FREE Sample Here
... A) Hydrogen bonds can occur within a single molecule. B) Hydrogen bonds are strong attractive forces between hydrogen atoms and negatively charged atoms. C) Hydrogen bonds can form between neighboring molecules. D) Hydrogen bonds are important forces for holding large molecules together. E) Hydrogen ...
... A) Hydrogen bonds can occur within a single molecule. B) Hydrogen bonds are strong attractive forces between hydrogen atoms and negatively charged atoms. C) Hydrogen bonds can form between neighboring molecules. D) Hydrogen bonds are important forces for holding large molecules together. E) Hydrogen ...
Ms. Breinlinger`s AP Chemistry Course Syllabus
... BIG IDEA 6: Any bond or intermolecular attraction that can be formed can be broken. These two processes are in a dynamic competition, sensitive to initial conditions and external perturbations. SCIENCE PRACTICE 1: The student can use representations and models to communicate scientific phenomena and ...
... BIG IDEA 6: Any bond or intermolecular attraction that can be formed can be broken. These two processes are in a dynamic competition, sensitive to initial conditions and external perturbations. SCIENCE PRACTICE 1: The student can use representations and models to communicate scientific phenomena and ...
AP Chemistry Jeopardy
... States of Matter $200 Under what conditions would a substance sublimate at room conditions (25 °C and 1 atm)? A) the critical temperature must be below the triple point B) the slope of the fusion line should be negative C) the triple point must be at a pressure greater than 1 atm and 25°C D) the so ...
... States of Matter $200 Under what conditions would a substance sublimate at room conditions (25 °C and 1 atm)? A) the critical temperature must be below the triple point B) the slope of the fusion line should be negative C) the triple point must be at a pressure greater than 1 atm and 25°C D) the so ...
Chapter 1 Matter on the Atomic Scale
... Nonmetals Occur in all physical states. solids: sulfur, phosphorus, carbon. liquid: bromine. gases: oxygen, helium, nitrogen. ...
... Nonmetals Occur in all physical states. solids: sulfur, phosphorus, carbon. liquid: bromine. gases: oxygen, helium, nitrogen. ...
Power point types of chemical rxn
... 1. Elements that form ionic compounds: Magnesium metal reacts with oxygen gas to form magnesium oxide. • 2Mg + O2 2MgO 2. Elements that form covalent compounds: Nitrogen gas and oxygen gas join to form dinitrogen monoxide. • 2N2 + O2 2N2O SYNTHESIS REACTION (iron + sulphur): http://www.youtube.c ...
... 1. Elements that form ionic compounds: Magnesium metal reacts with oxygen gas to form magnesium oxide. • 2Mg + O2 2MgO 2. Elements that form covalent compounds: Nitrogen gas and oxygen gas join to form dinitrogen monoxide. • 2N2 + O2 2N2O SYNTHESIS REACTION (iron + sulphur): http://www.youtube.c ...
are physical changes - Chemistry Information Site
... - also called "chemical reactions" Examples: ...
... - also called "chemical reactions" Examples: ...
Final Review: L17-25
... Chemical reactions can be divided into five categories: I. Combination Reactions ...
... Chemical reactions can be divided into five categories: I. Combination Reactions ...
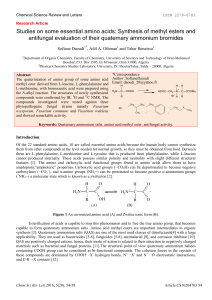
Studies on some essential amino acids: Synthesis of methyl esters
... using BUCHI 540 apparatus and are uncorrected, IR spectra were recorded as potassium bromide pellets on a Shimadzu 8300 spectrophotometer (ῡ max in cm−1), The 1H and 13C NMR spectra were recorded in D2O on a BrukerAM , NMR spectrometer (300 MHz) using TMS as internal standard (δ in ppm). Proceeding ...
... using BUCHI 540 apparatus and are uncorrected, IR spectra were recorded as potassium bromide pellets on a Shimadzu 8300 spectrophotometer (ῡ max in cm−1), The 1H and 13C NMR spectra were recorded in D2O on a BrukerAM , NMR spectrometer (300 MHz) using TMS as internal standard (δ in ppm). Proceeding ...
naming-and-formulas-chem-1-ab
... Molecular Formulas: A formula that specifies the actual number of atoms of each element in one molecule of the substance. ...
... Molecular Formulas: A formula that specifies the actual number of atoms of each element in one molecule of the substance. ...
Classification of Matter
... A combination of substances Two or more substances that are not chemically ...
... A combination of substances Two or more substances that are not chemically ...
Chemistry: Chemical Reactions Notes STOP
... a. For elements the subscript is one, unless it is a diatomic molecule then the subscript is 2. The diatomic molecules end in “gen” or “ine”, they are nicknamed the Aunt Genine molecules. The ...
... a. For elements the subscript is one, unless it is a diatomic molecule then the subscript is 2. The diatomic molecules end in “gen” or “ine”, they are nicknamed the Aunt Genine molecules. The ...
SOL Essential Knowledge
... 2. Ionization energy is the energy required to remove the most easily held electron. 3. Elements with low ionization energy form ions easily. F. Recognize that transition metals can have multiple oxidation states. G. Summarize the following concepts about covalent bonding: 1. Covalent bonds involve ...
... 2. Ionization energy is the energy required to remove the most easily held electron. 3. Elements with low ionization energy form ions easily. F. Recognize that transition metals can have multiple oxidation states. G. Summarize the following concepts about covalent bonding: 1. Covalent bonds involve ...
AP Chemistry Syllabus
... course sequence in COLLEGE CHEMISTRY. The course is designed for college-bound students who either would like to earn college credit (by AP examination) or would like to prepare for college chemistry while in high school. This is accomplished through an intensive, in-depth approach. It is highly rec ...
... course sequence in COLLEGE CHEMISTRY. The course is designed for college-bound students who either would like to earn college credit (by AP examination) or would like to prepare for college chemistry while in high school. This is accomplished through an intensive, in-depth approach. It is highly rec ...
Hints for Names and Formulas (Ch. 4 in Zumdahl Chemistry)
... (2) ionic compounds are generally classified as salts, acids, or bases (3) ionic compounds are orderly, infinite arrangements of positive and negative ions (4) ionic compounds are built with foam balls and toothpicks, not the molecular model kits (5) The positive ion (cation) is written first, and i ...
... (2) ionic compounds are generally classified as salts, acids, or bases (3) ionic compounds are orderly, infinite arrangements of positive and negative ions (4) ionic compounds are built with foam balls and toothpicks, not the molecular model kits (5) The positive ion (cation) is written first, and i ...
SAMPLE PAPER Class - XII SUBJECT
... Which point defect lowers the density of ionic crystal? Q.15. Calculate the efficiency of packing in case of a metal crystal for (a) ...
... Which point defect lowers the density of ionic crystal? Q.15. Calculate the efficiency of packing in case of a metal crystal for (a) ...
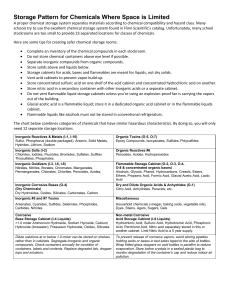
Storage Pattern for Chemicals Where Space is Limited
... Store concentrated sulfuric acid on one shelf of the acid cabinet and concentrated hydrochloric acid on another. Store nitric acid in a secondary container with other inorganic acids or a separate cabinet. Do not vent flammable liquid storage cabinets unless you’re using an explosion-proof fan is ca ...
... Store concentrated sulfuric acid on one shelf of the acid cabinet and concentrated hydrochloric acid on another. Store nitric acid in a secondary container with other inorganic acids or a separate cabinet. Do not vent flammable liquid storage cabinets unless you’re using an explosion-proof fan is ca ...
Chemistry Major Understandings
... 4.4a Each radioactive isotope has a specific mode and rate of decay (half-life). 4.4b Nuclear reactions include natural and artificial transmutation, fission, and fusion. 4.4c Nuclear reactions can be represented by equations that include symbols which represent atomic nuclei (with mass number and a ...
... 4.4a Each radioactive isotope has a specific mode and rate of decay (half-life). 4.4b Nuclear reactions include natural and artificial transmutation, fission, and fusion. 4.4c Nuclear reactions can be represented by equations that include symbols which represent atomic nuclei (with mass number and a ...
Classification of Matter
... smaller subunits by ordinary chemical processes. 3. Elements are organized by atomic number on the periodic table. 4. Elements are identified by their symbols. ...
... smaller subunits by ordinary chemical processes. 3. Elements are organized by atomic number on the periodic table. 4. Elements are identified by their symbols. ...
Eighth Grade Review - PAMS-Doyle
... Essential Question: Groups are also known as Families of Elements. They share chemical properties. WHY? Answer: They have the same number of valence electrons. ...
... Essential Question: Groups are also known as Families of Elements. They share chemical properties. WHY? Answer: They have the same number of valence electrons. ...
Hydrothermal Reactions from Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate to Phenol
... On the basis of the observation of the final product phenol and intermittent formic acid and formaldehyde in the hydrothermal reactions, we propose a possible reaction mechanism for phenol formation. Scheme 1 illustrates the main process of the hydrothermal reactions (see details in Supporting Infor ...
... On the basis of the observation of the final product phenol and intermittent formic acid and formaldehyde in the hydrothermal reactions, we propose a possible reaction mechanism for phenol formation. Scheme 1 illustrates the main process of the hydrothermal reactions (see details in Supporting Infor ...
Review for Midyear - 1 KEY - Ms. Robbins` PNHS Science Classes
... Diatomics are elements who’s atoms are never found lone in nature, but in covalently bonded pairs. Br2 I2 N2 Cl2 H2 O2 F2 Write the balanced chemical equation for the following reaction. Be sure to include the symbols for the correct state of matter. Can you classify each reaction also? Crystal suga ...
... Diatomics are elements who’s atoms are never found lone in nature, but in covalently bonded pairs. Br2 I2 N2 Cl2 H2 O2 F2 Write the balanced chemical equation for the following reaction. Be sure to include the symbols for the correct state of matter. Can you classify each reaction also? Crystal suga ...
+ 2 HCL(aq) CaCl2(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
... Chemical Formula: States what elements a compound contains and the exact number of atoms of these elements. Oxidation Number: positive or negative number on the periodic table that indicates how many electrons an element has gained, lost or shared when bonding with another element. Polyatomic Atom: ...
... Chemical Formula: States what elements a compound contains and the exact number of atoms of these elements. Oxidation Number: positive or negative number on the periodic table that indicates how many electrons an element has gained, lost or shared when bonding with another element. Polyatomic Atom: ...
8492_Chemichal Weapons Production Indicators
... The vapors of chlorinated solvents exposed to high temperatures have been known to produce phosgene. Chlorinated solvents are chlorine-containing chemicals that are typically used in industrial processes to dissolve or clean other materials, such as in paint stripping, metal cleaning, and dry cleani ...
... The vapors of chlorinated solvents exposed to high temperatures have been known to produce phosgene. Chlorinated solvents are chlorine-containing chemicals that are typically used in industrial processes to dissolve or clean other materials, such as in paint stripping, metal cleaning, and dry cleani ...
Organic chemistry

Organic chemistry is a chemistry subdiscipline involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms. Study of structure includes many physical and chemical methods to determine the chemical composition and the chemical constitution of organic compounds and materials. Study of properties includes both physical properties and chemical properties, and uses similar methods as well as methods to evaluate chemical reactivity, with the aim to understand the behavior of the organic matter in its pure form (when possible), but also in solutions, mixtures, and fabricated forms. The study of organic reactions includes probing their scope through use in preparation of target compounds (e.g., natural products, drugs, polymers, etc.) by chemical synthesis, as well as the focused study of the reactivities of individual organic molecules, both in the laboratory and via theoretical (in silico) study.The range of chemicals studied in organic chemistry include hydrocarbons (compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen), as well as myriad compositions based always on carbon, but also containing other elements, especially oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorus (these, included in many organic chemicals in biology) and the radiostable elements of the halogens.In the modern era, the range extends further into the periodic table, with main group elements, including:Group 1 and 2 organometallic compounds, i.e., involving alkali (e.g., lithium, sodium, and potassium) or alkaline earth metals (e.g., magnesium)Metalloids (e.g., boron and silicon) or other metals (e.g., aluminium and tin)In addition, much modern research focuses on organic chemistry involving further organometallics, including the lanthanides, but especially the transition metals; (e.g., zinc, copper, palladium, nickel, cobalt, titanium and chromium)Finally, organic compounds form the basis of all earthly life and constitute a significant part of human endeavors in chemistry. The bonding patterns open to carbon, with its valence of four—formal single, double, and triple bonds, as well as various structures with delocalized electrons—make the array of organic compounds structurally diverse, and their range of applications enormous. They either form the basis of, or are important constituents of, many commercial products including pharmaceuticals; petrochemicals and products made from them (including lubricants, solvents, etc.); plastics; fuels and explosives; etc. As indicated, the study of organic chemistry overlaps with organometallic chemistry and biochemistry, but also with medicinal chemistry, polymer chemistry, as well as many aspects of materials science.