Product formation and phosphoglucomutase activities
... glucose utilization, it was found to be higher in maltosegrown lactococci. Unlike the constitutive expression of a-PGM, the synthesis of p-PGM has been found to be induced by maltose and repressed by glucose. The molecular mass of the a-PGM polypeptide is approximately 65 kDa and its isoelectric poi ...
... glucose utilization, it was found to be higher in maltosegrown lactococci. Unlike the constitutive expression of a-PGM, the synthesis of p-PGM has been found to be induced by maltose and repressed by glucose. The molecular mass of the a-PGM polypeptide is approximately 65 kDa and its isoelectric poi ...
effect of glucose concentration in the growth medium upon neutral
... L. J. TURTON, *D. B. DRUCKER AND L. A. GANGULI Microbiology Laboratory, Hope Hospital, Salford, M6 8HD, and *Department of Bacteriology and Virology, University of Manchester, Manchester M I 3 9PT. ...
... L. J. TURTON, *D. B. DRUCKER AND L. A. GANGULI Microbiology Laboratory, Hope Hospital, Salford, M6 8HD, and *Department of Bacteriology and Virology, University of Manchester, Manchester M I 3 9PT. ...
effect of glucose concentration in the growth medium upon neutral
... L. J. TURTON, *D. B. DRUCKER AND L. A. GANGULI Microbiology Laboratory, Hope Hospital, Salford, M6 8HD, and *Department of Bacteriology and Virology, University of Manchester, Manchester M I 3 9PT. ...
... L. J. TURTON, *D. B. DRUCKER AND L. A. GANGULI Microbiology Laboratory, Hope Hospital, Salford, M6 8HD, and *Department of Bacteriology and Virology, University of Manchester, Manchester M I 3 9PT. ...
Cardiac Energy Dependence on Glucose Increases
... acyl-CoAs.9 In contrast, overexpression of ACSL1 in heart causes toxicity and cell death, probably due to a mismatch between the production of acyl-CoAs and their incorporation into downstream pathways.11 Endogenous ACSL1 in heart directs its acyl-CoA product towards b-oxidation rather than towards ...
... acyl-CoAs.9 In contrast, overexpression of ACSL1 in heart causes toxicity and cell death, probably due to a mismatch between the production of acyl-CoAs and their incorporation into downstream pathways.11 Endogenous ACSL1 in heart directs its acyl-CoA product towards b-oxidation rather than towards ...
28 Gluconeogenesis In animals, glucose is required by the brain
... any of these compounds. Because the breakdown of fat results nearly exclusively in acetyl-CoA, fat (with minor exceptions) cannot be used to synthesize glucose. Instead, most glucose is synthesized either from lactate (produced during anaerobic glycolysis) or from amino acids (derived from breakdown ...
... any of these compounds. Because the breakdown of fat results nearly exclusively in acetyl-CoA, fat (with minor exceptions) cannot be used to synthesize glucose. Instead, most glucose is synthesized either from lactate (produced during anaerobic glycolysis) or from amino acids (derived from breakdown ...
Why Glycogen as an Energy Storage Molecule?
... - Buildup of substrate lactate (lactic acid) causing acidosis (rarely overt) - Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) in undernourished people. Can lead to irreversible CNS damage ...
... - Buildup of substrate lactate (lactic acid) causing acidosis (rarely overt) - Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) in undernourished people. Can lead to irreversible CNS damage ...
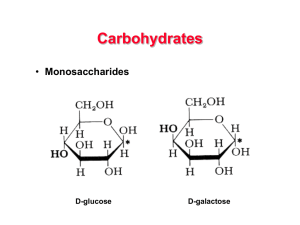
Carbohydrates
... proinsulin (A, B and C peptides) insulin + C-peptide » anabolic (synthesis) » promotes cellular uptake of glucose » increased: • lipogenesis • protein synthesis • glycogenesis » decreased: • lipolysis • ketone formation • gluconeogenesis • glycogenolysis ...
... proinsulin (A, B and C peptides) insulin + C-peptide » anabolic (synthesis) » promotes cellular uptake of glucose » increased: • lipogenesis • protein synthesis • glycogenesis » decreased: • lipolysis • ketone formation • gluconeogenesis • glycogenolysis ...
SOLUTE TRANSPORT
... Sugar Phosphotransferase System of Gram-Negative Bacteria is classic example: ...
... Sugar Phosphotransferase System of Gram-Negative Bacteria is classic example: ...
Insightful directed evolution of Escherichia coli quorum sensing
... (N-acyl-homoserine lactones) and AI-2 based species communication systems have been developed as tools for exogenously controlling bacterial phenotype and protein expression (22,23). For example, the luxCDABE operon of the bioluminescent bacterium Photorhabdus luminescens, based on AHL, has proven t ...
... (N-acyl-homoserine lactones) and AI-2 based species communication systems have been developed as tools for exogenously controlling bacterial phenotype and protein expression (22,23). For example, the luxCDABE operon of the bioluminescent bacterium Photorhabdus luminescens, based on AHL, has proven t ...
Chapter 14 Glycolysis Glucose 2 Pyruvate → → → 2 Lactate (sent to
... → Cells often have transport systems built into their membranes for uptake of fuel molecules such as glucose. Phosphorylated glucose is no longer recognized by the glucose transport system and is therefore trapped in the cell. There is no transport system for phosphorylated glucose. The glucose tran ...
... → Cells often have transport systems built into their membranes for uptake of fuel molecules such as glucose. Phosphorylated glucose is no longer recognized by the glucose transport system and is therefore trapped in the cell. There is no transport system for phosphorylated glucose. The glucose tran ...
BIOMOLECULES
... of amino acids form polypetide chain in proteins? 39. α-Helix is a secondary structure of proteins formed by twisting of polypeptide chain into right handed screw like structures. Which type of interactions are responsible for making the α-helix structure stable? 40. Some enzymes are named after the ...
... of amino acids form polypetide chain in proteins? 39. α-Helix is a secondary structure of proteins formed by twisting of polypeptide chain into right handed screw like structures. Which type of interactions are responsible for making the α-helix structure stable? 40. Some enzymes are named after the ...
ATP - Mhanafi123`s Blog
... lactate include brain, gastrointestinal tract, renal medulla, retina, and skin. Lactate production is also increased in septic shock, and many cancers also produce lactate. ...
... lactate include brain, gastrointestinal tract, renal medulla, retina, and skin. Lactate production is also increased in septic shock, and many cancers also produce lactate. ...
LAB 4. CELLULAR RESPIRATION and GLUCOSE
... PART 1. INTRODUCTION TO CELLULAR RESPIRATION Most cellular reactions require a source of chemical energy, ATP. The major source of ATP is the oxidation of glucose. Glucose oxidation can be broken down into two major phases. ...
... PART 1. INTRODUCTION TO CELLULAR RESPIRATION Most cellular reactions require a source of chemical energy, ATP. The major source of ATP is the oxidation of glucose. Glucose oxidation can be broken down into two major phases. ...
PDF - Biotechnology for Biofuels
... The primary soluble metabolites at the end of fermentation were formate, acetate and butyrate, followed by ethanol and lactate (Figure 1G). To highlight the impact of pH on the gene expression for the H2-producing enzymes, that is, the hydrogenases and the nitrogenase, the comparative results for H2 ...
... The primary soluble metabolites at the end of fermentation were formate, acetate and butyrate, followed by ethanol and lactate (Figure 1G). To highlight the impact of pH on the gene expression for the H2-producing enzymes, that is, the hydrogenases and the nitrogenase, the comparative results for H2 ...
BIOCHEMISTRY Carbohydrate Metabolism
... • An enzymatic anaerobic reduction of Pyruvate to Lactate occurs mainly in muscles – leads to tiredness & pain. • Purpose – conversion of NADH to NAD+ for increased rate of glycolysis. • Lactate is converted back to Pyruvate when aerobic conditions are reestablished in the cell. • Muscle fatigue ass ...
... • An enzymatic anaerobic reduction of Pyruvate to Lactate occurs mainly in muscles – leads to tiredness & pain. • Purpose – conversion of NADH to NAD+ for increased rate of glycolysis. • Lactate is converted back to Pyruvate when aerobic conditions are reestablished in the cell. • Muscle fatigue ass ...
Revisiting the role of yeast Sfp1 in ribosome biogenesis and cell
... cerevisiae strain CEN.PK 113-7D (MATa MAL2-8c SUC2) and the isogenic strain CEN.PK 111-32D sfp1D (MATa MAL2-8c SUC2 leu23,112 sfp1D : : KlLEU2) were used in this study. Cells were grown at 30 uC in 2 l chemostats (Applikon), with a working volume of 1.0 l. Cultures were fed with a defined mineral me ...
... cerevisiae strain CEN.PK 113-7D (MATa MAL2-8c SUC2) and the isogenic strain CEN.PK 111-32D sfp1D (MATa MAL2-8c SUC2 leu23,112 sfp1D : : KlLEU2) were used in this study. Cells were grown at 30 uC in 2 l chemostats (Applikon), with a working volume of 1.0 l. Cultures were fed with a defined mineral me ...
PowerPoint Presentation - AGRI-MIS
... (+) oversensitive response (0) insensitive response Without hormone application: (-) auxotrophic / deficient phenotype ...
... (+) oversensitive response (0) insensitive response Without hormone application: (-) auxotrophic / deficient phenotype ...
Role of N-terminal protein formylation in central metabolic processes
... and other carbon sources slower than the wild type. While the turnover of several metabolites remained unaltered fmt inactivation led to increases pyruvate release and, concomitantly, reduced pyruvate dehydrogenase activity. In parallel, the release of the pyruvate-derived metabolites lactate, aceto ...
... and other carbon sources slower than the wild type. While the turnover of several metabolites remained unaltered fmt inactivation led to increases pyruvate release and, concomitantly, reduced pyruvate dehydrogenase activity. In parallel, the release of the pyruvate-derived metabolites lactate, aceto ...
Use of Gene Replacement Transformation to Elucidate
... HE quinic acid (qa) gene cluster of Neurospora crassa is a well characterized system to study genetic regulation in a multicellular yet relatively simple organism. T h e qa gene cluster of N. crassa is located on approximately 17.2 kb of DNA on Neurospora linkage group VI1 (GILESet al. 1985). T h e ...
... HE quinic acid (qa) gene cluster of Neurospora crassa is a well characterized system to study genetic regulation in a multicellular yet relatively simple organism. T h e qa gene cluster of N. crassa is located on approximately 17.2 kb of DNA on Neurospora linkage group VI1 (GILESet al. 1985). T h e ...
Sugar Transport in (Hyper-)Thermophilic Archaea
... the nanomolar range are usually observed only for substrates such as vitamins and iron which are found in very low concentrations in the environment. Uptake of substrates by hyperthermophilic archaea is usually optimal around the growth temperature. ...
... the nanomolar range are usually observed only for substrates such as vitamins and iron which are found in very low concentrations in the environment. Uptake of substrates by hyperthermophilic archaea is usually optimal around the growth temperature. ...
Glucose Homeostasis
... absorption of glucose, So, Glucose given orally stimulates more insulin than intravenous glucose. ...
... absorption of glucose, So, Glucose given orally stimulates more insulin than intravenous glucose. ...
Acidaminococcus fermentans type strain (VR4T)
... tree was inferred from 1,348 aligned characters [10,11] of the 16S rRNA gene sequence under the maximum likelihood criterion [12] and rooted with the type strain of Anaerococcus prevotii, a member of the neighboring family Peptococcaceae. The branches are scaled in terms of the expected number of su ...
... tree was inferred from 1,348 aligned characters [10,11] of the 16S rRNA gene sequence under the maximum likelihood criterion [12] and rooted with the type strain of Anaerococcus prevotii, a member of the neighboring family Peptococcaceae. The branches are scaled in terms of the expected number of su ...
Carbohydrates
... The Glycosidic Bond • Reaction of anomeric carbon with hydroxyl or amino group forms O-glycosidic or N-glycosidic bond ...
... The Glycosidic Bond • Reaction of anomeric carbon with hydroxyl or amino group forms O-glycosidic or N-glycosidic bond ...
... inactivation of glycogen synthase. Lac Repressor • Binding of lactose causes it to release from DNA, allowing mRNA to be made. Normally this allows the bacteria to turn on genes required for lactose metabolism. Glycolysis • PFK and F16bisphosphatase are allosterically regulated by AMP, ADP and ATP t ...
Identification of Pseudomonas proteins coordinately
... when supplied as the sole source of carbon and nitrogen (Sonawane et al., 2003). All of these amino acids strongly and specifically induce periplasmic glutaminase/asparaginase (PGA) (Hüser et al., 1999). On the other hand, PGA is subject to carbon catabolite repression by glucose and dicarboxylic a ...
... when supplied as the sole source of carbon and nitrogen (Sonawane et al., 2003). All of these amino acids strongly and specifically induce periplasmic glutaminase/asparaginase (PGA) (Hüser et al., 1999). On the other hand, PGA is subject to carbon catabolite repression by glucose and dicarboxylic a ...
Lac operon

lac operon (lactose operon) is an operon required for the transport and metabolism of lactose in Escherichia coli and many other enteric bacteria. Although glucose is the preferred carbon source for most bacteria, the lac operon allows for the effective digestion of lactose when glucose is not available. Gene regulation of the lac operon was the first genetic regulatory mechanism to be understood clearly, so it has become a foremost example of prokaryotic gene regulation. It is often discussed in introductory molecular and cellular biology classes at universities for this reason.Bacterial operons are polycistronic transcripts that are able to produce multiple proteins from one mRNA transcript. In this case, when lactose is required as a sugar source for the bacterium, the three genes of the lac operon can be expressed and their subsequent proteins translated: lacZ, lacY, and lacA. The gene product of lacZ is β-galactosidase which cleaves lactose, a disaccharide, into glucose and galactose. LacY encodes lactose permease, a protein which becomes embedded in the cytoplasmic membrane to enable transport of lactose into the cell. Finally, lacA encodes galactoside O-acetyltransferase. Layout of the lac operon.It would be wasteful to produce the enzymes when there is no lactose available or if there is a more preferable energy source available, such as glucose. The lac operon uses a two-part control mechanism to ensure that the cell expends energy producing the enzymes encoded by the lac operon only when necessary. In the absence of lactose, the lac repressor halts production of the enzymes encoded by the lac operon. In the presence of glucose, the catabolite activator protein (CAP), required for production of the enzymes, remains inactive, and EIIAGlc shuts down lactose permease to prevent transport of lactose into the cell. This dual control mechanism causes the sequential utilization of glucose and lactose in two distinct growth phases, known as diauxie.