enzymes provide an alternative mechanism that is compatible with the conditions of life ...
... organic solvent Biological reactions in aqueous medium inside cells They are promoted by catalysts that lower the activation barrier The catalysts are usually proteins, called enzymes Enzymes provide an alternative mechanism that is compatible with the conditions of life ...
Empirical Formula
... Net Ionic Equations • After you cross out your spectator ions, you are left with a Net Ionic Equation, typically resulting in a “precipitate” ...
... Net Ionic Equations • After you cross out your spectator ions, you are left with a Net Ionic Equation, typically resulting in a “precipitate” ...
File
... is used for all saturated hydrocarbons. This is important to remember because later other endings will be used for other functional groups. 2. Alkanes without branches are named according to the number of carbon atoms. ...
... is used for all saturated hydrocarbons. This is important to remember because later other endings will be used for other functional groups. 2. Alkanes without branches are named according to the number of carbon atoms. ...
Students will review concepts from their quiz and then correct it at
... A pure substance containing two or more kinds of __atoms__. The atoms are ___chemically___ combined in some way. Often times (but not always) they come together to form groups of atoms called molecules. A compound is always homogeneous (uniform). Compounds ___cannot___ be separated by physical means ...
... A pure substance containing two or more kinds of __atoms__. The atoms are ___chemically___ combined in some way. Often times (but not always) they come together to form groups of atoms called molecules. A compound is always homogeneous (uniform). Compounds ___cannot___ be separated by physical means ...
Unit 3C Standards for Quiz
... 1. The Periodic Table displays the elements in increasing atomic number and shows how periodicity of the physical and chemical properties of the elements relates to atomic structure. As a basis for understanding this concept, students know: e. the nucleus is much smaller in size than the atom yet co ...
... 1. The Periodic Table displays the elements in increasing atomic number and shows how periodicity of the physical and chemical properties of the elements relates to atomic structure. As a basis for understanding this concept, students know: e. the nucleus is much smaller in size than the atom yet co ...
Ch 2 Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... - Polyatomic ions have a charge and consist of two or more atoms bonded together. See Table 2.6. - They are primarily anions, but there are two polyatomic cations: Ammonium is NH4+1 and mercury (I) is Hg22+ - Oxoanions contain oxygen along with another element. Oxygen (almost) always has –2 charge. ...
... - Polyatomic ions have a charge and consist of two or more atoms bonded together. See Table 2.6. - They are primarily anions, but there are two polyatomic cations: Ammonium is NH4+1 and mercury (I) is Hg22+ - Oxoanions contain oxygen along with another element. Oxygen (almost) always has –2 charge. ...
12-3: Lewis Structures
... Lewis structures—represent valence electrons; use dots placed around the chemical symbol All atoms want to achieve a noble gas configuration o Octet Rule—most elements will be surrounded by 8 dots, representing noble gas configuration Hydrogen is full with 2 electrons (2 dots on one side)—so i ...
... Lewis structures—represent valence electrons; use dots placed around the chemical symbol All atoms want to achieve a noble gas configuration o Octet Rule—most elements will be surrounded by 8 dots, representing noble gas configuration Hydrogen is full with 2 electrons (2 dots on one side)—so i ...
Chemical Reactions
... • Product – what is made during the chemical reaction • Law of conservation of mass (or matter)- mass is neither created or destroyed in ordinary chemical or physical changes • Subscript - number (representing atoms) written below and to the right of a chemical symbol ...
... • Product – what is made during the chemical reaction • Law of conservation of mass (or matter)- mass is neither created or destroyed in ordinary chemical or physical changes • Subscript - number (representing atoms) written below and to the right of a chemical symbol ...
AP Chemistry Placement Test To be successful in AP Chemistry
... chemistry and math through Algebra 2. This placement test is a 40 question, multiple-choice test. The test covers some important math skills and topics covered in the first half of introductory chemistry such as definitions of elements, compounds, mixtures, atoms, molecules, ions and types of bonds. ...
... chemistry and math through Algebra 2. This placement test is a 40 question, multiple-choice test. The test covers some important math skills and topics covered in the first half of introductory chemistry such as definitions of elements, compounds, mixtures, atoms, molecules, ions and types of bonds. ...
Chem Curr - New Haven Science
... Chemistry is a study of the fundamental structure of matter that serves as a basic understanding of science needed in today’s world. It is a study of matter, energy, atomic and molecular structure, composition, bonding, the periodic law, chemical equations, acid-base reactions, solutions, gas laws, ...
... Chemistry is a study of the fundamental structure of matter that serves as a basic understanding of science needed in today’s world. It is a study of matter, energy, atomic and molecular structure, composition, bonding, the periodic law, chemical equations, acid-base reactions, solutions, gas laws, ...
chemical reaction - MRS. STOTTS CHEMISTRY
... separates from the solution is known as a precipitate. 4. Color change ...
... separates from the solution is known as a precipitate. 4. Color change ...
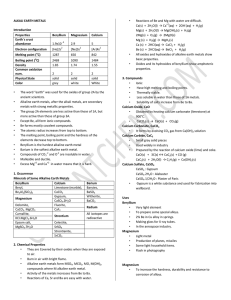
ALKALI EARTH METALS Introduction Properties Beryllium
... The word “earth” was used for the oxides of group 2A by the ancient scientists. Alkaline earth metals, after the alkali metals, are secondary metals with strong metallic properties. The group 2A elements are less active than those of 1A, but more active than those of group 3A. Except Be, all form io ...
... The word “earth” was used for the oxides of group 2A by the ancient scientists. Alkaline earth metals, after the alkali metals, are secondary metals with strong metallic properties. The group 2A elements are less active than those of 1A, but more active than those of group 3A. Except Be, all form io ...
200 ways to pass the regents
... The functional groups on organic molecules are listed on Reference Table R. Structural isomers of organic compounds have different structural formulas but the same molecular formula. Number the parent carbon chain in an organic molecule from the end closest to the alkyl group(s). Combustion reaction ...
... The functional groups on organic molecules are listed on Reference Table R. Structural isomers of organic compounds have different structural formulas but the same molecular formula. Number the parent carbon chain in an organic molecule from the end closest to the alkyl group(s). Combustion reaction ...
Using mass to calculate molecular formula
... Empirical formula and Molecular formula Benzene consists of 7.69% H and 92.31%C. Converting this to a formula gives CH. This is the simplest integer ratio. In fact a molecule of benzene has the formula C6H6. Empirical formula CH – simplest whole number ratio. Molecular formula C6H6 – actual number o ...
... Empirical formula and Molecular formula Benzene consists of 7.69% H and 92.31%C. Converting this to a formula gives CH. This is the simplest integer ratio. In fact a molecule of benzene has the formula C6H6. Empirical formula CH – simplest whole number ratio. Molecular formula C6H6 – actual number o ...
1.Using the table above, decide if the element mercury (Hg) should
... become more interlinked and complex. Structures progress from momomeric SiO4- anions to dimers, rings, chains, double chains, sheets, and, finally, three-dimensional cages. b. Describe the bonding. What's bonded to what, and what kinds of bonds are involved (ionic, covalent, intermolecular forces, e ...
... become more interlinked and complex. Structures progress from momomeric SiO4- anions to dimers, rings, chains, double chains, sheets, and, finally, three-dimensional cages. b. Describe the bonding. What's bonded to what, and what kinds of bonds are involved (ionic, covalent, intermolecular forces, e ...
Balancing Chemical Equations
... another. An element is a substance consisting of one kind of atom, such as aluminum (Al) or oxygen gas (O2). A compound is a substance made of more than one kind of atom, such as water (H2O) or table salt (NaCl). Question: How are chemical reactions classified? 1. Match: Most chemical reactions can ...
... another. An element is a substance consisting of one kind of atom, such as aluminum (Al) or oxygen gas (O2). A compound is a substance made of more than one kind of atom, such as water (H2O) or table salt (NaCl). Question: How are chemical reactions classified? 1. Match: Most chemical reactions can ...
Chapter 12 - "Chemical Formulas and Equations"
... volumes when the temperature and pressure are the same for each volume. (A) One volume of hydrogen gas combines with one volume of chlorine gas to yield two volumes of hydrogen chloride gas. (B) Two volumes of hydrogen gas combine with one volume of oxygen gas to yield two volumes of water vapor. ...
... volumes when the temperature and pressure are the same for each volume. (A) One volume of hydrogen gas combines with one volume of chlorine gas to yield two volumes of hydrogen chloride gas. (B) Two volumes of hydrogen gas combine with one volume of oxygen gas to yield two volumes of water vapor. ...
semester two final review key units 5 and 6 only
... Biochemistry: sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms Hydrocarbon: are the simplest organic compounds. Containing only carbon and hydrogen, they can be straight-chain, branched chain or cyclic Carbohydrate: is a biological mol ...
... Biochemistry: sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms Hydrocarbon: are the simplest organic compounds. Containing only carbon and hydrogen, they can be straight-chain, branched chain or cyclic Carbohydrate: is a biological mol ...
Document
... 13) List 5 properties of nonmetals. Where are the nonmetals located on the Periodic Table? Where is the most reactive nonmetal located? Brittle, don’t conduct, may be solids, liquids or gases, not ductile, not malleable Right of the zig-zag line Fluorine 14) Name and describe the two main classifica ...
... 13) List 5 properties of nonmetals. Where are the nonmetals located on the Periodic Table? Where is the most reactive nonmetal located? Brittle, don’t conduct, may be solids, liquids or gases, not ductile, not malleable Right of the zig-zag line Fluorine 14) Name and describe the two main classifica ...
Elements, mixtures and compounds lecture
... I. Element (ie: oxygen, hydrogen, lead, gold, krypton): A. exists as only one type of atom: it is, therefore a pure substance (This does not often occur in nature); gold necklace? Oxygen is the most common pure element on Earth (occurs as a dioxide: O2 , what does “di” mean?) B. cannot be broken do ...
... I. Element (ie: oxygen, hydrogen, lead, gold, krypton): A. exists as only one type of atom: it is, therefore a pure substance (This does not often occur in nature); gold necklace? Oxygen is the most common pure element on Earth (occurs as a dioxide: O2 , what does “di” mean?) B. cannot be broken do ...
RXN-4-STUDENTS - Rothschild Science
... element you have NH3 (one nitrogen, three hydrogen)- DON’T mess with these!! Coefficients – small whole number that appears ...
... element you have NH3 (one nitrogen, three hydrogen)- DON’T mess with these!! Coefficients – small whole number that appears ...
Organic chemistry

Organic chemistry is a chemistry subdiscipline involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms. Study of structure includes many physical and chemical methods to determine the chemical composition and the chemical constitution of organic compounds and materials. Study of properties includes both physical properties and chemical properties, and uses similar methods as well as methods to evaluate chemical reactivity, with the aim to understand the behavior of the organic matter in its pure form (when possible), but also in solutions, mixtures, and fabricated forms. The study of organic reactions includes probing their scope through use in preparation of target compounds (e.g., natural products, drugs, polymers, etc.) by chemical synthesis, as well as the focused study of the reactivities of individual organic molecules, both in the laboratory and via theoretical (in silico) study.The range of chemicals studied in organic chemistry include hydrocarbons (compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen), as well as myriad compositions based always on carbon, but also containing other elements, especially oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorus (these, included in many organic chemicals in biology) and the radiostable elements of the halogens.In the modern era, the range extends further into the periodic table, with main group elements, including:Group 1 and 2 organometallic compounds, i.e., involving alkali (e.g., lithium, sodium, and potassium) or alkaline earth metals (e.g., magnesium)Metalloids (e.g., boron and silicon) or other metals (e.g., aluminium and tin)In addition, much modern research focuses on organic chemistry involving further organometallics, including the lanthanides, but especially the transition metals; (e.g., zinc, copper, palladium, nickel, cobalt, titanium and chromium)Finally, organic compounds form the basis of all earthly life and constitute a significant part of human endeavors in chemistry. The bonding patterns open to carbon, with its valence of four—formal single, double, and triple bonds, as well as various structures with delocalized electrons—make the array of organic compounds structurally diverse, and their range of applications enormous. They either form the basis of, or are important constituents of, many commercial products including pharmaceuticals; petrochemicals and products made from them (including lubricants, solvents, etc.); plastics; fuels and explosives; etc. As indicated, the study of organic chemistry overlaps with organometallic chemistry and biochemistry, but also with medicinal chemistry, polymer chemistry, as well as many aspects of materials science.