Examining Social Life
... • Sociologist: interest in social interaction; how people relate to one another and influence each other’s behavior. • Focus on group rather than individual • Social phenomena: observable facts or events that involve human society ...
... • Sociologist: interest in social interaction; how people relate to one another and influence each other’s behavior. • Focus on group rather than individual • Social phenomena: observable facts or events that involve human society ...
Weberian Theory
... that people held in generating changes in the social structure. He saw these ideas as a major reason why capitalism developed first in Western Europe. He therefore combined social action and structuralist theories as he studied the meaning of Protestantism to Protestants as well as the influence of ...
... that people held in generating changes in the social structure. He saw these ideas as a major reason why capitalism developed first in Western Europe. He therefore combined social action and structuralist theories as he studied the meaning of Protestantism to Protestants as well as the influence of ...
Significant Sociologists
... aggregation of men, originates in some quality of man himself. A little consideration shows us, for instance, that the very existence of society, implies some natural affinity in its members for such a union. It is pretty clear too, that without a certain fitness in mankind for ruling, and being rul ...
... aggregation of men, originates in some quality of man himself. A little consideration shows us, for instance, that the very existence of society, implies some natural affinity in its members for such a union. It is pretty clear too, that without a certain fitness in mankind for ruling, and being rul ...
2011 Essay 2
... kin selection, reciprocal altruism, parent-offspring conflict, and sexual selection.. State what these mechanisms are and why, in the light of the kinds and frequency of social behaviors we find in animals and humans (aggressive, cooperative, conflict, selfishness, altruistic, spite, etc), these mec ...
... kin selection, reciprocal altruism, parent-offspring conflict, and sexual selection.. State what these mechanisms are and why, in the light of the kinds and frequency of social behaviors we find in animals and humans (aggressive, cooperative, conflict, selfishness, altruistic, spite, etc), these mec ...
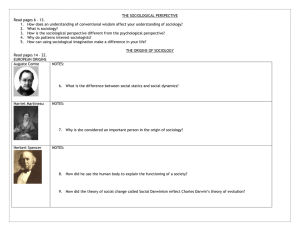
THE SOCIOLOGICAL PERSPECTIVE Read pages 6 – 13. How
... 3. How is the sociological perspective different from the psychological perspective? 4. Why do patterns interest sociologists? 5. How can using sociological imagination make a difference in your life? THE ORIGINS OF SOCIOLOGY Read pages 14 – 22. EUROPEAN ORIGINS Auguste Comte ...
... 3. How is the sociological perspective different from the psychological perspective? 4. Why do patterns interest sociologists? 5. How can using sociological imagination make a difference in your life? THE ORIGINS OF SOCIOLOGY Read pages 14 – 22. EUROPEAN ORIGINS Auguste Comte ...
Basic Concepts of Sociology
... Objectives: 1. Tell what sociology is 2. Define social patterns and social characteristics 3. Explain why social patterns are important to sociologists 4. Describe the sociological perspective 1. Read the introduction on pages 3 and 4. The Sociological Point of View 2. How would a sociologist approa ...
... Objectives: 1. Tell what sociology is 2. Define social patterns and social characteristics 3. Explain why social patterns are important to sociologists 4. Describe the sociological perspective 1. Read the introduction on pages 3 and 4. The Sociological Point of View 2. How would a sociologist approa ...
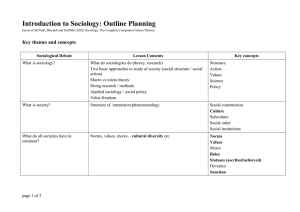
Introduction to Sociology
... What do sociologists do (theory, research) Two basic approaches to study of society (social structure / social action). Macro vs micro theory Doing research / methods Applied sociology / social policy Value-freedom ...
... What do sociologists do (theory, research) Two basic approaches to study of society (social structure / social action). Macro vs micro theory Doing research / methods Applied sociology / social policy Value-freedom ...
Darwinism and the Age of Earth Victor Stenger, Reality Check
... age of the world have been for some time one of my sorest troubles.” If Thomson’s conclusions had been correct, evolution by natural selection would have been falsified. But Thomson’s conclusions were wrong, and Darwin’s theory was not falsified. Thomson cannot be faulted, for he used the best info ...
... age of the world have been for some time one of my sorest troubles.” If Thomson’s conclusions had been correct, evolution by natural selection would have been falsified. But Thomson’s conclusions were wrong, and Darwin’s theory was not falsified. Thomson cannot be faulted, for he used the best info ...
File
... Readings/films to review: Chapter 1 (all sections), “The Importance of Being Beautiful” (Sidney Katz), The Truman Show Essential Questions: What is sociology and why do we study it? What is the significance of one’s sociological imagination? In what ways does sociology overlap with other socia ...
... Readings/films to review: Chapter 1 (all sections), “The Importance of Being Beautiful” (Sidney Katz), The Truman Show Essential Questions: What is sociology and why do we study it? What is the significance of one’s sociological imagination? In what ways does sociology overlap with other socia ...
Famous Sociologist Notes
... root of social order - Men are bound together by the need for the labor others provide ...
... root of social order - Men are bound together by the need for the labor others provide ...
The Sociological Point of View
... • Focused on social order and social change • Said social statics hold society together and social dynamics were the ways society changed • Never completed his college education ...
... • Focused on social order and social change • Said social statics hold society together and social dynamics were the ways society changed • Never completed his college education ...
THE STUDY OF SOCIOLOGY
... Couples who live together before they marry usually report higher satisfaction with their marriages than couples who do not live together before they marry. ...
... Couples who live together before they marry usually report higher satisfaction with their marriages than couples who do not live together before they marry. ...
Sociology Mid -Term Exam
... Sociology Mid -Term Exam- Review 1. The ability to see the connection between the larger world and your personal life is what sociologist C. Wright Mills called 2. People who focus on the forces in society that promote competition and change employ the 3. The phrase “survival of the fittest,” or the ...
... Sociology Mid -Term Exam- Review 1. The ability to see the connection between the larger world and your personal life is what sociologist C. Wright Mills called 2. People who focus on the forces in society that promote competition and change employ the 3. The phrase “survival of the fittest,” or the ...
CHAPTER 1 LEARNING GOALS What is sociology? How is the
... How is the sociological perspective different from the psychological perspective? Why do patterns interest sociologists? How can using your sociological imagination make a difference in your life? What is the difference between social statics and social dynamics? Why is Harriet Martineau considered ...
... How is the sociological perspective different from the psychological perspective? Why do patterns interest sociologists? How can using your sociological imagination make a difference in your life? What is the difference between social statics and social dynamics? Why is Harriet Martineau considered ...
Famous Sociologists
... Spencer developed an all-embracing conception of evolution as the progressive development of the physical world, biological organisms, the human mind, and human culture and societies. He was "an enthusiastic exponent of evolution" and even "wrote about evolution before Darwin did."[1] Spencer was "t ...
... Spencer developed an all-embracing conception of evolution as the progressive development of the physical world, biological organisms, the human mind, and human culture and societies. He was "an enthusiastic exponent of evolution" and even "wrote about evolution before Darwin did."[1] Spencer was "t ...