KS3 Science
... Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems All organisms carry out seven life processes (movement, reproduction, sensitivity, growth, respiration, excretion, nutrition). All organisms are made from cells: ...
... Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems All organisms carry out seven life processes (movement, reproduction, sensitivity, growth, respiration, excretion, nutrition). All organisms are made from cells: ...
CS 8.1 - 8.4 Assessment Event
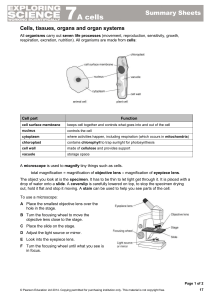
... B) Calculate the magnification of the following cell, which is shown under the high power field of view. (CS 8.2) ...
... B) Calculate the magnification of the following cell, which is shown under the high power field of view. (CS 8.2) ...
Biology Review
... 5. What is the basic unit of all living things? 6. Where is the cell’s genetic information found? ...
... 5. What is the basic unit of all living things? 6. Where is the cell’s genetic information found? ...
1-3 Studying Life: Read pages 16-22 carefully
... 3. Circle the letter of each sentence that is TRUE about cells. a. A cell is the smallest unit of an organism that is considered alive. b. A multicellular organism may contain trillions of cells. c. A living thing that consists of a single cell is a multicellular organism. d. Organisms are made up o ...
... 3. Circle the letter of each sentence that is TRUE about cells. a. A cell is the smallest unit of an organism that is considered alive. b. A multicellular organism may contain trillions of cells. c. A living thing that consists of a single cell is a multicellular organism. d. Organisms are made up o ...
1-3 Studying Life
... 6. Plants, some bacteria, and most algae obtain their energy directly from ___________. 7. A _______________ is a signal to which an organism responds. 8. Give 2 examples of external stimuli: _______________________________________. 9. The process by which organisms maintain constant internal condit ...
... 6. Plants, some bacteria, and most algae obtain their energy directly from ___________. 7. A _______________ is a signal to which an organism responds. 8. Give 2 examples of external stimuli: _______________________________________. 9. The process by which organisms maintain constant internal condit ...
1-3_studying_life
... 3. Circle the letter of each sentence that is TRUE about cells. a. A cell is the smallest unit of an organism that is considered alive. b. A multicellular organism may contain trillions of cells. c. A living thing that consists of a single cell is a multicellular organism. d. Organisms are made up o ...
... 3. Circle the letter of each sentence that is TRUE about cells. a. A cell is the smallest unit of an organism that is considered alive. b. A multicellular organism may contain trillions of cells. c. A living thing that consists of a single cell is a multicellular organism. d. Organisms are made up o ...
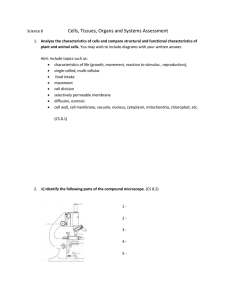
Comparing Cell Organelles to the Human Body and
... Grow growth Endocrine system body when to Ribosomes Makes protein grow for growth/repair ...
... Grow growth Endocrine system body when to Ribosomes Makes protein grow for growth/repair ...
Cells and Systems Review Outine
... Osmosis Because the cell membrane allows SOME matter to move in and out – it is said to be ________________________. Cells combine together to form tissue. 4 types of animal tissue: ...
... Osmosis Because the cell membrane allows SOME matter to move in and out – it is said to be ________________________. Cells combine together to form tissue. 4 types of animal tissue: ...
Ann Marie Goode MST, Auburn University
... • Take the DNA and put in into another bacterium • Test products produced for potential antibiotic activity ...
... • Take the DNA and put in into another bacterium • Test products produced for potential antibiotic activity ...
Levels of Organization
... Individual cells may perform specific functions and also work together for the good of the entire organism. The cells become dependent on one ...
... Individual cells may perform specific functions and also work together for the good of the entire organism. The cells become dependent on one ...
Chapter 4 – Structure + Function of the Cell
... Anton van Leeuwenhoek – identified the first living cell using a microscope ...
... Anton van Leeuwenhoek – identified the first living cell using a microscope ...
Facts to Remember to help you pass the NYS Science Assessment
... dominant gene. A hybrid contains one dominant and one recessive gene in the pair. 42.) Genetic engineering, selective breeding, cloning, and gene splicing are examples of modern genetic techniques. 43.) A life cycle is described as a series of changes in the development of an organism. 44.) An examp ...
... dominant gene. A hybrid contains one dominant and one recessive gene in the pair. 42.) Genetic engineering, selective breeding, cloning, and gene splicing are examples of modern genetic techniques. 43.) A life cycle is described as a series of changes in the development of an organism. 44.) An examp ...
Fun with Cells with the Amoeba Sisters
... But, wait. There are basically 2 kinds of cells, right? One that is found in simple life forms like amoeba. And such cells are called as prokaryotes. And the other that is found in complex life forms like humans, for example. We call them eukaryotes. Let us hear their differences first. ...
... But, wait. There are basically 2 kinds of cells, right? One that is found in simple life forms like amoeba. And such cells are called as prokaryotes. And the other that is found in complex life forms like humans, for example. We call them eukaryotes. Let us hear their differences first. ...
Cell Theory
... The three main parts of the Cell theory are: 1. All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of the organization of living things. 3. All cells come from pre-existing cells. The cell theory was originally developed by Theodor Schwann, and fully accepted by th ...
... The three main parts of the Cell theory are: 1. All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of the organization of living things. 3. All cells come from pre-existing cells. The cell theory was originally developed by Theodor Schwann, and fully accepted by th ...
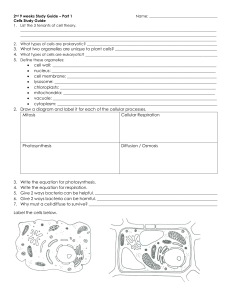
3. What two organelles are unique to plant cells? • cell wall: ______
... ____________________ to give the body its final shape ____________________ makes blood cells and stores minerals ____________________ to change food to a form that the body cells can use ____________________ to move oxygen into the body ____________________ cleans blood and rids body of waste in blo ...
... ____________________ to give the body its final shape ____________________ makes blood cells and stores minerals ____________________ to change food to a form that the body cells can use ____________________ to move oxygen into the body ____________________ cleans blood and rids body of waste in blo ...
Biology Final Jeopary 2
... A: The type of memory cell that will produce antibodies quickly in response to a pathogen the body has “seen” before; responsible for immunity. ...
... A: The type of memory cell that will produce antibodies quickly in response to a pathogen the body has “seen” before; responsible for immunity. ...
Dictyostelium discoideum
Dictyostelium discoideum is a species of soil-living amoeba belonging to the phylum Amoebozoa, infraphylum Mycetozoa. Commonly referred to as slime mold, D. discoideum is a eukaryote that transitions from a collection of unicellular amoebae into a multicellular slug and then into a fruiting body within its lifetime. Its unique asexual lifecycle consists of four stages: vegetative, aggregation, migration, and culmination. The lifecycle of D. discoideum is relatively short, which allows for timely viewing of all stages. The cells involved in the lifecycle undergo movement, chemical signaling, and development, which are applicable to human cancer research. The simplicity of its lifecycle makes D. discoideum a valuable model organism to study genetic, cellular, and biochemical processes in other organisms.