Atomic Theory and Models
... pass right through the foil in a straight line. The gold atoms would not have enough positive charge in any one region to strongly repel the charged particles. Rutherford’s team observed that most of the particles passed through the foil undisturbed, as expected. But, to their surprise, a few partic ...
... pass right through the foil in a straight line. The gold atoms would not have enough positive charge in any one region to strongly repel the charged particles. Rutherford’s team observed that most of the particles passed through the foil undisturbed, as expected. But, to their surprise, a few partic ...
Mass/Mole Conversions
... • __________: atoms of the same element that have _______________ due to different numbers of __________. • _____________: the total number of _______ and _________ that make up the nucleus of an isotope ~ Isotopes are written with the _____________ written after the element name or symbol with a __ ...
... • __________: atoms of the same element that have _______________ due to different numbers of __________. • _____________: the total number of _______ and _________ that make up the nucleus of an isotope ~ Isotopes are written with the _____________ written after the element name or symbol with a __ ...
Reviewing Chemistry: Mastering the TEKS - Student
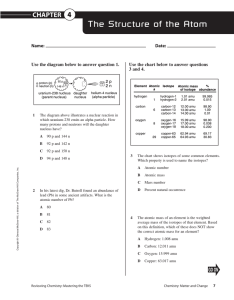
... Use the chart below to answer questions 3 and 4. ...
... Use the chart below to answer questions 3 and 4. ...
“atom”?
... was found to be identical to that of the electron and the mass was found to be 1.6726 x 10-24 g. ...
... was found to be identical to that of the electron and the mass was found to be 1.6726 x 10-24 g. ...
Chem101 - Lecture 2 Elements Elements as Pure
... - Chlorine (Cl) also has two naturally occurring isotopes: one has 18 neutrons and represents 75.78% of all naturally occurring chlorine, the other has 20 neutrons and represents the remaining 24.22% of all naturally occurring chlorine. - Magnesium (Mg) has three naturally occurring isotopes: one ha ...
... - Chlorine (Cl) also has two naturally occurring isotopes: one has 18 neutrons and represents 75.78% of all naturally occurring chlorine, the other has 20 neutrons and represents the remaining 24.22% of all naturally occurring chlorine. - Magnesium (Mg) has three naturally occurring isotopes: one ha ...
2015 VCE Chemistry Unit 1 -Miss Fitzsimmons
... decimal numbers for the mass numbers? Most elements have more than one isotope. The relative atomic mass of the element is the average mass of the isotopes taking into account the abundance of each isotope. Example: what is the Ar of boron? In a sample of boron, 20% of the atoms are 10Br and 80% are ...
... decimal numbers for the mass numbers? Most elements have more than one isotope. The relative atomic mass of the element is the average mass of the isotopes taking into account the abundance of each isotope. Example: what is the Ar of boron? In a sample of boron, 20% of the atoms are 10Br and 80% are ...
Chapter 11
... Protons (+ electric charge), p Electrons (– electric charge), e Neutrons (no charge), n Proton and Neutron have about the same mass Electron is about 2000 times less massive than proton Electrical Forces produce attraction between electrons and the protons in the nucleus (they are oppositely charged ...
... Protons (+ electric charge), p Electrons (– electric charge), e Neutrons (no charge), n Proton and Neutron have about the same mass Electron is about 2000 times less massive than proton Electrical Forces produce attraction between electrons and the protons in the nucleus (they are oppositely charged ...
Once scientists concluded that all matter contains negatively
... After a hypothesis has been formed, scientists conduct experiments to test its validity. Experiments are systematic observations or measurements, preferably made under controlled conditions—that is, under conditions in which a single variable changes. For example, in our extinction scenario, iridiu ...
... After a hypothesis has been formed, scientists conduct experiments to test its validity. Experiments are systematic observations or measurements, preferably made under controlled conditions—that is, under conditions in which a single variable changes. For example, in our extinction scenario, iridiu ...
TOPIC 24 Nucleus - jmr physics website
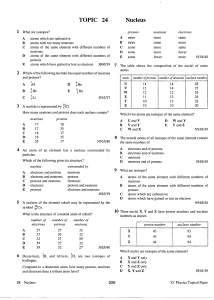
... 25 A chlorine atom, proton number 17, can gain an electron and become a chlorine ion. A sodium atom, proton number 11, can lose an electron and become a sodium ion. (a) What is the sign of the charge on (i) a chlorine ion, ...
... 25 A chlorine atom, proton number 17, can gain an electron and become a chlorine ion. A sodium atom, proton number 11, can lose an electron and become a sodium ion. (a) What is the sign of the charge on (i) a chlorine ion, ...
Chapter 8. The Periodic Table
... family, the second alkaline earths,, the lanthanides and actinides together are called rare earths, and the last three representative families are called calcogens, halogens and noble gases. (The remaining representative families are named for their top members, boron, nitrogen and carbon.) Because ...
... family, the second alkaline earths,, the lanthanides and actinides together are called rare earths, and the last three representative families are called calcogens, halogens and noble gases. (The remaining representative families are named for their top members, boron, nitrogen and carbon.) Because ...
- Angelo State University
... and most of the mass (~99.9%) of the atom was concentrated in the center, called the nucleus. Most of the volume of the atom was empty space, through which the electrons were dispersed in some fashion. • The positively charged particles within the nucleus are called protons; there must be one electr ...
... and most of the mass (~99.9%) of the atom was concentrated in the center, called the nucleus. Most of the volume of the atom was empty space, through which the electrons were dispersed in some fashion. • The positively charged particles within the nucleus are called protons; there must be one electr ...
AP Chemistry
... The Law of Conservation of Mass: mass is neither lost nor gained during an ordinary chemical reaction. In other words, the products of a reaction must have the same number of type of atoms as the reactants. Law of Definite Proportion: a given compound always contains exactly proportions of elements ...
... The Law of Conservation of Mass: mass is neither lost nor gained during an ordinary chemical reaction. In other words, the products of a reaction must have the same number of type of atoms as the reactants. Law of Definite Proportion: a given compound always contains exactly proportions of elements ...
average atomic mass
... Isotopes have mass numbers Isotopes are atoms of the same element (the same number of p+ and e-) but with different masses due to having different numbers of n0. ...
... Isotopes have mass numbers Isotopes are atoms of the same element (the same number of p+ and e-) but with different masses due to having different numbers of n0. ...
GCSE Chemistry Textbook sample
... From understanding and preparing to teach new specifications, through to developing subject expertise and moving leadership, AQA has a training offering for you. Continued professional development training is provided to over 30,000 teachers each year, either through face to face, online or in-schoo ...
... From understanding and preparing to teach new specifications, through to developing subject expertise and moving leadership, AQA has a training offering for you. Continued professional development training is provided to over 30,000 teachers each year, either through face to face, online or in-schoo ...
Chemical Change
... According to Dalton’s atomic theory, and element is composed of only one kind of atom, and a compound is composed of particles that are chemical combinations of different kinds of atoms. 1. All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms 2. Atoms of the same element are identica ...
... According to Dalton’s atomic theory, and element is composed of only one kind of atom, and a compound is composed of particles that are chemical combinations of different kinds of atoms. 1. All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms 2. Atoms of the same element are identica ...
ppt
... In row 6, a new type of orbital, 4f, appears in between elements 57 and 72. All the elements with 4f electrons have very similar chemical properties. They are known as the Lanthanides (after element Z=57, Lanthanum) or rare earths. A similar pattern repeats in row 7, with the 5f orbitals filling bet ...
... In row 6, a new type of orbital, 4f, appears in between elements 57 and 72. All the elements with 4f electrons have very similar chemical properties. They are known as the Lanthanides (after element Z=57, Lanthanum) or rare earths. A similar pattern repeats in row 7, with the 5f orbitals filling bet ...
Ch.3-Atoms-The Building Blocks of Matter
... atom is the smallest particle of an element that retains the chemical properties of that element. • The nucleus is a very small region located at the center of an atom. • The nucleus is made up of at least one positively charged particle called a proton and usually one or more neutral particle calle ...
... atom is the smallest particle of an element that retains the chemical properties of that element. • The nucleus is a very small region located at the center of an atom. • The nucleus is made up of at least one positively charged particle called a proton and usually one or more neutral particle calle ...
Adaptif DALTON ATOMIC THEORY
... 1. Every matter compiled by small particle so-called with atom 2. Atom is a real small solid ball 3. Element is matter which consist of atom that is specific and differs from atom from other element. 4. Compound is matter compiled by two or more atom type with ...
... 1. Every matter compiled by small particle so-called with atom 2. Atom is a real small solid ball 3. Element is matter which consist of atom that is specific and differs from atom from other element. 4. Compound is matter compiled by two or more atom type with ...
CHAPTER 11 Introduction to Atoms
... • The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is the atomic number. The atomic number identifies the atoms of a particular element. • Isotopes of an atom have the same number of protons but have different numbers of neutrons. Isotopes share most of the same chemical and physical properties. • Th ...
... • The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is the atomic number. The atomic number identifies the atoms of a particular element. • Isotopes of an atom have the same number of protons but have different numbers of neutrons. Isotopes share most of the same chemical and physical properties. • Th ...
Topic 2 Atomic Structure File
... 6. If the mass number of the atom of a given element is known, the number of neutrons in its nucleus can be calculated by subtracting the _______________________ from the _______________________. For example, if an atom of the element sodium, atomic number 11, has a mass of 23, the atom has ________ ...
... 6. If the mass number of the atom of a given element is known, the number of neutrons in its nucleus can be calculated by subtracting the _______________________ from the _______________________. For example, if an atom of the element sodium, atomic number 11, has a mass of 23, the atom has ________ ...
Activity 6 Atoms with More than One Electron
... while they are able to recognize the patterns, they may not be able to articulate correctly how these patterns are related to the organization of the periodic table. In writing electron configurations, students often have difficulty remembering that the sublevels begin to overlap at higher energy le ...
... while they are able to recognize the patterns, they may not be able to articulate correctly how these patterns are related to the organization of the periodic table. In writing electron configurations, students often have difficulty remembering that the sublevels begin to overlap at higher energy le ...
atom
... identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds In chemical reactions, atoms are comb ...
... identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds In chemical reactions, atoms are comb ...