THE PERIODIC TABLE
... 4 valence electrons Exists as both non-metals and metals Metallic character increases down the group Carbon important element for all living organisms, form basis of branch of organic chemistry Silicon is a metalloid and is also abundant e.g. sand Germanium is a metalloid, used in electronics as sem ...
... 4 valence electrons Exists as both non-metals and metals Metallic character increases down the group Carbon important element for all living organisms, form basis of branch of organic chemistry Silicon is a metalloid and is also abundant e.g. sand Germanium is a metalloid, used in electronics as sem ...
Classification of
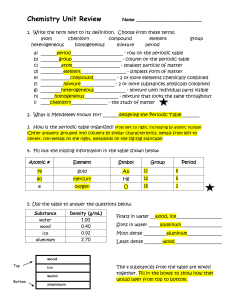
... 2 other elements in this same group: _H, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Fr________ 8. Examine the pictures of substances shown below. Label each substance as an element, compound or mixture. ...
... 2 other elements in this same group: _H, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Fr________ 8. Examine the pictures of substances shown below. Label each substance as an element, compound or mixture. ...
File
... deflection for one gold foil turned out to be about 1°. 3) A very, very few (1 in 8000 for platinum foil) alpha particles were turned through an angle of 90° or more. All Rutherford had to do was explain how it all fit together. ...
... deflection for one gold foil turned out to be about 1°. 3) A very, very few (1 in 8000 for platinum foil) alpha particles were turned through an angle of 90° or more. All Rutherford had to do was explain how it all fit together. ...
Ch 4 Powerpoint
... Elements are able to be subdivided into smaller and smaller particles – these are the atoms, and they still have properties of that element If you could line up 100,000,000 copper atoms in a single file, they would be approximately 1 cm long Despite their small size, individual atoms are observa ...
... Elements are able to be subdivided into smaller and smaller particles – these are the atoms, and they still have properties of that element If you could line up 100,000,000 copper atoms in a single file, they would be approximately 1 cm long Despite their small size, individual atoms are observa ...
atom - West Ada
... are combined with oxygen atoms in the form of water. The living things on Earth are composed mostly of the elements oxygen, carbon, nitrogen and hydrogen. ...
... are combined with oxygen atoms in the form of water. The living things on Earth are composed mostly of the elements oxygen, carbon, nitrogen and hydrogen. ...
Topic 2 Microscopic World I
... Both statements are true and the 2nd statement is a correct explanation of the 1st statement. Both statements are true but the 2nd statement is NOT a correct explanation of the 1st statement. The 1st statement is false but the 2nd statement is true. Both statements are false. ...
... Both statements are true and the 2nd statement is a correct explanation of the 1st statement. Both statements are true but the 2nd statement is NOT a correct explanation of the 1st statement. The 1st statement is false but the 2nd statement is true. Both statements are false. ...
Word List
... in their nuclei. All atoms of the same element must have the same number of protons (and thus the same number of electrons) which is equal to the atomic number. However, atoms of the same element can have different numbers of neutrons and thus a different mass number. The difference in mass does not ...
... in their nuclei. All atoms of the same element must have the same number of protons (and thus the same number of electrons) which is equal to the atomic number. However, atoms of the same element can have different numbers of neutrons and thus a different mass number. The difference in mass does not ...
theory1 (osergienko v1)
... Cathode rays have identical properties regardless of the element used to produce them. All elements must contain identically charged electrons. Atoms are neutral, so there must be positive particles in the atom to balance the negative charge of the electrons Electrons have so little mass that a ...
... Cathode rays have identical properties regardless of the element used to produce them. All elements must contain identically charged electrons. Atoms are neutral, so there must be positive particles in the atom to balance the negative charge of the electrons Electrons have so little mass that a ...
Chapter 4:ааAtomic Structure Section 4.1анаDefining the Atom
... ○ atoms have not net electric charge; they are neutral ○ electric charges are carried by particles of matter ○ electric charges always exist in wholenumber multiples of a single basic unit ○ when a given number of negatively charged particles combines with an equal number of positively charged ...
... ○ atoms have not net electric charge; they are neutral ○ electric charges are carried by particles of matter ○ electric charges always exist in wholenumber multiples of a single basic unit ○ when a given number of negatively charged particles combines with an equal number of positively charged ...
Atomic Theory Class #5
... The Bohr Model, you should be able to explain how orbits are also energy levels, ground state, excited state, how to become excited, what happens when electrons return to the ground state, maximum number of electrons per orbital (think group 18), Spectra, spectra lines, uses for spectra, problems w ...
... The Bohr Model, you should be able to explain how orbits are also energy levels, ground state, excited state, how to become excited, what happens when electrons return to the ground state, maximum number of electrons per orbital (think group 18), Spectra, spectra lines, uses for spectra, problems w ...
- Catalyst
... Question 7: Fill in the blanks of the statements below with the words in the box. Note, you will only use each word once. A. atom ...
... Question 7: Fill in the blanks of the statements below with the words in the box. Note, you will only use each word once. A. atom ...
CHEMISTRY: MIDTERM EXAM REVIEW SPRING 2013 Multiple
... b. moves within its atomic orbital c. jumps from a lower to a higher energy level d. drops from a higher to a lower energy level ____ 27. What must be done to be certain that a chemical change has taken place? a. Demonstrate that a release of energy occurred after the change. b. Check for the produc ...
... b. moves within its atomic orbital c. jumps from a lower to a higher energy level d. drops from a higher to a lower energy level ____ 27. What must be done to be certain that a chemical change has taken place? a. Demonstrate that a release of energy occurred after the change. b. Check for the produc ...
Bonding
... Answer the following questions about the element selenium, Se (atomic number 34). c.In terms of atomic structure, explain why the first ionization energy of selenium is i. less than that of bromine (atomic number 35), and ii.greater than that of tellurium (atomic number 52). d.Selenium reacts with f ...
... Answer the following questions about the element selenium, Se (atomic number 34). c.In terms of atomic structure, explain why the first ionization energy of selenium is i. less than that of bromine (atomic number 35), and ii.greater than that of tellurium (atomic number 52). d.Selenium reacts with f ...
Chapter 4 - Germainium.net
... • What happens to the atomic mass number and the atomic number of a radioisotope when it undergoes alpha emission? • High speed electrons emitted by an unstable nucleus are ________ particles. • What isotope of what element is produced if krypton-81 undergoes beta decay? Write out the nuclear reacti ...
... • What happens to the atomic mass number and the atomic number of a radioisotope when it undergoes alpha emission? • High speed electrons emitted by an unstable nucleus are ________ particles. • What isotope of what element is produced if krypton-81 undergoes beta decay? Write out the nuclear reacti ...
sample
... iron, have been known for thousands of years. Others have been discovered much more recently. Helium, often used in balloons, was discovered in 1895. Americium, used in smoke alarms, was discovered only in 1944. Scientists continue to discover new elements today. The atomic number (proton number) of ...
... iron, have been known for thousands of years. Others have been discovered much more recently. Helium, often used in balloons, was discovered in 1895. Americium, used in smoke alarms, was discovered only in 1944. Scientists continue to discover new elements today. The atomic number (proton number) of ...
Atoms
... interaction is called electromagnetic field. Electromagnetic field is a property similar to speed or force: it has not only a size, but also a direction – you know from experience that it makes a very big difference whether you travel 40 mph towards or 40 mph away from your home! The measure of this ...
... interaction is called electromagnetic field. Electromagnetic field is a property similar to speed or force: it has not only a size, but also a direction – you know from experience that it makes a very big difference whether you travel 40 mph towards or 40 mph away from your home! The measure of this ...
know thy reference tables!
... Knowing your reference tables well is a big help on the NYS Chemistry Regents exam since about half of the questions can be answered using the tables. This compilation of Reference Table related questions from the June 2010‐January 2011 NYS Chemistry Regents exams will help you to recognize quest ...
... Knowing your reference tables well is a big help on the NYS Chemistry Regents exam since about half of the questions can be answered using the tables. This compilation of Reference Table related questions from the June 2010‐January 2011 NYS Chemistry Regents exams will help you to recognize quest ...
Chapter 2
... John Dalton and the Atomic Theory of Matter • 1. All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. • 2. All atoms of a given element are alike and differ from the atoms of any other element. • 3. Compounds are formed when atoms of different elements combine in fixed proportions. • 4 ...
... John Dalton and the Atomic Theory of Matter • 1. All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. • 2. All atoms of a given element are alike and differ from the atoms of any other element. • 3. Compounds are formed when atoms of different elements combine in fixed proportions. • 4 ...
Chem102_ch03_atoms_and_the_periodic_table
... Definitions Electrons in the highest occupied energy level are the greatest stable distance from the nucleus. These outermost electrons are known as valence electrons. Shell is a principal energy level defined by a given value of n, where n can be 1,2,3,4 etc… and is capable of holding 2n2 electron ...
... Definitions Electrons in the highest occupied energy level are the greatest stable distance from the nucleus. These outermost electrons are known as valence electrons. Shell is a principal energy level defined by a given value of n, where n can be 1,2,3,4 etc… and is capable of holding 2n2 electron ...
Atomic Structure Paper Plate Model Plate 1: Front
... in the proper locations (2 in the first shell, up to 8 in the second shell, up to 8 in the third shell) Back- Draw the square that you find on the periodic table that represents your element. Label the atomic number, symbol, name, and atomic mass. Be sure your name is on the plate somewhere. Plate 2 ...
... in the proper locations (2 in the first shell, up to 8 in the second shell, up to 8 in the third shell) Back- Draw the square that you find on the periodic table that represents your element. Label the atomic number, symbol, name, and atomic mass. Be sure your name is on the plate somewhere. Plate 2 ...