2. Chapter 2
... You may recall that an element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down or separated into simpler substances. The reason an element cannot be broken down further is that it is already very simple: each element is made of only one kind of atom. Elements can be found in your pencils, your coins, ...
... You may recall that an element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down or separated into simpler substances. The reason an element cannot be broken down further is that it is already very simple: each element is made of only one kind of atom. Elements can be found in your pencils, your coins, ...
Atomic Structure Practice Test
... REF: 1 OBJ: 3 STA: SC.B.1.4.2 26. ANS: The atomic number equals the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom and also equals the number of electrons in the neutral atom. The mass number is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons and can be used, with the atomic number, to find the number of ...
... REF: 1 OBJ: 3 STA: SC.B.1.4.2 26. ANS: The atomic number equals the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom and also equals the number of electrons in the neutral atom. The mass number is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons and can be used, with the atomic number, to find the number of ...
weighted average atomic mass
... • Find out the names that 110, 111, 112, 114, and 116 have now been given. What is the latest news about element 118? • Who/what makes the decisions about element names? • How long does it take for a name to be decided upon? • Record your source(s) using MLA formatting. Read your notes about Chromat ...
... • Find out the names that 110, 111, 112, 114, and 116 have now been given. What is the latest news about element 118? • Who/what makes the decisions about element names? • How long does it take for a name to be decided upon? • Record your source(s) using MLA formatting. Read your notes about Chromat ...
Atomic Structure Practice Test
... REF: 1 OBJ: 3 STA: SC.B.1.4.2 26. ANS: The atomic number equals the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom and also equals the number of electrons in the neutral atom. The mass number is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons and can be used, with the atomic number, to find the number of ...
... REF: 1 OBJ: 3 STA: SC.B.1.4.2 26. ANS: The atomic number equals the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom and also equals the number of electrons in the neutral atom. The mass number is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons and can be used, with the atomic number, to find the number of ...
Matter
... of varying density surrounding the nucleus. • The varying density shows where an electron is more or less likely to be. ...
... of varying density surrounding the nucleus. • The varying density shows where an electron is more or less likely to be. ...
Matter
... of varying density surrounding the nucleus. • The varying density shows where an electron is more or less likely to be. ...
... of varying density surrounding the nucleus. • The varying density shows where an electron is more or less likely to be. ...
Chapter 4 Atoms, Elements, Compounds and
... of varying density surrounding the nucleus. • The varying density shows where an electron is more or less likely to be. ...
... of varying density surrounding the nucleus. • The varying density shows where an electron is more or less likely to be. ...
Chapter 17
... of varying density surrounding the nucleus. • The varying density shows where an electron is more or less likely to be. ...
... of varying density surrounding the nucleus. • The varying density shows where an electron is more or less likely to be. ...
notes - unit 2 - atomic theory_key_2012
... d. That electrons travel around the nucleus in well-defined paths called orbits. 2. J.J. Thomson’s Cathode Ray Tube experiment led to the discovery of a. the positively charged subatomic particle called the electron b. the positively charged subatomic particle called the proton c. the positively cha ...
... d. That electrons travel around the nucleus in well-defined paths called orbits. 2. J.J. Thomson’s Cathode Ray Tube experiment led to the discovery of a. the positively charged subatomic particle called the electron b. the positively charged subatomic particle called the proton c. the positively cha ...
atom - Social Circle City Schools
... More on that practice sheet • What else can you fill in????? ...
... More on that practice sheet • What else can you fill in????? ...
Practice Packet Unit 3: Atomics - Mr. Palermo`s Flipped Chemistry
... that of a noble gas. For example, look at the electron configuration of oxygen. The unstable atom of oxygen has an electron configuration of 2-‐6. ...
... that of a noble gas. For example, look at the electron configuration of oxygen. The unstable atom of oxygen has an electron configuration of 2-‐6. ...
GCSE Chemistry Textbook sample
... a positively charged nucleus and much of the atom was empty space. This was the nuclear model of the atom. ...
... a positively charged nucleus and much of the atom was empty space. This was the nuclear model of the atom. ...
CHM 312
... Alfred Werner developed a model of coordination complexs which explains the following observations. At least three different cobalt(III) complexes can be isolated when CoCl2 is dissolved in aqueous ammonia and then oxidized by air to the +3 oxidation state. A fourth complex can be made by slightly d ...
... Alfred Werner developed a model of coordination complexs which explains the following observations. At least three different cobalt(III) complexes can be isolated when CoCl2 is dissolved in aqueous ammonia and then oxidized by air to the +3 oxidation state. A fourth complex can be made by slightly d ...
Word - My eCoach
... d. either greater than or less than __C__ 12. According to Dalton's atomic theory, atoms a. are destroyed in chemical reactions. b. can be divided. c. of each element are identical in size, mass, and other properties. d. of different elements cannot combine. __A__ 13. Which of the following statemen ...
... d. either greater than or less than __C__ 12. According to Dalton's atomic theory, atoms a. are destroyed in chemical reactions. b. can be divided. c. of each element are identical in size, mass, and other properties. d. of different elements cannot combine. __A__ 13. Which of the following statemen ...
6-2 Notes: The Atom
... The charges or protons and electrons are opposite but _________, so the charges cancel out. If the numbers of electrons and protons become unequal, the atom becomes a charged particle called an ______. An atom that loses one or more electrons becomes a _______________ charged ion. An atom that gains ...
... The charges or protons and electrons are opposite but _________, so the charges cancel out. If the numbers of electrons and protons become unequal, the atom becomes a charged particle called an ______. An atom that loses one or more electrons becomes a _______________ charged ion. An atom that gains ...
Atom 3 Isotopes - Solon City Schools
... Isotopes •According to international convention all atomic masses derive from the isotope carbon-12. •One atomic mass unit (amu) is exactly 1/12 of the mass of a C-12 atom. •The natural atomic mass of an element is the average of the atomic masses of the isotopes: ...
... Isotopes •According to international convention all atomic masses derive from the isotope carbon-12. •One atomic mass unit (amu) is exactly 1/12 of the mass of a C-12 atom. •The natural atomic mass of an element is the average of the atomic masses of the isotopes: ...
Name - TeacherWeb
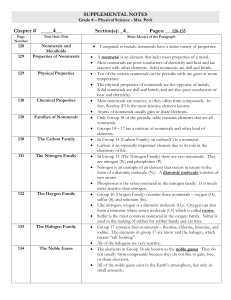
... The elements in Group 18 are known as the noble gases. They do not usually form compounds because they do not like to gain, lose, or share electrons. All of the noble gases exist in the Earth’s atmosphere, but only in small amounts. ...
... The elements in Group 18 are known as the noble gases. They do not usually form compounds because they do not like to gain, lose, or share electrons. All of the noble gases exist in the Earth’s atmosphere, but only in small amounts. ...
atom
... • The atomic number of an atom is given by its number of protons. The mass number of an atom is the sum of its neutrons and protons. atomic number = number of protons = number of electrons mass number = atomic number + number of neutrons ...
... • The atomic number of an atom is given by its number of protons. The mass number of an atom is the sum of its neutrons and protons. atomic number = number of protons = number of electrons mass number = atomic number + number of neutrons ...
Atomic Structure Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice
... ____ 16. Because any element used in the cathode produced electrons, scientists concluded that a. all atoms contained electrons. c. atoms were indivisible. b. only metals contained electrons. d. atoms carried a negative charge. ____ 17. If you change the number of protons in an atom, what is affecte ...
... ____ 16. Because any element used in the cathode produced electrons, scientists concluded that a. all atoms contained electrons. c. atoms were indivisible. b. only metals contained electrons. d. atoms carried a negative charge. ____ 17. If you change the number of protons in an atom, what is affecte ...
Atomic Structure Practice Test
... ____ 16. Because any element used in the cathode produced electrons, scientists concluded that a. all atoms contained electrons. c. atoms were indivisible. b. only metals contained electrons. d. atoms carried a negative charge. ____ 17. If you change the number of protons in an atom, what is affecte ...
... ____ 16. Because any element used in the cathode produced electrons, scientists concluded that a. all atoms contained electrons. c. atoms were indivisible. b. only metals contained electrons. d. atoms carried a negative charge. ____ 17. If you change the number of protons in an atom, what is affecte ...
Introduction to Chemical Bonding
... The bond of Sodium and Fluorine is an example of Ionic bonding: electrons have been transferred in order for the atoms to have a full outer level. When an atom loses or gains electrons, it becomes what is called an ion. An ion is no longer neutrally charged because it has different numbers of proton ...
... The bond of Sodium and Fluorine is an example of Ionic bonding: electrons have been transferred in order for the atoms to have a full outer level. When an atom loses or gains electrons, it becomes what is called an ion. An ion is no longer neutrally charged because it has different numbers of proton ...
CHAPTER 3 - THE ATOM answer key
... 3. Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and chemical properties. 4. Different atoms combine in simple whole- number ratios to form Compounds 5. In a chemical reaction, atoms are separated, combined or rearranged. Atom – the smallest particle of an element that can exist, either alon ...
... 3. Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and chemical properties. 4. Different atoms combine in simple whole- number ratios to form Compounds 5. In a chemical reaction, atoms are separated, combined or rearranged. Atom – the smallest particle of an element that can exist, either alon ...