* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CIVIL WAR In the spring of 1861, decades of simmering tensions
Battle of Antietam wikipedia , lookup
Arkansas in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
List of American Civil War generals wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Lexington wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Namozine Church wikipedia , lookup
Reconstruction era wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
Battle of New Bern wikipedia , lookup
East Tennessee bridge burnings wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Wilson's Creek wikipedia , lookup
Blockade runners of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Texas in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Bull Run wikipedia , lookup
Secession in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Lost Cause of the Confederacy wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Jubal Early wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Anaconda Plan wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Pacific Coast Theater of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Confederate privateer wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
CIVIL WAR
In the spring of 1861, decades of simmering tensions between the northern and southern United
States over issues including states' rights versus federal authority, westward expansion and slavery
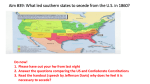
exploded into the American Civil War (1861-65). The election of the anti-slavery Republican
Abraham Lincoln as president in 1860 caused seven southern states to secede from the Union to
form the Confederate States of America; four more joined them after the first shots of the Civil
War were fired. Four years of brutal conflict were marked by historic battles at Bull Run
(Manassas), Antietam, Chancellorsville, Gettysburg and Vicksburg, among others. The War
Between the States, as the Civil War was also known, pitted neighbor against neighbor and in
some cases, brother against brother. By the time it ended in Confederate surrender in 1865, the
Civil War proved to be the costliest war ever fought on American soil, with some 620,000 of 2.4
million soldiers killed, millions more injured and the population and territory of the South
devastated.
CIVIL WAR II
The American Civil War (1861–1865) was a civil war fought in the United States of America. In
response to the election of Abraham Lincoln as President of the United States, 11 southern slave
states declared their secession from the United States and formed the Confederate States of
America ("the Confederacy"); the other 25 states supported the federal government ("the Union").
After four years of warfare, mostly within the Southern states, the Confederacy surrendered and
slavery was outlawed everywhere in the nation. Issues that led to war were partially resolved in the
Reconstruction Era that followed, though others remained unresolved. Hostilities began on April
12, 1861, when Confederate forces attacked a U.S. military installation at Fort Sumter in South
Carolina. Lincoln responded by calling for a volunteer army from each state to recapture federal
property, which led to declarations of secession by four more slave states. Both sides raised armies
as the Union seized control of the border states early in the war and established a naval blockade.
Land warfare in the East was inconclusive in 1861–62, as the Confederacy beat back Union efforts
to capture its capital, Richmond, Virginia, notably during the Peninsular Campaign. In September
1862, the confederate campaign in Maryland ended in defeat at the Battle of Antietam, which
dissuaded the British from intervening.[2] Days after that battle, Lincoln issued the Emancipation
Proclamation, which made ending slavery a war goal.[3]
CIVIL WAR III
The Civil War was a fight to preserve the Union which was the United States of America. From
the conception of the Constitution, there were two differing opinions on the role of the federal
government. Federalists believed that the federal government and the executive needed to maintain
their power in order to ensure the survival of the union. On the other hand, anti-federalists held that
states should retain much of their sovereignty within the new nation. Basically they believed that
each state should have the right to determine the laws within its own borders and should not be
forced to follow the mandates of the federal government unless absolutely necessary.
As time passed the rights of the states would often collide with various actions the federal
government was taking. Arguments arose over taxation, tariffs, internal improvements, the
military, and of course slavery.