Chapter 3—Time and Geology
... atom (34): The smallest particle of matter that can exist as a chemical element. atomic mass (34): A quantity essentially equivalent to the number of neutrons plus the number of protons in an atomic nucleus. atomic number (34): The number of protons in the nuclei of atoms of a particular element. An ...
... atom (34): The smallest particle of matter that can exist as a chemical element. atomic mass (34): A quantity essentially equivalent to the number of neutrons plus the number of protons in an atomic nucleus. atomic number (34): The number of protons in the nuclei of atoms of a particular element. An ...
Atomic Structure - Mr Andrews` Science Space!
... The atoms of any particular element always contain the same number of protons. For example: hydrogen atoms always contain 1 proton; carbon atoms always contain 6 protons; magnesium atoms always contain 12 protons, The number of protons in an atom is known as its atomic number or proton number. ...
... The atoms of any particular element always contain the same number of protons. For example: hydrogen atoms always contain 1 proton; carbon atoms always contain 6 protons; magnesium atoms always contain 12 protons, The number of protons in an atom is known as its atomic number or proton number. ...
Atomic Model Stations - Moore Public Schools
... A. electron-- ______________________________________________________________________________ ...
... A. electron-- ______________________________________________________________________________ ...
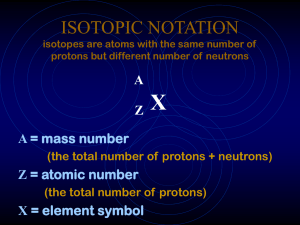
ISOTOPIC NOTATION isotopes are atoms with the same number
... • Generally the formula used is: % X + % Y + % Z… = atomic mass. An instrument called the mass spectrometer is generally used to determine the percentages and individual masses of each isotope. ...
... • Generally the formula used is: % X + % Y + % Z… = atomic mass. An instrument called the mass spectrometer is generally used to determine the percentages and individual masses of each isotope. ...
Unit PowerPoint
... What structural characteristics do all oxygen atoms have in common? All oxygen atoms have the same number of protons and electrons. What differences exist between the isotopes of oxygen? The mass number, number of neutrons and mass of each isotope are different. ...
... What structural characteristics do all oxygen atoms have in common? All oxygen atoms have the same number of protons and electrons. What differences exist between the isotopes of oxygen? The mass number, number of neutrons and mass of each isotope are different. ...
the Language of Chemistry
... Living Science Chemistry for Class IX covers the latest syllabus for Chemistry as prescribed by the Council for the Indian School Certificate Examinations (ICSE), New Delhi. The sequencing of the chapters follows the distinct directives of the Board. I have presented the various scientific concepts ...
... Living Science Chemistry for Class IX covers the latest syllabus for Chemistry as prescribed by the Council for the Indian School Certificate Examinations (ICSE), New Delhi. The sequencing of the chapters follows the distinct directives of the Board. I have presented the various scientific concepts ...
Types of reactions: redox reactions
... If you look back to chapter , you will remember that we discussed how, during a chemical reaction, an exchange of electrons takes place between the elements that are involved. ...
... If you look back to chapter , you will remember that we discussed how, during a chemical reaction, an exchange of electrons takes place between the elements that are involved. ...
Medical Chemistry Lecture By : Asst. Lect. Tariq-H-Almgheer
... At the turn of the century it was discovered that the number of positive charges on the nuclei increases by one from atom to atom as one moves from one group to the next in any period of the periodic table. For example, the positive charge on the hydrogen nucleus is +1; on helium, +2; on lithium, +3 ...
... At the turn of the century it was discovered that the number of positive charges on the nuclei increases by one from atom to atom as one moves from one group to the next in any period of the periodic table. For example, the positive charge on the hydrogen nucleus is +1; on helium, +2; on lithium, +3 ...
February Homework Packet
... location of an electron in the third shell of an atom compare to the energy and the most probable location of an electron in the first shell of the same atom? (1) In the third shell, an electron has more energy and is closer to the nucleus. (2) In the third shell, an electron has less energy and is ...
... location of an electron in the third shell of an atom compare to the energy and the most probable location of an electron in the first shell of the same atom? (1) In the third shell, an electron has more energy and is closer to the nucleus. (2) In the third shell, an electron has less energy and is ...
4 The Structure of the Atom
... Explain radioactivity by completing the paragraph below. ln chemical reactions, atoms maY be ...
... Explain radioactivity by completing the paragraph below. ln chemical reactions, atoms maY be ...
02 Atomic Structure [ppt 1MB]
... I can use nuclide notation to present information about atomic and mass numbers of atoms I can explain what is meant by the term isotope I can state that the electrons of an atom are arranged in energy levels I can state that an atom is neutral and explain why ...
... I can use nuclide notation to present information about atomic and mass numbers of atoms I can explain what is meant by the term isotope I can state that the electrons of an atom are arranged in energy levels I can state that an atom is neutral and explain why ...
Problems - El Camino College
... c) The mass or an electron 1s about the same as the mass ofa proton. d) There are subatom ic particles in addition to the electron, proton. and neutron. e) The mass of an atom i~ uniformly distributed throughout the atom. f) Most of the particles fucd i11to the gold foi l in the Rutherford experimen ...
... c) The mass or an electron 1s about the same as the mass ofa proton. d) There are subatom ic particles in addition to the electron, proton. and neutron. e) The mass of an atom i~ uniformly distributed throughout the atom. f) Most of the particles fucd i11to the gold foi l in the Rutherford experimen ...
CHAPTER 3 - THE ATOM
... 3. Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and chemical properties. 4. Different atoms combine in simple whole- number ratios to form Compounds 5. In a chemical reaction, atoms are separated, combined or rearranged. Atom – the smallest particle of an element that can exist, either alon ...
... 3. Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and chemical properties. 4. Different atoms combine in simple whole- number ratios to form Compounds 5. In a chemical reaction, atoms are separated, combined or rearranged. Atom – the smallest particle of an element that can exist, either alon ...
6.022 X 10 23 atoms - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... Dalton stated that elements consisted of tiny particles called atoms He also called the elements pure substances because all atoms of an element were identical and that in particular they had the same mass. ...
... Dalton stated that elements consisted of tiny particles called atoms He also called the elements pure substances because all atoms of an element were identical and that in particular they had the same mass. ...
Notes Unit 3
... Neutron stars can be formed when stars use up all of their fuel. Protons and electrons in the star merge to form neutrons and neutrinos. The neutrons form the neutron star, which is usually around 20 km in diameter, but can be over twice the mass of the sun. Nuclear fission reactions occur when a fr ...
... Neutron stars can be formed when stars use up all of their fuel. Protons and electrons in the star merge to form neutrons and neutrinos. The neutrons form the neutron star, which is usually around 20 km in diameter, but can be over twice the mass of the sun. Nuclear fission reactions occur when a fr ...
Atomic Theory
... Neutron stars can be formed when stars use up all of their fuel. Protons and electrons in the star merge to form neutrons and neutrinos. The neutrons form the neutron star, which is usually around 20 km in diameter, but can be over twice the mass of the sun. Nuclear fission reactions occur when a fr ...
... Neutron stars can be formed when stars use up all of their fuel. Protons and electrons in the star merge to form neutrons and neutrinos. The neutrons form the neutron star, which is usually around 20 km in diameter, but can be over twice the mass of the sun. Nuclear fission reactions occur when a fr ...
Nontes Unit 3 pdf
... Neutron stars can be formed when stars use up all of their fuel. Protons and electrons in the star merge to form neutrons and neutrinos. The neutrons form the neutron star, which is usually around 20 km in diameter, but can be over twice the mass of the sun. Nuclear fission reactions occur when a fr ...
... Neutron stars can be formed when stars use up all of their fuel. Protons and electrons in the star merge to form neutrons and neutrinos. The neutrons form the neutron star, which is usually around 20 km in diameter, but can be over twice the mass of the sun. Nuclear fission reactions occur when a fr ...
Class Notes KEY
... 1. Which elements have outer shells that are full of electrons? Where are they located on the periodic table? 2. Which elements have only 1 electron in their outer shell? Where are they located on the periodic table? 3. What do you notice about the number of valence electrons (electrons in the outer ...
... 1. Which elements have outer shells that are full of electrons? Where are they located on the periodic table? 2. Which elements have only 1 electron in their outer shell? Where are they located on the periodic table? 3. What do you notice about the number of valence electrons (electrons in the outer ...
Chapter 03 - La Salle University
... Valence electrons: Electrons in an outermost shell of an atom. These electrons are loosely held, they are most important in determining an element’s properties. ...
... Valence electrons: Electrons in an outermost shell of an atom. These electrons are loosely held, they are most important in determining an element’s properties. ...
Protons Neutrons Electrons
... provided in chart, atoms C, D, F, G, H and I all have a filled second shell (total of 10 electrons: 2 in first shell, 8 in second) ...
... provided in chart, atoms C, D, F, G, H and I all have a filled second shell (total of 10 electrons: 2 in first shell, 8 in second) ...
What are elements?
... • In the center is circles. Each circle represents a single neutron or proton. Protons should have a plus or P written on them. Neutrons should be blank or have an N. • In a circle around the nucleus are the electrons. Electrons should have a dot for Created by G.Baker each electron ...
... • In the center is circles. Each circle represents a single neutron or proton. Protons should have a plus or P written on them. Neutrons should be blank or have an N. • In a circle around the nucleus are the electrons. Electrons should have a dot for Created by G.Baker each electron ...
Document
... Any given element can have more than one isotope. To distinguish between the different isotopes of an atom, the element is named with its mass number, for example, lithium-7. Remember that the mass number is the number of protons and neutrons added together. When symbols are used to represent an iso ...
... Any given element can have more than one isotope. To distinguish between the different isotopes of an atom, the element is named with its mass number, for example, lithium-7. Remember that the mass number is the number of protons and neutrons added together. When symbols are used to represent an iso ...
The Atom - dgordonocdsb
... each other? • Each element or atom has its very own number of protons • For example, calcium has 20 protons, while magnesium has 12 • The number of protons in an atom is called the atomic number ...
... each other? • Each element or atom has its very own number of protons • For example, calcium has 20 protons, while magnesium has 12 • The number of protons in an atom is called the atomic number ...









![02 Atomic Structure [ppt 1MB]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000821172_1-5bf1afd152b32026d524139a10b8292f-300x300.png)