DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY Course Book for M.Sc. in Chemistry
... 1. Svehla, G., Vogel's Textbook of macro and semimicro qualitative inorganic analysis, 5 th Edition,Longman Pubs 2. J. Mendham, R. C. Danney, J. D. Barnes & M. Thomas, Vogel’s Textbook of Quantitative Chemical Analysis, 6th Edition, Pearson Education Ltd. ...
... 1. Svehla, G., Vogel's Textbook of macro and semimicro qualitative inorganic analysis, 5 th Edition,Longman Pubs 2. J. Mendham, R. C. Danney, J. D. Barnes & M. Thomas, Vogel’s Textbook of Quantitative Chemical Analysis, 6th Edition, Pearson Education Ltd. ...
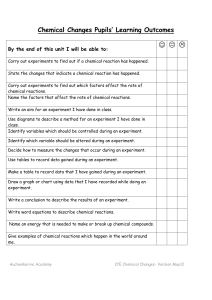
Chemical Reactions Unit Pupils` Learning Outcomes
... Identify variables which should be controlled during an experiment. Identify which variable should be altered during an experiment. Decide how to measure the changes that occur during an experiment. Use tables to record data gained during an experiment. Make a table to record data that I have gained ...
... Identify variables which should be controlled during an experiment. Identify which variable should be altered during an experiment. Decide how to measure the changes that occur during an experiment. Use tables to record data gained during an experiment. Make a table to record data that I have gained ...
Ch. 8 Notes (Chemical Reactions) Teacher 2010
... left side of the arrow, and the Reactants are on the ______ right yields products are on the __________ side. The arrow means “________”, or “reacts to produce” when read aloud. ...
... left side of the arrow, and the Reactants are on the ______ right yields products are on the __________ side. The arrow means “________”, or “reacts to produce” when read aloud. ...
An Overview of Chemistry Lecture 3 Lecture 3
... what makes up the world around them. - Early theories had the world made up of basic “elements” such as earth, water, air and fire. ...
... what makes up the world around them. - Early theories had the world made up of basic “elements” such as earth, water, air and fire. ...
rules for predicting products of chemical reactions
... Metal oxides react with water to make metallic hydroxides – MgO + H2O Mg(OH)2 Nonmetallic oxide react with water to make an acid – CO2 + H2O H2CO3 A metal react with non-metal to make a salt – 2Na + Cl2 -2 NaCl A few non-metals combine with each other – 3 P+ 3 Cl2 2 PCl3 ...
... Metal oxides react with water to make metallic hydroxides – MgO + H2O Mg(OH)2 Nonmetallic oxide react with water to make an acid – CO2 + H2O H2CO3 A metal react with non-metal to make a salt – 2Na + Cl2 -2 NaCl A few non-metals combine with each other – 3 P+ 3 Cl2 2 PCl3 ...
Hydrothermal Vents
... Found in depth >2500m Devoid of a digestive tract Symbiotic with the primary producers of the deep-sea: sulfuroxidizing bacteria ...
... Found in depth >2500m Devoid of a digestive tract Symbiotic with the primary producers of the deep-sea: sulfuroxidizing bacteria ...
SCIENCE 9
... TOPIC 3 WHAT ARE ELEMENTS? THE LAW OF CONSERVATION OF MASS- in a chemical change, the total mass of the new substances is always the same as the total mass of the original substances THE LAW OF DEFINITE COMPOSITON- compounds are pure substances that contain two or more elements combined together in ...
... TOPIC 3 WHAT ARE ELEMENTS? THE LAW OF CONSERVATION OF MASS- in a chemical change, the total mass of the new substances is always the same as the total mass of the original substances THE LAW OF DEFINITE COMPOSITON- compounds are pure substances that contain two or more elements combined together in ...
Chemical Reactions
... broken down by ordinary chemical means Atoms – more-or-less identical building blocks for each element Atomic symbol – one- or two-letter chemical shorthand for each element ...
... broken down by ordinary chemical means Atoms – more-or-less identical building blocks for each element Atomic symbol – one- or two-letter chemical shorthand for each element ...
CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... __ Na2S + __ AgNO3 _ NaNO3 + _ Ag2S ___ Mg + ___ HCl ___ H2 + ___ MgCl2 ...
... __ Na2S + __ AgNO3 _ NaNO3 + _ Ag2S ___ Mg + ___ HCl ___ H2 + ___ MgCl2 ...
chemical*equations
... Hydrogen'and'Oxygen'react'vigorously'to'form'water.'If' 275'hydrogen'molecules'are'reacted'with'125'oxygen' molecules'in'a'closed'container,'how'many'hydrogen,' oxygen,'and'water'molecules'will'remain'after'the' reaction'is'complete?' (a)'150'hydrogen'+'0'Oxygen'+'125'water' (b)'0'hydrogen'+'25'oxyg ...
... Hydrogen'and'Oxygen'react'vigorously'to'form'water.'If' 275'hydrogen'molecules'are'reacted'with'125'oxygen' molecules'in'a'closed'container,'how'many'hydrogen,' oxygen,'and'water'molecules'will'remain'after'the' reaction'is'complete?' (a)'150'hydrogen'+'0'Oxygen'+'125'water' (b)'0'hydrogen'+'25'oxyg ...
Chapter 1 Chemistry: Matter and Measurement
... Chemistry is concerned with matter and energy and how the two interact with each other. ...
... Chemistry is concerned with matter and energy and how the two interact with each other. ...
Chapter 14 – Chemical Reactions
... Reactants – the _____________ materials of a chemical _____________ Products – the substances _____________ as a _____________ of a chemical _____________ Coefficient – a _____________ placed in _____________ of a chemical _____________ or _____________ All chemical equations must be balanced. Steps ...
... Reactants – the _____________ materials of a chemical _____________ Products – the substances _____________ as a _____________ of a chemical _____________ Coefficient – a _____________ placed in _____________ of a chemical _____________ or _____________ All chemical equations must be balanced. Steps ...
aq - FCS Physics and Chemistry
... Physical properties describe how it looks, smells and feels. No change in composition occurs! ex – color, odor, volume and state of matter Chemical properties describe the substances ability to form new substances ex – ability of wood to burn, metal to rust, food to digest ...
... Physical properties describe how it looks, smells and feels. No change in composition occurs! ex – color, odor, volume and state of matter Chemical properties describe the substances ability to form new substances ex – ability of wood to burn, metal to rust, food to digest ...
NC Exam Questions - Rosshall Academy
... In the reaction, the carbon atom next to the carbonyl functional group of one molecule forms a bond with the carbonyl carbon atom of the second molecule. (a) Draw a structural formula for the product formed when propanone is used instead of ethanal in this type of reaction. (1) (b) Name an aldehyde ...
... In the reaction, the carbon atom next to the carbonyl functional group of one molecule forms a bond with the carbonyl carbon atom of the second molecule. (a) Draw a structural formula for the product formed when propanone is used instead of ethanal in this type of reaction. (1) (b) Name an aldehyde ...
PART 2 – CHEMISTRY
... The naming of substances is called “chemical nomenclature”. Many important substances that have been known for a long time, such as water, H2O, and ammonia, NH3, have individual, traditional names. For most substances, we rely on a systematic set of rules that lead to an informative and unique name ...
... The naming of substances is called “chemical nomenclature”. Many important substances that have been known for a long time, such as water, H2O, and ammonia, NH3, have individual, traditional names. For most substances, we rely on a systematic set of rules that lead to an informative and unique name ...
Atoms, molecules and ions
... • Atomic number: The number of protons in the nucleus of each atom of a given element • Atomic mass: The total number of neutrons and protons contained in the nucleus of an atom • All atoms of an element have the same number of protons, but not necessarily the same number of neutrons • Atoms that ha ...
... • Atomic number: The number of protons in the nucleus of each atom of a given element • Atomic mass: The total number of neutrons and protons contained in the nucleus of an atom • All atoms of an element have the same number of protons, but not necessarily the same number of neutrons • Atoms that ha ...
Key To T2 Review For Final Study Guide File - District 196 e
... 21. 11.0 g of a certain compound contains 2.82 g of magnesium and 8.18 g of chlorine. What is the empirical formula? MgCl2 22. A compound is tested and is found to be composed of 43.7% phosphorus and 56.3% oxygen. It has a molecular mass of 425.82 g/mol. Is the empirical and molecular formula the s ...
... 21. 11.0 g of a certain compound contains 2.82 g of magnesium and 8.18 g of chlorine. What is the empirical formula? MgCl2 22. A compound is tested and is found to be composed of 43.7% phosphorus and 56.3% oxygen. It has a molecular mass of 425.82 g/mol. Is the empirical and molecular formula the s ...
Chemical Reactions
... Chemical Reactions Everything that happens in an organism is based on chemical reactions. A chemical reaction is a process that changes one set of chemicals into another set of chemicals. The elements or compounds that enter into the reaction are the reactants. The elements or compounds produced by ...
... Chemical Reactions Everything that happens in an organism is based on chemical reactions. A chemical reaction is a process that changes one set of chemicals into another set of chemicals. The elements or compounds that enter into the reaction are the reactants. The elements or compounds produced by ...
Stoichiometry
... Working at 273.15K and 1atm (STP), I have 10.0g of carbon and 56L of oxygen. Under these conditions, I know 1mol of any gas has a volume of 22.4L (Molar volume at STP). What is the limiting ...
... Working at 273.15K and 1atm (STP), I have 10.0g of carbon and 56L of oxygen. Under these conditions, I know 1mol of any gas has a volume of 22.4L (Molar volume at STP). What is the limiting ...
1 - mvhs-fuhsd.org
... d. Carrying out tests to identify unknown substances: Analytical 8. Identify each of the following as an example of either basic research, applied research, or technological development: a. A new type of refrigerant is to be developed that is less damaging to the environment Applied b. A new element ...
... d. Carrying out tests to identify unknown substances: Analytical 8. Identify each of the following as an example of either basic research, applied research, or technological development: a. A new type of refrigerant is to be developed that is less damaging to the environment Applied b. A new element ...
AP Syllabus
... After completing these packets the students should be able to successfully: 1. Use the basic vocabulary adequately for each topic. 2. Work easily with the metric system, temperature scales, significant figures, and scientific notation, density, heat quantities, etc. 3. Distinguish between the three ...
... After completing these packets the students should be able to successfully: 1. Use the basic vocabulary adequately for each topic. 2. Work easily with the metric system, temperature scales, significant figures, and scientific notation, density, heat quantities, etc. 3. Distinguish between the three ...
File - docstover.org
... Using the periodic table, answer the following questions: 1. Which element stands alone in its family? ______________ 2. Which element has a larger atomic radius A or C? _____________ 3. Which element has a larger atomic radius C or D? _____________ 4. Which element has a higher electronegativity? A ...
... Using the periodic table, answer the following questions: 1. Which element stands alone in its family? ______________ 2. Which element has a larger atomic radius A or C? _____________ 3. Which element has a larger atomic radius C or D? _____________ 4. Which element has a higher electronegativity? A ...
Chapter 1: Matter, Measurement and Problem Solving
... of atom (some elements found as multi-atom molecules in nature) 2) combine together to make compounds ...
... of atom (some elements found as multi-atom molecules in nature) 2) combine together to make compounds ...
Organic chemistry

Organic chemistry is a chemistry subdiscipline involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms. Study of structure includes many physical and chemical methods to determine the chemical composition and the chemical constitution of organic compounds and materials. Study of properties includes both physical properties and chemical properties, and uses similar methods as well as methods to evaluate chemical reactivity, with the aim to understand the behavior of the organic matter in its pure form (when possible), but also in solutions, mixtures, and fabricated forms. The study of organic reactions includes probing their scope through use in preparation of target compounds (e.g., natural products, drugs, polymers, etc.) by chemical synthesis, as well as the focused study of the reactivities of individual organic molecules, both in the laboratory and via theoretical (in silico) study.The range of chemicals studied in organic chemistry include hydrocarbons (compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen), as well as myriad compositions based always on carbon, but also containing other elements, especially oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorus (these, included in many organic chemicals in biology) and the radiostable elements of the halogens.In the modern era, the range extends further into the periodic table, with main group elements, including:Group 1 and 2 organometallic compounds, i.e., involving alkali (e.g., lithium, sodium, and potassium) or alkaline earth metals (e.g., magnesium)Metalloids (e.g., boron and silicon) or other metals (e.g., aluminium and tin)In addition, much modern research focuses on organic chemistry involving further organometallics, including the lanthanides, but especially the transition metals; (e.g., zinc, copper, palladium, nickel, cobalt, titanium and chromium)Finally, organic compounds form the basis of all earthly life and constitute a significant part of human endeavors in chemistry. The bonding patterns open to carbon, with its valence of four—formal single, double, and triple bonds, as well as various structures with delocalized electrons—make the array of organic compounds structurally diverse, and their range of applications enormous. They either form the basis of, or are important constituents of, many commercial products including pharmaceuticals; petrochemicals and products made from them (including lubricants, solvents, etc.); plastics; fuels and explosives; etc. As indicated, the study of organic chemistry overlaps with organometallic chemistry and biochemistry, but also with medicinal chemistry, polymer chemistry, as well as many aspects of materials science.