Periodic Law
... The work of Schrödinger resulted in a model of the atom whereby the electrons follow certain complex paths, called orbitals, about the center of the atom, the nucleus. The constantly moving electrons are said to be located in so-called subshells that lie within certain shells in the atom. The closer ...
... The work of Schrödinger resulted in a model of the atom whereby the electrons follow certain complex paths, called orbitals, about the center of the atom, the nucleus. The constantly moving electrons are said to be located in so-called subshells that lie within certain shells in the atom. The closer ...
Groups of the Periodic Table
... because it contains two different isotopes. Elements and the Periodic Table All the different elements are arranged in a chart called the periodic table. Here are the main features of the table: the horizontal rows are called periods the vertical columns are called groups elements in the same ...
... because it contains two different isotopes. Elements and the Periodic Table All the different elements are arranged in a chart called the periodic table. Here are the main features of the table: the horizontal rows are called periods the vertical columns are called groups elements in the same ...
Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures
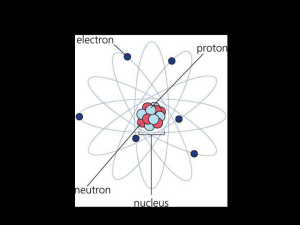
... Nucleus ( protons and neutrons) electrons in space around the nucleus. ...
... Nucleus ( protons and neutrons) electrons in space around the nucleus. ...
Class 9 CBSE Test paper Solved Chapter 3: Structure of...
... bounced back directly. Rutherford’s result lead him to believe that most of the foil was made of empty space, but had extremely small, dense lumps of matter inside, which is present only at the center because from center, few particles bounced back. All other particles deflected at different angles. ...
... bounced back directly. Rutherford’s result lead him to believe that most of the foil was made of empty space, but had extremely small, dense lumps of matter inside, which is present only at the center because from center, few particles bounced back. All other particles deflected at different angles. ...
Variation in Properties of Group II Compounds
... Each group of elements embodied in the periodic table has their own unique properties. As for group II elements, they are classified as one of the s-block elements, also named as alkaline earth metals. In this essay, the variation in properties of group II elements and their compounds are illustrate ...
... Each group of elements embodied in the periodic table has their own unique properties. As for group II elements, they are classified as one of the s-block elements, also named as alkaline earth metals. In this essay, the variation in properties of group II elements and their compounds are illustrate ...
Atoms, Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures
... be divided and still maintain its years, scientists have characteristics. designed many different models for this structure. Atoms are the building blocks of the universe. There are 92 Each one was the best different kinds of atoms that model at the time, but as occur naturally, although more ne ...
... be divided and still maintain its years, scientists have characteristics. designed many different models for this structure. Atoms are the building blocks of the universe. There are 92 Each one was the best different kinds of atoms that model at the time, but as occur naturally, although more ne ...
CHEM 1405 CHAPTER 4
... Each element has its own Absorption spectrum. So, it is used as a tool for qualitative and quantitative chemical analysis. Bohr Model of the Atom According to Bohr, atom has a positively center called nucleus. Protons and neutrons are present in the nucleus. The electrons revolve round the nucleus i ...
... Each element has its own Absorption spectrum. So, it is used as a tool for qualitative and quantitative chemical analysis. Bohr Model of the Atom According to Bohr, atom has a positively center called nucleus. Protons and neutrons are present in the nucleus. The electrons revolve round the nucleus i ...
What are the parts of an atom?
... moon, however, the electrons move at such great speed that it is impossible to see them. If the moon orbited the Earth at the same velocity, it would appear to be a solid ring, instead of an individual object. The area in which the electrons orbit is called the electron cloud. There is space in betw ...
... moon, however, the electrons move at such great speed that it is impossible to see them. If the moon orbited the Earth at the same velocity, it would appear to be a solid ring, instead of an individual object. The area in which the electrons orbit is called the electron cloud. There is space in betw ...
Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
... because it contains two different isotopes. Elements and the Periodic Table All the different elements are arranged in a chart called the periodic table. Here are the main features of the table: the horizontal rows are called periods the vertical columns are called groups elements in the same ...
... because it contains two different isotopes. Elements and the Periodic Table All the different elements are arranged in a chart called the periodic table. Here are the main features of the table: the horizontal rows are called periods the vertical columns are called groups elements in the same ...
Lecture Notes Part 2 - Dr. Samples` Chemistry Classes
... • The number underneath an Elemental Symbol on the Periodic Table is its atomic mass (the mass of 1 “average” atom in amu). • Is a formula mass very useful in the lab? Well, can we weigh out individual atoms or ions on a lab balance? They are too tiny to weigh or pick out individually! • Chemists we ...
... • The number underneath an Elemental Symbol on the Periodic Table is its atomic mass (the mass of 1 “average” atom in amu). • Is a formula mass very useful in the lab? Well, can we weigh out individual atoms or ions on a lab balance? They are too tiny to weigh or pick out individually! • Chemists we ...
Review - Final Exam
... 22. What are the valence electrons? What happens to the valence electrons across a row of representative elements and down a group? What information is gained from the valence electrons? Why do chemical families have similar properties? 23. Draw Lewis (Electron Dot) symbols for the elements across t ...
... 22. What are the valence electrons? What happens to the valence electrons across a row of representative elements and down a group? What information is gained from the valence electrons? Why do chemical families have similar properties? 23. Draw Lewis (Electron Dot) symbols for the elements across t ...
The atomic number tells how many protons Protons make an atom
... many protons AND neutrons there are in the nucleus The number of neutrons do NOT make a difference in the identity of an atom Atoms of the same element will ALWAYS have the same # of protons, but MAY have different neutrons ...
... many protons AND neutrons there are in the nucleus The number of neutrons do NOT make a difference in the identity of an atom Atoms of the same element will ALWAYS have the same # of protons, but MAY have different neutrons ...
Atom - Perry Local Schools
... Number of neutrons can be different Atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. atoms with more neutrons have more mass Isotopes of same element all have the same chemical behavior. the number of electrons is the only thing that ...
... Number of neutrons can be different Atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. atoms with more neutrons have more mass Isotopes of same element all have the same chemical behavior. the number of electrons is the only thing that ...
atom atomic symbol atomic number # protons atomic mass
... Number of Protons = Atomic Number (Use the large colored marshmallows for protons) Number of Neutrons = Atomic Mass – Atomic Number (Use the large white marshmallows for neutrons) Number of Electrons = Number of Protons (Use the small colored marshmallows for electrons) ...
... Number of Protons = Atomic Number (Use the large colored marshmallows for protons) Number of Neutrons = Atomic Mass – Atomic Number (Use the large white marshmallows for neutrons) Number of Electrons = Number of Protons (Use the small colored marshmallows for electrons) ...
Big Science from the Small World of Atom
... electron occupation in the different shells (energy levels) so that the number of core electrons and the valence electrons can be counted. Students will learn how elements are arranged in the periodic table, how the number of valence electrons is correlated with group number in the periodic table. V ...
... electron occupation in the different shells (energy levels) so that the number of core electrons and the valence electrons can be counted. Students will learn how elements are arranged in the periodic table, how the number of valence electrons is correlated with group number in the periodic table. V ...
Johnston Middle School Lesson Plan 2015-2016
... TSW describe the structure of atoms including the masses, electrical charges and locations of protons and neutrons in the nucleus and electrons in the electron cloud. TSW identify that protons determine an element's identity, and valence electrons determine its chemical properties and reactivity TSW ...
... TSW describe the structure of atoms including the masses, electrical charges and locations of protons and neutrons in the nucleus and electrons in the electron cloud. TSW identify that protons determine an element's identity, and valence electrons determine its chemical properties and reactivity TSW ...
Science 9 Unit B 2.0 - Vegreville Composite High
... this was difficult because different scientists used different properties • John Dalton first attempted to categorize and order the elements in the early 1800’s. He developed a new system of symbols ...
... this was difficult because different scientists used different properties • John Dalton first attempted to categorize and order the elements in the early 1800’s. He developed a new system of symbols ...
Notes - Zion Central Middle School
... Atoms are made up of subatomic particles—protons, neutrons and electrons. o Protons and neutrons are in the nucleus of an atom. o Electrons occupy orbitals or electron clouds that surround the nucleus. Protons are found in the nucleus of atoms and have an electric charge of +1. Neutrons are found in ...
... Atoms are made up of subatomic particles—protons, neutrons and electrons. o Protons and neutrons are in the nucleus of an atom. o Electrons occupy orbitals or electron clouds that surround the nucleus. Protons are found in the nucleus of atoms and have an electric charge of +1. Neutrons are found in ...
Chapter 4 Quiz ____ 1. The Greek philosopher Democritus coined
... b. All atoms of the same element have the same mass. c. Atoms contain subatomic particles. d. A compound contains atoms of more than one element. ____ 3. Rutherford’s gold foil experiment provided evidence for which of the following statements? a. Negative and positive charges are spread evenly thro ...
... b. All atoms of the same element have the same mass. c. Atoms contain subatomic particles. d. A compound contains atoms of more than one element. ____ 3. Rutherford’s gold foil experiment provided evidence for which of the following statements? a. Negative and positive charges are spread evenly thro ...
Atoms
... • Atomic Mass = Protons + Neutrons • Neutrons = atomic mass – atomic number • Atomic symbols – First letter is ALWAYS upper case – Second letter is ALWAYS lower case ...
... • Atomic Mass = Protons + Neutrons • Neutrons = atomic mass – atomic number • Atomic symbols – First letter is ALWAYS upper case – Second letter is ALWAYS lower case ...
Nature of Matter: The Atom
... • A neutron has no electrical charge • Electrons are very small particles located outside the nucleus. They associated with it, we say it has a orbit (circle around) the nucleus at charge of 0. high speeds, like the Earth orbits the A neutron is found in the nucleus ...
... • A neutron has no electrical charge • Electrons are very small particles located outside the nucleus. They associated with it, we say it has a orbit (circle around) the nucleus at charge of 0. high speeds, like the Earth orbits the A neutron is found in the nucleus ...
ATOM ATOMIC SYMBOL ATOMIC NUMBER
... Number of Protons = Atomic Number (Use the large colored marshmallows for protons) Number of Neutrons = Atomic Mass – Atomic Number (Use the large white marshmallows for neutrons) Number of Electrons = Number of Protons (Use the small colored marshmallows for electrons) ...
... Number of Protons = Atomic Number (Use the large colored marshmallows for protons) Number of Neutrons = Atomic Mass – Atomic Number (Use the large white marshmallows for neutrons) Number of Electrons = Number of Protons (Use the small colored marshmallows for electrons) ...
atomic mass number - Magoffin County Schools
... The number of PROTONS in an atom’s nucleus is called the ATOMIC NUMBER of the atom. Atoms can have from 1 to 109 protons, depending on which element is being ...
... The number of PROTONS in an atom’s nucleus is called the ATOMIC NUMBER of the atom. Atoms can have from 1 to 109 protons, depending on which element is being ...