Precipitation and Redox Reactions
... Check your states of matter CuCl2 is soluble so, CuCl2 (aq) AgNO3 is soluble so, AgNO3 (aq) Cu(NO3)2 is soluble so Cu(NO3)2 (aq) AgCl is insoluble so AgCl (s) CuCl2(aq) + 2 AgNO3(aq) Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2 AgCl(s) A solid formed so a reaction will occur NOTICE: Cl had a 2 subscript in the reactants but ...
... Check your states of matter CuCl2 is soluble so, CuCl2 (aq) AgNO3 is soluble so, AgNO3 (aq) Cu(NO3)2 is soluble so Cu(NO3)2 (aq) AgCl is insoluble so AgCl (s) CuCl2(aq) + 2 AgNO3(aq) Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2 AgCl(s) A solid formed so a reaction will occur NOTICE: Cl had a 2 subscript in the reactants but ...
An element is a fundamental substance that cannot be chemically
... Compound: a pure substance that is formed when atoms of two or more different elements combine and create a new material with properties completely unlike those of its constituent elements. ...
... Compound: a pure substance that is formed when atoms of two or more different elements combine and create a new material with properties completely unlike those of its constituent elements. ...
Atomic History and Structure:
... 1. matter is composed of indivisible particles Atoms Can Be Divided, but only in a nuclear reaction 2. all atoms of a particular element are identical Does Not Account for Isotopes (atoms of the same element but a different mass due to a different number of neutrons)! 3. different elements have diff ...
... 1. matter is composed of indivisible particles Atoms Can Be Divided, but only in a nuclear reaction 2. all atoms of a particular element are identical Does Not Account for Isotopes (atoms of the same element but a different mass due to a different number of neutrons)! 3. different elements have diff ...
Units and Unit Conversions 6. Define the problem: If the nucleus
... Check your answers: Pounds and kilograms are both larger units than grams, so it makes sense that the number of kilograms and the number of pounds would be smaller than the number of grams. 32. Define the problem: Given the identity of an element (cobalt) and the atom’s mass number (60), find the nu ...
... Check your answers: Pounds and kilograms are both larger units than grams, so it makes sense that the number of kilograms and the number of pounds would be smaller than the number of grams. 32. Define the problem: Given the identity of an element (cobalt) and the atom’s mass number (60), find the nu ...
Chapter 23 (Section 3) Pregnancy, Birth, and
... of Triads stated there were groups of “3” ELEMENTS where the middle ELEMENT’S atomic MASS was the average of the other “2” ELEMENTS *a. (e.g.) calcium [Ca] = 40.08; strontium [Sr] = 87.62; barium [Ba] = 137.33 *2. In 1856, Newlands proposed the Law of Octaves stated that some of the 56 ELEMENTS ...
... of Triads stated there were groups of “3” ELEMENTS where the middle ELEMENT’S atomic MASS was the average of the other “2” ELEMENTS *a. (e.g.) calcium [Ca] = 40.08; strontium [Sr] = 87.62; barium [Ba] = 137.33 *2. In 1856, Newlands proposed the Law of Octaves stated that some of the 56 ELEMENTS ...
AGS General Science Chapt 2
... developed models of atoms. The first model was developed over 2,000 years ago. But as scientists gather new information about atoms, they change their models. In the early 1900s, a scientist developed a model of an atom like those shown at the bottom of the page. Although scientists know more about ...
... developed models of atoms. The first model was developed over 2,000 years ago. But as scientists gather new information about atoms, they change their models. In the early 1900s, a scientist developed a model of an atom like those shown at the bottom of the page. Although scientists know more about ...
Avogadro`s Law is relation between
... a. 10–8 M c. 3.0 × 10–4 M b. 10–10 M d. 2.5 × 10–11 M 8- Calculate the value of [–OH] from the given [H3O+] and label the solution as acidic or basic. a. 10–1 M c. 2.6 × 10–7 M b. 10–13 M d. 1.2 × 10–12 M 9- Calculate the value of [H3O+] from the given [–OH] and label the solution as acidic or basic ...
... a. 10–8 M c. 3.0 × 10–4 M b. 10–10 M d. 2.5 × 10–11 M 8- Calculate the value of [–OH] from the given [H3O+] and label the solution as acidic or basic. a. 10–1 M c. 2.6 × 10–7 M b. 10–13 M d. 1.2 × 10–12 M 9- Calculate the value of [H3O+] from the given [–OH] and label the solution as acidic or basic ...
1 - PTO
... 3. Using the arrow notations to represent guests, diagram what the hotel would look like with 34 guests. You can diagram this on the first hotel blueprint. Make sure to follow all of the rules! 4. Using the arrow notations to represent guests, diagram what the hotel would look like with 45 guests. Y ...
... 3. Using the arrow notations to represent guests, diagram what the hotel would look like with 34 guests. You can diagram this on the first hotel blueprint. Make sure to follow all of the rules! 4. Using the arrow notations to represent guests, diagram what the hotel would look like with 45 guests. Y ...
Tutorial 3 - Atomic Theory
... What about neutrons? A mass spectrometer is an instrument used by chemists to determine the mass of a given element. Not all atoms of a particular element have the same mass. Example: Neon (Ne) gives 3 types of atoms, each heavier than the last. Explanation: There must be a third type of subatomic ...
... What about neutrons? A mass spectrometer is an instrument used by chemists to determine the mass of a given element. Not all atoms of a particular element have the same mass. Example: Neon (Ne) gives 3 types of atoms, each heavier than the last. Explanation: There must be a third type of subatomic ...
Materials Required
... as the students take their seats. As class begins a bag of candy for the activity will be pulled out and the students will be asked what the bag contains while emphasizing what is written on the board. For today this candy will be subatomic particles. Stimulating the recall of prerequisite learning: ...
... as the students take their seats. As class begins a bag of candy for the activity will be pulled out and the students will be asked what the bag contains while emphasizing what is written on the board. For today this candy will be subatomic particles. Stimulating the recall of prerequisite learning: ...
Midterm Review Teacher Answer Key December 21, 2011 `see
... 22. Explain, in terms of protons and neutrons, why U-235 and U-238 are different isotopes of uranium. [1] Isotopes of an element have the same atomic number but different mass numbers. This means that each isotope has the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. A U-235 atom has 92 ...
... 22. Explain, in terms of protons and neutrons, why U-235 and U-238 are different isotopes of uranium. [1] Isotopes of an element have the same atomic number but different mass numbers. This means that each isotope has the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. A U-235 atom has 92 ...
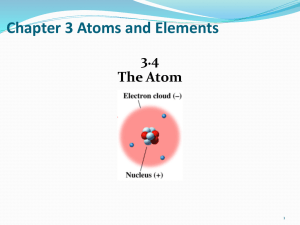
Chapter 3 Atoms and Elements
... several isotopes with the following abundances Isotope % abundance 32S ...
... several isotopes with the following abundances Isotope % abundance 32S ...
Atoms, Molecules, Formula, and Subatomic Particles - Ars
... The masses in the periodic table are not mass numbers, in general. They are relative average atomic masses. Why are they relative? Because the masses are defined relative to something. That something is the isotope of carbon with a mass number of 12. This isotope is defined to have a mass of ...
... The masses in the periodic table are not mass numbers, in general. They are relative average atomic masses. Why are they relative? Because the masses are defined relative to something. That something is the isotope of carbon with a mass number of 12. This isotope is defined to have a mass of ...
Chapter 5 Review - Net Start Class
... Atomic Theory was for the most part correct, except for the fact that atoms can be ________. divided ...
... Atomic Theory was for the most part correct, except for the fact that atoms can be ________. divided ...
Chemical Foundations: Elements, Atoms and Ions
... His ideas carried through middle ages. Alchemists change lead to gold ...
... His ideas carried through middle ages. Alchemists change lead to gold ...
chapt4 - Northside Middle School
... Blend these in different proportions to get all substances ...
... Blend these in different proportions to get all substances ...
Chapter 3 Atoms and the Periodic Table
... – electrons are going in the s orbital – Group 1 • H down to Fr • only one electron in the outer most energy level • 1 electron in the s orbital • these elements have 1 valence electron – Group 2 • Be down to Ra • 2 electrons in the outer most energy level • 2 electrons in the s orbital and it is no ...
... – electrons are going in the s orbital – Group 1 • H down to Fr • only one electron in the outer most energy level • 1 electron in the s orbital • these elements have 1 valence electron – Group 2 • Be down to Ra • 2 electrons in the outer most energy level • 2 electrons in the s orbital and it is no ...
Hewitt/Lyons/Suchocki/Yeh, Conceptual Integrated Science
... • Composed of only one kind of atom – Lightest and most abundant is hydrogen. • To date, about 115 are known. – 90 occur in nature. – Others produced in laboratory are unstable. Words atom and element can be used interchangeably. © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... • Composed of only one kind of atom – Lightest and most abundant is hydrogen. • To date, about 115 are known. – 90 occur in nature. – Others produced in laboratory are unstable. Words atom and element can be used interchangeably. © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
1 - Intro to Electrochemistry
... A reducing agent causes another substance to be ____________________ It is ________________ in the process 2 Ag+ + Cu(s) 2 Ag(s) + Cu2+ Cu(s) is the reducing agent as it causes Ag+ to be __________________ ...
... A reducing agent causes another substance to be ____________________ It is ________________ in the process 2 Ag+ + Cu(s) 2 Ag(s) + Cu2+ Cu(s) is the reducing agent as it causes Ag+ to be __________________ ...
Chapter 4 Atoms and Elements
... • The properties of atoms determine the properties of matter. • An atom is the smallest identifiable unit of an element. • An element is a substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances. • There are about 91 different elements in nature, and consequently about 91 different kinds of ato ...
... • The properties of atoms determine the properties of matter. • An atom is the smallest identifiable unit of an element. • An element is a substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances. • There are about 91 different elements in nature, and consequently about 91 different kinds of ato ...
1.1 - cloudfront.net
... contains six electrons, allowing the atom to remain electrically neutral. However the number of neutrons varies from six to eight. Isotopes are atoms that have the same atomic number but different mass numbers due to a change in the number of neutrons. The three isotopes of carbon can be referred to ...
... contains six electrons, allowing the atom to remain electrically neutral. However the number of neutrons varies from six to eight. Isotopes are atoms that have the same atomic number but different mass numbers due to a change in the number of neutrons. The three isotopes of carbon can be referred to ...
TEST on Atomic Structure
... _4 _ Use the periodic table to determine the number of electrons in a neutral atom of beryllium. ...
... _4 _ Use the periodic table to determine the number of electrons in a neutral atom of beryllium. ...