change over time
... reproductive: members of 2 pops. can’t interbreed behavioral: two pops. have different habits ...
... reproductive: members of 2 pops. can’t interbreed behavioral: two pops. have different habits ...
Introduction to Biology
... constantly to build molecules (synthesis) and cells and to break down (digest) substances (such as breaking down food for nutrition) b. Organisms must transport nutrients to be used in cellular respiration to produce energy. c. An organisms’ chemical reactions are called its metabolism ...
... constantly to build molecules (synthesis) and cells and to break down (digest) substances (such as breaking down food for nutrition) b. Organisms must transport nutrients to be used in cellular respiration to produce energy. c. An organisms’ chemical reactions are called its metabolism ...
Spring Semester Biology Review
... adaptations include catcus with spines for protection and the closing of the stomata for prevention of water loss. Animals that are camouflaged or mimic other animals are also examples of adaptations. Dichotomous Keys can be used for identification of organisms using opposing statements. In each pai ...
... adaptations include catcus with spines for protection and the closing of the stomata for prevention of water loss. Animals that are camouflaged or mimic other animals are also examples of adaptations. Dichotomous Keys can be used for identification of organisms using opposing statements. In each pai ...
Lecture 7b Invertebrates: Sponges, Cnidaria, Flatworms, Nematodes
... Sessile animals Lack true tissues; Have only a few cell types, cells kind of independent • Most have no symmetry • Body resembles a sac perforated with holes, system of canals. • Strengthened by fibers of spongin, spicules ...
... Sessile animals Lack true tissues; Have only a few cell types, cells kind of independent • Most have no symmetry • Body resembles a sac perforated with holes, system of canals. • Strengthened by fibers of spongin, spicules ...
CP Biology Name Date Period HOMEWORK PACKET UNIT 1A
... a. breaks down food into smaller molecules that cells can absorb and use ...
... a. breaks down food into smaller molecules that cells can absorb and use ...
Name Marine Biology--Mr. Nelson LAB: SPONGES AND
... comes from hard structures called spicules or from flexible protein called spongin. Spicules are made of either calcium carbonate or silicon dioxide. Some sponges have both spicules and spongin. Coelenterates have true tissues. Their bodies consist of two layers; an outer ectoderm and an inner endod ...
... comes from hard structures called spicules or from flexible protein called spongin. Spicules are made of either calcium carbonate or silicon dioxide. Some sponges have both spicules and spongin. Coelenterates have true tissues. Their bodies consist of two layers; an outer ectoderm and an inner endod ...
Evolution Guided Notes
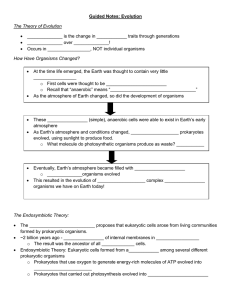
... These ________________ (simple), anaerobic cells were able to exist in Earth’s early atmosphere As Earth’s atmosphere and conditions changed, ___________________ prokaryotes evolved, using sunlight to produce food. o What molecule do photosynthetic organisms produce as waste? ___________ ...
... These ________________ (simple), anaerobic cells were able to exist in Earth’s early atmosphere As Earth’s atmosphere and conditions changed, ___________________ prokaryotes evolved, using sunlight to produce food. o What molecule do photosynthetic organisms produce as waste? ___________ ...
big
... cells and somatic cells – Germ cells (gametes) are cells whose genes will be (directly) passed on to offspring: eggs and sperm – Somatic cells are all other cells in the body. Although these cells may (or may not) divide, they will not directly contribute to the creation of offspring ...
... cells and somatic cells – Germ cells (gametes) are cells whose genes will be (directly) passed on to offspring: eggs and sperm – Somatic cells are all other cells in the body. Although these cells may (or may not) divide, they will not directly contribute to the creation of offspring ...
Lecture 19
... cells and somatic cells – Germ cells (gametes) are cells whose genes will be (directly) passed on to offspring: eggs and sperm – Somatic cells are all other cells in the body. Although these cells may (or may not) divide, they will not directly contribute to the creation of offspring ...
... cells and somatic cells – Germ cells (gametes) are cells whose genes will be (directly) passed on to offspring: eggs and sperm – Somatic cells are all other cells in the body. Although these cells may (or may not) divide, they will not directly contribute to the creation of offspring ...
CH 17 Taxonomy TErev07v22013
... Classificationthe grouping of objects or information based on similarities. ...
... Classificationthe grouping of objects or information based on similarities. ...
Animals – Invertebrates Part 1
... In deuterostomes o Cleavage pattern: In most protostomes early cell division leads to an eight-celled embryo twisted in arrangement called In deuterostomes, cells divide into eight-celled embryos with cells that are lined up atop the other in an arrangement called ...
... In deuterostomes o Cleavage pattern: In most protostomes early cell division leads to an eight-celled embryo twisted in arrangement called In deuterostomes, cells divide into eight-celled embryos with cells that are lined up atop the other in an arrangement called ...
Evolution PPT
... Evidence for Evolution All living things contain similar DNA, RNA, and proteins. By comparing DNA sequences of two organisms, scientists can determine whether or not the organisms are closely related. The relationship can then be used to construct evolutionary pathways. ...
... Evidence for Evolution All living things contain similar DNA, RNA, and proteins. By comparing DNA sequences of two organisms, scientists can determine whether or not the organisms are closely related. The relationship can then be used to construct evolutionary pathways. ...
Chapter 7
... background so the birds would not feed on them as easily or as often. The trees often had dark bark due to the pollution in the air. As time passed, the dark colored moths survived more often and passed on the dark traits to later generations. As more people became aware that pollution was harmful a ...
... background so the birds would not feed on them as easily or as often. The trees often had dark bark due to the pollution in the air. As time passed, the dark colored moths survived more often and passed on the dark traits to later generations. As more people became aware that pollution was harmful a ...
Evolution Notes
... Geographic Distribution of Living Species: Separation by a large body of water, or land, that does not allow species to come back into contact with each other for continued gene flow. ...
... Geographic Distribution of Living Species: Separation by a large body of water, or land, that does not allow species to come back into contact with each other for continued gene flow. ...
Chapter Six Section one and two Study Guide Outline Teacher Copy
... c. Selection- nature “selects” organisms to survive based on how well they can adapt. d. Variation- differences between members of the same species. e. Environmental Change – different events that can cause organisms to leave an area or die out. ...
... c. Selection- nature “selects” organisms to survive based on how well they can adapt. d. Variation- differences between members of the same species. e. Environmental Change – different events that can cause organisms to leave an area or die out. ...
Evolution Notes Pages
... Some of that oxygen was generated by photosynthetic cyanobacteria Some came from the chemical separation of water molecules into oxygen and hydrogen. Oxygen drove some life forms to extinction Others evolved ways of using oxygen for respiration ...
... Some of that oxygen was generated by photosynthetic cyanobacteria Some came from the chemical separation of water molecules into oxygen and hydrogen. Oxygen drove some life forms to extinction Others evolved ways of using oxygen for respiration ...
Clues About Evolution - Science327-8
... organisms that lived in the past. However, the fossil record is incomplete, or has gaps, much like a book with missing pages. • Scientist can use fossils to show that many simpler forms of life existed earlier in Earth’s history. • Fossils provide evidence that evolution has occurred on Earth. ...
... organisms that lived in the past. However, the fossil record is incomplete, or has gaps, much like a book with missing pages. • Scientist can use fossils to show that many simpler forms of life existed earlier in Earth’s history. • Fossils provide evidence that evolution has occurred on Earth. ...
Organism
... Many millions of kinds of organisms, or species, have appeared and disappeared over time Each kind is unique in some aspects of its body form or behavior ...
... Many millions of kinds of organisms, or species, have appeared and disappeared over time Each kind is unique in some aspects of its body form or behavior ...
Ch. 27 Invertebrates
... Invertebrates are organisms that do not have a backbone! Phylum Porifera Sponges - about 9,000 species Characteristics: ~ asymmetrical ~ lack tissues and organs ~ body wall has 2 cell layers with many pores ~ internal cavity lined with food filtering choanocytes (collar cells) ~ live in marine water ...
... Invertebrates are organisms that do not have a backbone! Phylum Porifera Sponges - about 9,000 species Characteristics: ~ asymmetrical ~ lack tissues and organs ~ body wall has 2 cell layers with many pores ~ internal cavity lined with food filtering choanocytes (collar cells) ~ live in marine water ...
Chapter 4 Notes - Geneva Area City Schools
... • Communities are groups of various species that live in the same habitat and interact with each other. • Every population is part of a community. ...
... • Communities are groups of various species that live in the same habitat and interact with each other. • Every population is part of a community. ...
Chapter 4 The Organization of Life
... • Communities are groups of various species that live in the same habitat and interact with each other. • Every population is part of a community. ...
... • Communities are groups of various species that live in the same habitat and interact with each other. • Every population is part of a community. ...
How are living things organized?
... How are Living Things Organized? • An organism is a living thing that can carry out life processes by itself. • Unicellular organisms are made up of just one cell that performs all the functions necessary for life. • Unicellular organisms do not have levels of organization. ...
... How are Living Things Organized? • An organism is a living thing that can carry out life processes by itself. • Unicellular organisms are made up of just one cell that performs all the functions necessary for life. • Unicellular organisms do not have levels of organization. ...
Animal Physiology Powerpoint
... Circulation in Sponges • The simplest circulatory system is in sponges – Probably similar to the first circulatory system in our common ancestor ...
... Circulation in Sponges • The simplest circulatory system is in sponges – Probably similar to the first circulatory system in our common ancestor ...
Precambrian body plans

Until the late 1950’s, the Precambrian era was not believed to have hosted multicellular organisms. However, with radiometric dating techniques, it has been found that fossils initially found in the Ediacara Hills in Southern Australia date back to the late Precambrian era. These fossils are body impressions of organisms shaped like disks, fronds and some with ribbon patterns that were most likely tentacles.These are the earliest multicellular organisms in Earth’s history, despite the fact that unicellularity had been around for a long time before that. The requirements for multicellularity were embedded in the genes of some of these cells, specifically choanoflagellates. These are thought to be the precursors for all multicellular organisms. They are highly related to sponges (Porifera), which are the simplest multicellular organisms.In order to understand the transition to multicellularity during the Precambrian, it is important to look at the requirements for multicellularity—both biological and environmental.