Atoms, Molecules and Ions
... always a small whole number • law states that when two elements form a series of compounds the ratios of the masses to second element to 1g of the first element can always be reduced to small whole numbers ...
... always a small whole number • law states that when two elements form a series of compounds the ratios of the masses to second element to 1g of the first element can always be reduced to small whole numbers ...
03 Atoms – Nuclides
... a positively charged alpha particle (α), which is the same as a helium nuclei consisting of two neutrons and two protons a negatively charged beta minus particle (β-), which is the same as an electron a positively charged beta plus particle (β+), which is the same as a positron, a particle of equal ...
... a positively charged alpha particle (α), which is the same as a helium nuclei consisting of two neutrons and two protons a negatively charged beta minus particle (β-), which is the same as an electron a positively charged beta plus particle (β+), which is the same as a positron, a particle of equal ...
Atomic - My CCSD
... electron. He sprayed oil and used X-rays to give the oil a negative charged. Then measured how different magnetic charges changed the rate the oil fell. He calculated the mass of the e- to be 9.11 X 10-19 grams. ...
... electron. He sprayed oil and used X-rays to give the oil a negative charged. Then measured how different magnetic charges changed the rate the oil fell. He calculated the mass of the e- to be 9.11 X 10-19 grams. ...
The Structure of the Atom
... The ancient Greek philosopher Democritus coined what word for a tiny piece of matter that cannot be divided? a) Element b) Electron c) Atom d) Molecule Dalton’s theory (~1800; based on behavior of gasses) included all but one of the following points. Which is not from Dalton? a) All elements are com ...
... The ancient Greek philosopher Democritus coined what word for a tiny piece of matter that cannot be divided? a) Element b) Electron c) Atom d) Molecule Dalton’s theory (~1800; based on behavior of gasses) included all but one of the following points. Which is not from Dalton? a) All elements are com ...
09/09/03 lecture
... • Different elements have different numbers of protons in their atoms. • Atomic number: number of protons in the atom; different elements have different atomic numbers. • A neutral atom (i.e., one with no net charge) will have the same number of electrons as protons). • Most chemical properties are ...
... • Different elements have different numbers of protons in their atoms. • Atomic number: number of protons in the atom; different elements have different atomic numbers. • A neutral atom (i.e., one with no net charge) will have the same number of electrons as protons). • Most chemical properties are ...
Name
... 27. _____________________ is the particles or energy emitted from an atomic nucleus when it is unstable due to stronger ________________ repulsive forces than ______________ attractive forces. ...
... 27. _____________________ is the particles or energy emitted from an atomic nucleus when it is unstable due to stronger ________________ repulsive forces than ______________ attractive forces. ...
File
... How many electrons are moved? – Fluorine makes ions with a 1- charge. Are electrons lost or gained? How many electrons are moved? – An ion has 13 p+ and 10 e-. Give the symbol and charge for the ion. – An ion has 34 p+ and 36 e-. Give the symbol and charge for the ion. ...
... How many electrons are moved? – Fluorine makes ions with a 1- charge. Are electrons lost or gained? How many electrons are moved? – An ion has 13 p+ and 10 e-. Give the symbol and charge for the ion. – An ion has 34 p+ and 36 e-. Give the symbol and charge for the ion. ...
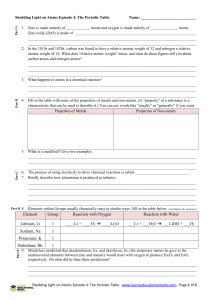
Element Group Reaction with Oxygen Reaction with Water Lithium
... Zinc oxide (ZnO) is made of ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ 2. In the 1810s and 1820s, carbon w ...
... Zinc oxide (ZnO) is made of ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ 2. In the 1810s and 1820s, carbon w ...
Speed of reactions
... At the centre of the atom is a very small core called the nucleus. The nucleus is very small compared to the size of the rest of the atom; if atoms were magnified to the size of a football park, then the nucleus would be about the size of a pin-head. Protons are found in the nucleus. Protons have a ...
... At the centre of the atom is a very small core called the nucleus. The nucleus is very small compared to the size of the rest of the atom; if atoms were magnified to the size of a football park, then the nucleus would be about the size of a pin-head. Protons are found in the nucleus. Protons have a ...
Atomic Structure Notes file
... The atoms of an element can differ in mass from each other because they have differing numbers of neutrons. Those with more neutrons will weigh more and be more massive. The atomic mass (often referred to as atomic weight) of an element is calculated by adding together the number of protons and the ...
... The atoms of an element can differ in mass from each other because they have differing numbers of neutrons. Those with more neutrons will weigh more and be more massive. The atomic mass (often referred to as atomic weight) of an element is calculated by adding together the number of protons and the ...
Atomic Structure-PRACTICE TEST
... TRUE or FALSE - the atomic mass increases by ONE from element to element (atomic number) TRUE or FALSE - the elements become more non metallic TRUE or FALSE - the ionization energy of the elements generally decreases TRUE or FALSE - the elements are arranged according to increasing atomic number TRU ...
... TRUE or FALSE - the atomic mass increases by ONE from element to element (atomic number) TRUE or FALSE - the elements become more non metallic TRUE or FALSE - the ionization energy of the elements generally decreases TRUE or FALSE - the elements are arranged according to increasing atomic number TRU ...
The Atom - cloudfront.net
... subatomic particle which he called a neutron. A neutron has about the same mass as a proton and is also found in the nucleus of the atom. However, unlike the proton, the neutron does not have an electric charge. ...
... subatomic particle which he called a neutron. A neutron has about the same mass as a proton and is also found in the nucleus of the atom. However, unlike the proton, the neutron does not have an electric charge. ...
Chapter 3
... – Greek philosopher, Democritus, proposed that matter is composed of small indivisible particles, called “atomos” (means “uncuttable”) ...
... – Greek philosopher, Democritus, proposed that matter is composed of small indivisible particles, called “atomos” (means “uncuttable”) ...
Chemistry 30 Review of Basic Chemistry 20
... Compounds that dissolve in water may produce ions. These solutions are called electrolytes. Some compounds may dissolve in water but form no ions. These solutions are called nonelectrolytes. When electrolytes are formed, dissociation equations can be shown. ...
... Compounds that dissolve in water may produce ions. These solutions are called electrolytes. Some compounds may dissolve in water but form no ions. These solutions are called nonelectrolytes. When electrolytes are formed, dissociation equations can be shown. ...
UNIT 1: THE ATOM
... number of electrons in a neutral atom. It is used to identify an element and it does not change for a specific element. Elements on the periodic table are arranged according to increasing atomic number. Often called the nuclear charge. 7. Mass Number: number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of ...
... number of electrons in a neutral atom. It is used to identify an element and it does not change for a specific element. Elements on the periodic table are arranged according to increasing atomic number. Often called the nuclear charge. 7. Mass Number: number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of ...
The Development of Atomic Theory
... Neutrally charged Atoms will have the same number of electrons as protons ...
... Neutrally charged Atoms will have the same number of electrons as protons ...
Physical Properties
... Mendeleev and Meyer • Published nearly identical schemes for classifying elements • Arranged elements by ______________________ • Mendeleev generally given more credit – Published first – More successful at demonstrating value of table – Predicted discovery of new elements, properties of new elemen ...
... Mendeleev and Meyer • Published nearly identical schemes for classifying elements • Arranged elements by ______________________ • Mendeleev generally given more credit – Published first – More successful at demonstrating value of table – Predicted discovery of new elements, properties of new elemen ...
Unit 2
... • Substances keep most of their identities and own properties • Vary in amounts • Can be separated by physical means based on the physical properties of the various parts of the ...
... • Substances keep most of their identities and own properties • Vary in amounts • Can be separated by physical means based on the physical properties of the various parts of the ...
Inside an Atom
... same number of protons, but can have different number of neutrons Ex. Carbon has 6 protons, but can ...
... same number of protons, but can have different number of neutrons Ex. Carbon has 6 protons, but can ...
Matching - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... ____ 15. Which of the following is true about subatomic particles? a. Electrons are negatively charged and are the heaviest subatomic particle. b. Protons are positively charged and the lightest subatomic particle. c. Neutrons have no charge and are the lightest subatomic particle. d. The mass of a ...
... ____ 15. Which of the following is true about subatomic particles? a. Electrons are negatively charged and are the heaviest subatomic particle. b. Protons are positively charged and the lightest subatomic particle. c. Neutrons have no charge and are the lightest subatomic particle. d. The mass of a ...
gallagher chapter 41
... charge, and a relative mass of 1 (or 1840 times that of an electron) 5. 1932 – James Chadwick confirmed the existence of the “neutron” – a particle with no charge, but a mass nearly equal to a proton ...
... charge, and a relative mass of 1 (or 1840 times that of an electron) 5. 1932 – James Chadwick confirmed the existence of the “neutron” – a particle with no charge, but a mass nearly equal to a proton ...
Physical Science Week 1
... • Create a diagram showing the correct number and placement (relative) of neutrons, protons, and electrons. Color and neatness count. • Create a legend (key) • Add the square from periodic table for your element. ...
... • Create a diagram showing the correct number and placement (relative) of neutrons, protons, and electrons. Color and neatness count. • Create a legend (key) • Add the square from periodic table for your element. ...