Ch 9-View of Earth`s Past
... based on relative ages of rocks in which oldest rocks are at bottom – Use column to estimate age of rock layers, cannot be dated radiometrically – Compare rocks w/ similar layers that have same fossils or same relative position ...
... based on relative ages of rocks in which oldest rocks are at bottom – Use column to estimate age of rock layers, cannot be dated radiometrically – Compare rocks w/ similar layers that have same fossils or same relative position ...
File
... 1. Archaebacteria – unicellular (one-celled) prokaryotes that often live in extreme environments. Some are autotrophs (make their own food), some are heterotrophs (consume their food). Examples: bacteria that live in hot springs. 2. Eubacteria – unicellular prokaryotes that may or may not make their ...
... 1. Archaebacteria – unicellular (one-celled) prokaryotes that often live in extreme environments. Some are autotrophs (make their own food), some are heterotrophs (consume their food). Examples: bacteria that live in hot springs. 2. Eubacteria – unicellular prokaryotes that may or may not make their ...
Introduction to Physiology The Human Body
... 4- System: A system is a group of organs that act together to perform a specialized function. a. cardiovascular system, b. respiratory system, c. urinary system, d. digestive system, e. nervous system, f. respiratory system, g. endocrine system, h. musculoskeletal system, i. integument system. 5- Hu ...
... 4- System: A system is a group of organs that act together to perform a specialized function. a. cardiovascular system, b. respiratory system, c. urinary system, d. digestive system, e. nervous system, f. respiratory system, g. endocrine system, h. musculoskeletal system, i. integument system. 5- Hu ...
Chapter 1 - Los Angeles City College
... Species by Means of Natural Selection” (1859) in which he proposed the theory of evolution. Evidence that led to the principle of evolution: – Fossils: Most species that ever existed are extinct; appear to be gradual progression – Artificial selection of domestic/farm animals – Adaptations: Organism ...
... Species by Means of Natural Selection” (1859) in which he proposed the theory of evolution. Evidence that led to the principle of evolution: – Fossils: Most species that ever existed are extinct; appear to be gradual progression – Artificial selection of domestic/farm animals – Adaptations: Organism ...
Animal Cells/ Cellular Function
... Students describe the general structure and function of cells. They can explain that all living systems are composed of cells and that organisms may be unicellular or multicellular. They understand that cells are composed of biological macromolecules and that the complex processes of the cell allow ...
... Students describe the general structure and function of cells. They can explain that all living systems are composed of cells and that organisms may be unicellular or multicellular. They understand that cells are composed of biological macromolecules and that the complex processes of the cell allow ...
CHAPTER 15-17: EVOLUTION: EVIDENCE OF CHANGE
... The more fit the species, the more able that species will be to survive and reproduce. Common Descent: A principle whereby all organisms have __________________ Adaptation: To adapt to better fit your environment. (Now we now: By mutation!!!!!!!!) Eg. Long necked giraffes Evidence in Stone – pg 418- ...
... The more fit the species, the more able that species will be to survive and reproduce. Common Descent: A principle whereby all organisms have __________________ Adaptation: To adapt to better fit your environment. (Now we now: By mutation!!!!!!!!) Eg. Long necked giraffes Evidence in Stone – pg 418- ...
The Animal Kingdom and Sponges Laboratory
... • composed of cells not surrounded by a cell wall and rely on structural proteins (like collagen) for support • composed of specialized tissues (exception : sponges) which arise from embryonic germ layers • typically motile; not sessile like plants • diploid and reproduce sexually Most zoologists ag ...
... • composed of cells not surrounded by a cell wall and rely on structural proteins (like collagen) for support • composed of specialized tissues (exception : sponges) which arise from embryonic germ layers • typically motile; not sessile like plants • diploid and reproduce sexually Most zoologists ag ...
Evolution and Natural Selection Unit Notes
... Evolution: evolution is change of a population of organisms from one generation to the next. Usually an advancement. Evidence of Evolution The fossil record of changes in plants and animals over millions of years. From simple to more complicated. Chemical and anatomical similarities of related ...
... Evolution: evolution is change of a population of organisms from one generation to the next. Usually an advancement. Evidence of Evolution The fossil record of changes in plants and animals over millions of years. From simple to more complicated. Chemical and anatomical similarities of related ...
FCA #4 ANSWER KEY 1. Evolution – a process in which descendants
... Analogous Structures: Structures that perform similar functions but organisms are NOT related Example: Wings of insects, bats, ...
... Analogous Structures: Structures that perform similar functions but organisms are NOT related Example: Wings of insects, bats, ...
Cnidarians - College Heights Secondary School
... divide it into two like halves. Most sponges. Asymmetrical animals are plant-like and ...
... divide it into two like halves. Most sponges. Asymmetrical animals are plant-like and ...
document
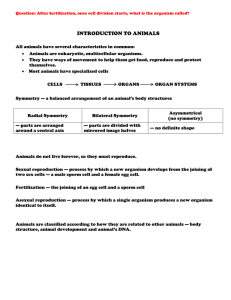
... Question: After fertilization, once cell division starts, what is the organism called? ...
... Question: After fertilization, once cell division starts, what is the organism called? ...
Key - Edquest
... discovered micro-organisms floating in spoiled batches of beer and wine. The micro-organisms were actually … spoiled grapes alcohol insects yeast anthrax A disorder common in half a million children in Canada, can be triggered by many different environmental factors. This disorder is ... bronchitis ...
... discovered micro-organisms floating in spoiled batches of beer and wine. The micro-organisms were actually … spoiled grapes alcohol insects yeast anthrax A disorder common in half a million children in Canada, can be triggered by many different environmental factors. This disorder is ... bronchitis ...
Chapter 7 Evolution Card Sort
... more likely to survive and reproduce than others of the same species ...
... more likely to survive and reproduce than others of the same species ...
Animalia PowerPoint
... • About 95% of animals are invertebrates • Invertebrates occupy all terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems and have existed for hundreds of millions of years ...
... • About 95% of animals are invertebrates • Invertebrates occupy all terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems and have existed for hundreds of millions of years ...
Chapter 3
... • How do scientists arrange organisms in natural groups? • What is the most fundamental taxonomic division of life? • What kinds of organisms constitute the Protista and Fungi? ...
... • How do scientists arrange organisms in natural groups? • What is the most fundamental taxonomic division of life? • What kinds of organisms constitute the Protista and Fungi? ...
Cellular Structure and Function Web Research 100 pts
... cells divide during the process of mitosis. Next, students learn how cell specialization takes place in vertebrate embryos. They explore a gallery of different kinds of specialized cells and compare each cell's structure and function. After making drawings of these cells, they place their drawings i ...
... cells divide during the process of mitosis. Next, students learn how cell specialization takes place in vertebrate embryos. They explore a gallery of different kinds of specialized cells and compare each cell's structure and function. After making drawings of these cells, they place their drawings i ...
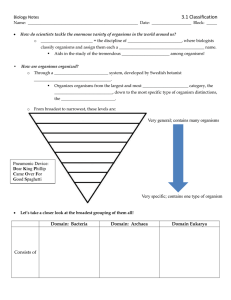
3.1 Classification
... _________________________ = the discipline of __________________________, where biologists classify organisms and assign them each a _________________________________________ name. ...
... _________________________ = the discipline of __________________________, where biologists classify organisms and assign them each a _________________________________________ name. ...
ALSO - Warren Hills Regional School District
... These smaller organisms eventually became mitochondria and chloroplasts inside eukaryotic cells. The first cells were thought to be simple, prokaryotic, anaerobic, and heterotrophic. (Bacteria cells) ...
... These smaller organisms eventually became mitochondria and chloroplasts inside eukaryotic cells. The first cells were thought to be simple, prokaryotic, anaerobic, and heterotrophic. (Bacteria cells) ...
Chapter 1 Lesson 1~ Cells cells split or divide to form new cells 1 ½
... SIMPLE INVERTEBRATES Sponges: only animal without real tissue or organs (asymmetrical) Cnidarians: soft-bodied, aquatic (radial symmetry) Worms: all have bilateral symmetry ...
... SIMPLE INVERTEBRATES Sponges: only animal without real tissue or organs (asymmetrical) Cnidarians: soft-bodied, aquatic (radial symmetry) Worms: all have bilateral symmetry ...
Darwin presents his case
... ______________________ for limited resources. 4. Individuals best suited to their environment (highest level of _________________) survive and reproduce most successfully. 5. These organisms pass their heritable ___________________ to their ...
... ______________________ for limited resources. 4. Individuals best suited to their environment (highest level of _________________) survive and reproduce most successfully. 5. These organisms pass their heritable ___________________ to their ...
Biology 1406 - HCC Learning Web
... 6. (P. 9 – 15) There is unity in diversity. All of biology is about this topic – the most important concept in biology, because it explains how living things that are so different can show so much similarity between them. The term diversity refers to the millions of different species that exist – co ...
... 6. (P. 9 – 15) There is unity in diversity. All of biology is about this topic – the most important concept in biology, because it explains how living things that are so different can show so much similarity between them. The term diversity refers to the millions of different species that exist – co ...
HISTORY OF LIFE Evolution part 1
... organisms come from only other living organisms – now the cornerstone of biology ...
... organisms come from only other living organisms – now the cornerstone of biology ...
Precambrian body plans

Until the late 1950’s, the Precambrian era was not believed to have hosted multicellular organisms. However, with radiometric dating techniques, it has been found that fossils initially found in the Ediacara Hills in Southern Australia date back to the late Precambrian era. These fossils are body impressions of organisms shaped like disks, fronds and some with ribbon patterns that were most likely tentacles.These are the earliest multicellular organisms in Earth’s history, despite the fact that unicellularity had been around for a long time before that. The requirements for multicellularity were embedded in the genes of some of these cells, specifically choanoflagellates. These are thought to be the precursors for all multicellular organisms. They are highly related to sponges (Porifera), which are the simplest multicellular organisms.In order to understand the transition to multicellularity during the Precambrian, it is important to look at the requirements for multicellularity—both biological and environmental.