Study Questions for Chapter 21 and 22 Test
... 1. Who was General McClellan? 2. Who was General Lee? 3. What happened at Bull Run? 4. Who helped to ruin the North’s chances at the Battle of Bull Run? 5. What happened at the Battle of Antietem? 6. What happened at Gettysburg? 7. Who gave the Gettysburg address and why? 8. What were the Monitor an ...
... 1. Who was General McClellan? 2. Who was General Lee? 3. What happened at Bull Run? 4. Who helped to ruin the North’s chances at the Battle of Bull Run? 5. What happened at the Battle of Antietem? 6. What happened at Gettysburg? 7. Who gave the Gettysburg address and why? 8. What were the Monitor an ...
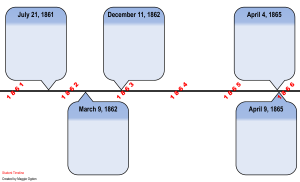
1861 The Civil War Begins - Sons of Union Veterans of the Civil War
... Lincoln alerted South Carolina of plans to supply Fort Sumter, SC feared a trick. April 12, Civil War began with shots fired on the fort. Fort Sumter eventually surrendered. ...
... Lincoln alerted South Carolina of plans to supply Fort Sumter, SC feared a trick. April 12, Civil War began with shots fired on the fort. Fort Sumter eventually surrendered. ...
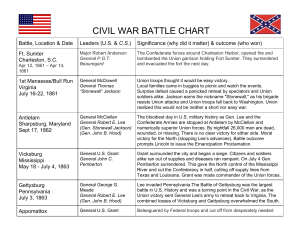
CIVIL WAR BATTLE CHART
... Surprise defeat caused a panicked retreat by spectators and Union soldiers alike. Jackson earns the nickname "Stonewall," as his brigade resists Union attacks and Union troops fall back to Washington. Union realized this would not be neither a short nor easy war. ...
... Surprise defeat caused a panicked retreat by spectators and Union soldiers alike. Jackson earns the nickname "Stonewall," as his brigade resists Union attacks and Union troops fall back to Washington. Union realized this would not be neither a short nor easy war. ...
The Civil War - The Goals of War Change
... Lincoln Changes His Mind WHY? Bloody fighting made many Northerners want to hurt the South as much as possible (Especially following the Battle of Antietam - September 1862) ...
... Lincoln Changes His Mind WHY? Bloody fighting made many Northerners want to hurt the South as much as possible (Especially following the Battle of Antietam - September 1862) ...
Study Guide Key
... Causes of the Civil War, Civil War, & Reconstruction Study Guide 1. What was the major type of labor used on Georgia’s plantations before the Civil War? Slavery 2. Which region of the United States believed the states should be able to govern themselves without interference from the national governm ...
... Causes of the Civil War, Civil War, & Reconstruction Study Guide 1. What was the major type of labor used on Georgia’s plantations before the Civil War? Slavery 2. Which region of the United States believed the states should be able to govern themselves without interference from the national governm ...
hr 3 Haillie and Brittney
... abolitionist movement. He wanted African Americans to become soldiers. At the end of the war 185,00 soldiers were in the war. ...
... abolitionist movement. He wanted African Americans to become soldiers. At the end of the war 185,00 soldiers were in the war. ...
first Battle of Bull Run - Virginia and the Civil War
... The Civil War ended at Appomattox Courthouse, Virginia, where Confederate General Robert E. Lee surrendered his army to Union General Ulysses S. Grant. This officially ended the American Civil War. ...
... The Civil War ended at Appomattox Courthouse, Virginia, where Confederate General Robert E. Lee surrendered his army to Union General Ulysses S. Grant. This officially ended the American Civil War. ...
Advantages of the North and South Read and highlight the handout
... militias. Most Southerners believed that "one good Southern boy could whip any ten Yankee [Northern] clerks and shopkeepers hands down." Southerners, after all, had been introduced to the horse and firearms early in childhood. Surely they were better than their Northern counterparts at such "manly p ...
... militias. Most Southerners believed that "one good Southern boy could whip any ten Yankee [Northern] clerks and shopkeepers hands down." Southerners, after all, had been introduced to the horse and firearms early in childhood. Surely they were better than their Northern counterparts at such "manly p ...
we here highly resolve that these dead shall not have died in vain
... Four score and seven years ago our fathers brought forth on this continent a new nation, conceived in liberty, and dedicated to the proposition that all men are created equal. Now we are engaged in a great civil war, testing whether that nation, or any nation, so conceived and so dedicated, can long ...
... Four score and seven years ago our fathers brought forth on this continent a new nation, conceived in liberty, and dedicated to the proposition that all men are created equal. Now we are engaged in a great civil war, testing whether that nation, or any nation, so conceived and so dedicated, can long ...
CIVIL WAR In the spring of 1861, decades of simmering tensions
... slavery was outlawed everywhere in the nation. Issues that led to war were partially resolved in the Reconstruction Era that followed, though others remained unresolved. Hostilities began on April 12, 1861, when Confederate forces attacked a U.S. military installation at Fort Sumter in South Carolin ...
... slavery was outlawed everywhere in the nation. Issues that led to war were partially resolved in the Reconstruction Era that followed, though others remained unresolved. Hostilities began on April 12, 1861, when Confederate forces attacked a U.S. military installation at Fort Sumter in South Carolin ...
Antietam Summary
... CW3.4.7 – Civil War Battle Stations Antietam (September, 1862) Following another loss at Bull Run in August of 1862, Union forces were on the run, not far from the capital of Washington, DC. The Confederate President Jefferson Davis, and Military General, Robert E. Lee, saw an opportunity to continu ...
... CW3.4.7 – Civil War Battle Stations Antietam (September, 1862) Following another loss at Bull Run in August of 1862, Union forces were on the run, not far from the capital of Washington, DC. The Confederate President Jefferson Davis, and Military General, Robert E. Lee, saw an opportunity to continu ...
Civil War Review Issues that divided the nation Slavery o While
... o Was leader of the Army of Northern Virginia o Was offered command of the Union forces at the beginning of the war, but chose not to fight against Virginia o Opposed secession, but did not believe the Union should be held together by force o Urged Southerners to accept defeat at the end of the war ...
... o Was leader of the Army of Northern Virginia o Was offered command of the Union forces at the beginning of the war, but chose not to fight against Virginia o Opposed secession, but did not believe the Union should be held together by force o Urged Southerners to accept defeat at the end of the war ...
Civil War Timeline
... States naval and land forces to begin a general advance by Feb 22, George Washington's birthday. ...
... States naval and land forces to begin a general advance by Feb 22, George Washington's birthday. ...
1 REVIEW FOR CHAPTERS 15, 16, AND 17 TEST Define the
... Second Battle of Bull Run – August, 1862 Another defeat for the Union army near Washington DC Antietam – September, 1862 Bloodiest day of fighting in USA history Chancellorsville – April, 1863 Confederate Victory (Stonewall Jackson was shot by own men) ...
... Second Battle of Bull Run – August, 1862 Another defeat for the Union army near Washington DC Antietam – September, 1862 Bloodiest day of fighting in USA history Chancellorsville – April, 1863 Confederate Victory (Stonewall Jackson was shot by own men) ...
Unit 1 _ ppt3 _ Regional Differences
... Let’s Review During the Antebellum period, there were many events leading up to the Civil War. Some would argue war was inevitable. But, was it inevitable that the North would win? ...
... Let’s Review During the Antebellum period, there were many events leading up to the Civil War. Some would argue war was inevitable. But, was it inevitable that the North would win? ...
Mississippi in Transition
... entitled "The Bonnie Blue Flag" which became the second most popular patriotic song of the Confederacy. The Confederate government did not adopt this flag but the people did and the lone star flags were adopted in some form in five of the southern States that adopted new flags in 1861. ...
... entitled "The Bonnie Blue Flag" which became the second most popular patriotic song of the Confederacy. The Confederate government did not adopt this flag but the people did and the lone star flags were adopted in some form in five of the southern States that adopted new flags in 1861. ...
Chapter 11-4: The War Continues
... – Kansas was admitted as a free state in 1861, and six more western territories were added. Lincoln appointed pro-Union officials to head the governments. – The draft was not enforced in the West, but California supplied volunteers and territorial mines provided vast amounts of gold and silver. – Th ...
... – Kansas was admitted as a free state in 1861, and six more western territories were added. Lincoln appointed pro-Union officials to head the governments. – The draft was not enforced in the West, but California supplied volunteers and territorial mines provided vast amounts of gold and silver. – Th ...
The War in the east
... Other Confederates were inspired and heartened by Jackson’s example. Southern reinforcements arrived, and the Union army retreated in defeat. The First Battle of Bull Run ruined Union hopes of a quick and easy war. http://www.history.com /topics/american-civil-war/first-battle-of-bull-run ...
... Other Confederates were inspired and heartened by Jackson’s example. Southern reinforcements arrived, and the Union army retreated in defeat. The First Battle of Bull Run ruined Union hopes of a quick and easy war. http://www.history.com /topics/american-civil-war/first-battle-of-bull-run ...
Compare and Contrast the Battle of Gettysburg
... Location: In the hills just south Gettysburg, PA., approximately 65 miles north of Washington, DC; 125 miles west of Philadelphia, PA. Date: July 1 - 3, 1863 Outcome: Union victory Casualties: Over 52,000 (22,000 Union and 30,000 Confederate) Significance: The Battle of Gettysburg was the biggest ba ...
... Location: In the hills just south Gettysburg, PA., approximately 65 miles north of Washington, DC; 125 miles west of Philadelphia, PA. Date: July 1 - 3, 1863 Outcome: Union victory Casualties: Over 52,000 (22,000 Union and 30,000 Confederate) Significance: The Battle of Gettysburg was the biggest ba ...
An ABC Book of Slavery and Emancipation
... L is for General Robert E Lee Robert E. Lee (1807-70) served as a U.S. military officer in the U.S. army ,a West Point commandant and the legendary general of the Confederacy of the American Civil War ...
... L is for General Robert E Lee Robert E. Lee (1807-70) served as a U.S. military officer in the U.S. army ,a West Point commandant and the legendary general of the Confederacy of the American Civil War ...
Chapter 22 The Civil War Vocabulary Review Directions: Match the
... she is being imprisoned lawfully 6.) a speech by President Abraham Lincoln in 1863 at the site of the Battle of Gettysburg in memory of the Union soldiers who had died trying to protect the ideals of freedom upon which the nation was founded 7.) a village in Virginia that was the site of the Confede ...
... she is being imprisoned lawfully 6.) a speech by President Abraham Lincoln in 1863 at the site of the Battle of Gettysburg in memory of the Union soldiers who had died trying to protect the ideals of freedom upon which the nation was founded 7.) a village in Virginia that was the site of the Confede ...
Unit 3 Day 6 1862
... Essential Question(s): How did the actions of political and military leaders influence the Civil War? Specified Content: Ironclads, Shiloh, New Orleans, Gen. Lee, Antietam, Fredericksburg State Standards: Strand 1 Concept 6 PO 2 ...
... Essential Question(s): How did the actions of political and military leaders influence the Civil War? Specified Content: Ironclads, Shiloh, New Orleans, Gen. Lee, Antietam, Fredericksburg State Standards: Strand 1 Concept 6 PO 2 ...
Battle of Wilson's Creek

The Battle of Wilson's Creek, also known as the Battle of Oak Hills, was the first major battle of the Trans-Mississippi Theater of the American Civil War. Fought on August 10, 1861, near Springfield, Missouri, between Union forces and the Missouri State Guard, it is sometimes called the ""Bull Run of the West.""Despite Missouri's neutral status at the beginning of the war, tensions escalated between Federal forces and state forces in the months leading up to the battle. In early August 1861, Confederate troops under the command of Brig. Gen. Benjamin McCulloch approached Brig. Gen. Nathaniel Lyon's Army of the West, which was camped at Springfield. On August 9, both sides formulated plans to attack the other. At about 5:00 a.m. on August 10, Lyon, in two columns commanded by himself and Col. Franz Sigel, attacked the Confederates on Wilson's Creek about 12 miles (19 km) southwest of Springfield. Confederate cavalry received the first blow and retreated from the high ground, later referred to as ""Bloody Hill,"" and infantry soon rushed up to stabilize their positions. The Confederates attacked the Union forces three times during the day but failed to break through the Union line. When General Lyon was killed during the battle and General Thomas William Sweeny wounded, Major Samuel D. Sturgis assumed command of the Union forces. Meanwhile, the Confederates had routed Sigel's column south of Skegg's Branch. Following the third Confederate attack, which ended at 11:00 a.m., the Union withdrew. When Sturgis realized that his men were exhausted and lacking ammunition, he ordered a retreat to Springfield. The Confederates were too disorganized and ill-equipped to pursue.The Confederate victory buoyed Southern sympathizers in Missouri and served as a springboard for a bold thrust north that carried Sterling Price and his Missouri State Guard as far as Lexington. In late October, a convention organized by Governor Claiborne Fox Jackson met in Neosho and passed out an ordinance of secession. Although the state remained in the Union for the remainder of the war, the Battle of Wilson's Creek effectively gave the Confederates control of southwestern Missouri. Today, the National Park Service operates Wilson's Creek National Battlefield on the site of the original conflict.