Biochemistry Objectives 43
... abundance of exogenous glucose; however, during the late post-absorptive state and early starvation, where protein catabolism for gluconeogenesis is necessary, cortisol synthesis and release is stimulated. Cortisol levels drop off during prolonged starvation in an effort to conserve proteins. ...
... abundance of exogenous glucose; however, during the late post-absorptive state and early starvation, where protein catabolism for gluconeogenesis is necessary, cortisol synthesis and release is stimulated. Cortisol levels drop off during prolonged starvation in an effort to conserve proteins. ...
Unit One: Introduction to Physiology: The Cell and General Physiology
... Fig. 69.2 Reversible equilibrium among the tissue proteins, plasma proteins, and plasma amino acids ...
... Fig. 69.2 Reversible equilibrium among the tissue proteins, plasma proteins, and plasma amino acids ...
Name CELLULAR RESPIRATION URL: http:://www.2.nl.edu/jste
... The ultimate energy source for life on Earth is the sun, by what process do living things convert light energy? into what form? What molecule is used to do work in cells of living things? GLYCOLYSIS Summarize what occurs in glycolysis in one sentence. Where does glycoloysis occur? Is the process aer ...
... The ultimate energy source for life on Earth is the sun, by what process do living things convert light energy? into what form? What molecule is used to do work in cells of living things? GLYCOLYSIS Summarize what occurs in glycolysis in one sentence. Where does glycoloysis occur? Is the process aer ...
Name Answer Key Date Period 3.7 Cell Respiration 1. Define cell
... Addition of a phosphate group to a molecule. Substrate level phosphorylation occurs when an enzyme transfers an electron directly from a substrate to a molecule of ADP. Oxidative phosphorylation occurs using the movement of electrons to generate energy used to add a phosphate to a molecule of ADP. M ...
... Addition of a phosphate group to a molecule. Substrate level phosphorylation occurs when an enzyme transfers an electron directly from a substrate to a molecule of ADP. Oxidative phosphorylation occurs using the movement of electrons to generate energy used to add a phosphate to a molecule of ADP. M ...
Cellular Respiration Chapter 7- Cfe Higher Human Biology
... PROTEINS AS RESPIRATORY SUBSTRATES Proteins in the diet are broken down to their component amino acids by the action of digestive enzymes. Amino acids in excess of the body’s requirements for protein synthesis undergo deamination, forming urea and respiratory pathway intermediates as shown opposite ...
... PROTEINS AS RESPIRATORY SUBSTRATES Proteins in the diet are broken down to their component amino acids by the action of digestive enzymes. Amino acids in excess of the body’s requirements for protein synthesis undergo deamination, forming urea and respiratory pathway intermediates as shown opposite ...
Glycolysis Quiz
... reduction of a substance can not operate without NAD+. What is NAD+ known as? (a) co-enzyme (b) co-factor (c) amino acid (d) protein ...
... reduction of a substance can not operate without NAD+. What is NAD+ known as? (a) co-enzyme (b) co-factor (c) amino acid (d) protein ...
Oxidative Phosphorylation and Electron Transport Chain(ETC)
... [FADH2], are passed through an elaborate and highly organized chain of proteins and coenzymes, therefore called electron transport chain, finally reaching O2 (molecular oxygen) is the terminal electron acceptor. • Each component of the chain can exist in (at least) two oxidation states, and each com ...
... [FADH2], are passed through an elaborate and highly organized chain of proteins and coenzymes, therefore called electron transport chain, finally reaching O2 (molecular oxygen) is the terminal electron acceptor. • Each component of the chain can exist in (at least) two oxidation states, and each com ...
AP Biology Summer Session Lecture 6
... actually makes ATP from ADP and Pi. ATP uses the energy of an existing proton gradient to power ATP synthesis. This proton gradient develops between the intermembrane space and the matrix. ...
... actually makes ATP from ADP and Pi. ATP uses the energy of an existing proton gradient to power ATP synthesis. This proton gradient develops between the intermembrane space and the matrix. ...
Questions and answers from course Environmental microbiology on
... Fermentation does only lead to ATP-production by substrate level phosphorylation in the oxidative branch. Respiration leads to electron transport phoyphorylation. ...
... Fermentation does only lead to ATP-production by substrate level phosphorylation in the oxidative branch. Respiration leads to electron transport phoyphorylation. ...
Protein kinases
... response are mostly proteins • Like falling dominoes, the receptor activates another protein, which activates another, and so on, until the protein producing the response is activated • At each step, the signal is transduced into a different form, usually a shape change in a protein ...
... response are mostly proteins • Like falling dominoes, the receptor activates another protein, which activates another, and so on, until the protein producing the response is activated • At each step, the signal is transduced into a different form, usually a shape change in a protein ...
Plant Cells and Tissues
... 3 major groups of secondary metabolites 1. Alkaloids 2. Terpenoids 3. Phenolics Glycosides: secondary metabolites combined with one or more sugars for transport. Minor Secondary Metabolites - Nitrogen-sulfur compounds - Non-protein amino acids - Cyanogenics ...
... 3 major groups of secondary metabolites 1. Alkaloids 2. Terpenoids 3. Phenolics Glycosides: secondary metabolites combined with one or more sugars for transport. Minor Secondary Metabolites - Nitrogen-sulfur compounds - Non-protein amino acids - Cyanogenics ...
Proteomics studies of post-translational modifications in plants
... molecules. PTMs of proteins thus largely increase protein complexity and dynamics, resulting in the intricate regulation of biological events. Despite the pivotal roles of PTMs in cellular functions, studies on PTMs have not really been feasible until recently. The identification of PTMs requires la ...
... molecules. PTMs of proteins thus largely increase protein complexity and dynamics, resulting in the intricate regulation of biological events. Despite the pivotal roles of PTMs in cellular functions, studies on PTMs have not really been feasible until recently. The identification of PTMs requires la ...
Structure and function of mitochondria (Slide
... ANAEROBIC RESPIRATION producing lactic acid and allowing further glycolysis to occur BUT NO MORE ATP is produced. Lactic acid can be metabolised back to glucose in the liver Anaerobic respiration also used by yeasts and simple ...
... ANAEROBIC RESPIRATION producing lactic acid and allowing further glycolysis to occur BUT NO MORE ATP is produced. Lactic acid can be metabolised back to glucose in the liver Anaerobic respiration also used by yeasts and simple ...
As Powerpoint Slide
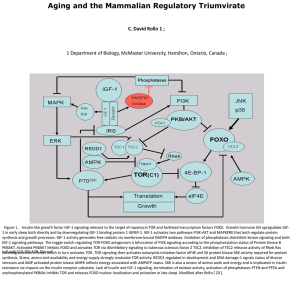
... 1 Department of Biology, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada ; ...
... 1 Department of Biology, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada ; ...
Cellular Respiration - Home - Mrs. Guida's AP Biology Class
... organic compounds to extract energy from chemical bonds ...
... organic compounds to extract energy from chemical bonds ...
Cell Respiration - Oxidative Phosphorylation Gibb`s Free Energy PPT
... • 2A2 Organisms capture and store free energy for use in biological processes. g. The electron transport chain captures free energy from electrons in a series of coupled reactions that establish an electrochemical gradient across membranes. ...
... • 2A2 Organisms capture and store free energy for use in biological processes. g. The electron transport chain captures free energy from electrons in a series of coupled reactions that establish an electrochemical gradient across membranes. ...
Cellular Respiration Part IV: Oxidative Phosphorylation
... • The energy stored in a H+ gradient across a membrane couples the redox reactions of the electron transport chain to ATP synthesis • The H+ gradient is responsible for establishing a proton-motive force, emphasizing its capacity to do work ...
... • The energy stored in a H+ gradient across a membrane couples the redox reactions of the electron transport chain to ATP synthesis • The H+ gradient is responsible for establishing a proton-motive force, emphasizing its capacity to do work ...
Rabbit anti-Phosphoserine 608 Retinoblastoma Protein
... Entry into S phase from late G1 is controlled by phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma protein (Rb). Mutations affecting Rb or proteins that control Rb phosphorylation are frequent in human tumors. The cell cycle distribution of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) cells shares many features ...
... Entry into S phase from late G1 is controlled by phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma protein (Rb). Mutations affecting Rb or proteins that control Rb phosphorylation are frequent in human tumors. The cell cycle distribution of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) cells shares many features ...
Module 10: Catabolism of Amino Acids
... 10. Phosphofructokinase is one of the enzyme in the glycolysis pathway subjected to more regulation. Concentrations of ATP and ADP can change the activity of the enzyme. a. From what you know about glycolysis. Will [ADP] will be an activator or an inhibitor of the enzyme. Why? b. The graph shown bel ...
... 10. Phosphofructokinase is one of the enzyme in the glycolysis pathway subjected to more regulation. Concentrations of ATP and ADP can change the activity of the enzyme. a. From what you know about glycolysis. Will [ADP] will be an activator or an inhibitor of the enzyme. Why? b. The graph shown bel ...
Step 2: Pyruvate Oxidation
... Recall Step 1 - Glycolysis • Happens in the cytoplasm • Does not require oxygen (anaerobic) • Inefficient (net 2 ATP produced) ...
... Recall Step 1 - Glycolysis • Happens in the cytoplasm • Does not require oxygen (anaerobic) • Inefficient (net 2 ATP produced) ...
Global in-depth quantitative proteomic analysis of HIV infected cells
... FIGURE 8. HIV arrests cells by bypassing the full DNA damage response. Our phosphoproteomics analysis indicates that Chk1-dependent cell cycle arrest is achieved while maintaining aurora kinase activity. The HIV proteins VIF and VPR are both required for cell cycle arrest2. The mechanisms by which t ...
... FIGURE 8. HIV arrests cells by bypassing the full DNA damage response. Our phosphoproteomics analysis indicates that Chk1-dependent cell cycle arrest is achieved while maintaining aurora kinase activity. The HIV proteins VIF and VPR are both required for cell cycle arrest2. The mechanisms by which t ...
Slides - Brown Computer Science
... that it contains two distinct proline rich regions which can bind to an SH3 domain. Grb2 has two such domains, and serves as an adaptor linking phosphorylated EGFR to Ras as in the next figure. ...
... that it contains two distinct proline rich regions which can bind to an SH3 domain. Grb2 has two such domains, and serves as an adaptor linking phosphorylated EGFR to Ras as in the next figure. ...
Glycobiology is the study of the structure, biosynthesis, biology and
... Most proteins contain sugars Almost all plasma proteins except albumin Proteins of cellular membranes Some blood group substances Certain hormones Occur in most organisms Many viruses ...
... Most proteins contain sugars Almost all plasma proteins except albumin Proteins of cellular membranes Some blood group substances Certain hormones Occur in most organisms Many viruses ...
Phosphorylation

Phosphorylation is the addition of a phosphate (PO43−) group to a protein or other organic molecule. Phosphorylation and its counterpart, dephosphorylation, turn many protein enzymes on and off, thereby altering their function and activity. Protein phosphorylation is one type of post-translational modification.Protein phosphorylation in particular plays a significant role in a wide range of cellular processes. Its prominent role in biochemistry is the subject of a very large body of research (as of March 2015, the Medline database returns over 240,000 articles on the subject, largely on protein phosphorylation).