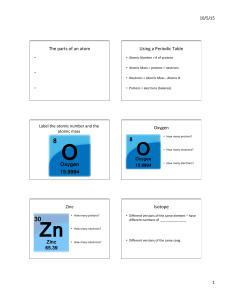
A an electron and an alpha particle B an electron and a proton C a
... In the early 1900s, Ernest Rutherford bombarded a very thin sheet of gold foil with alpha particles. After interpreting the results of the gold foil experiment, Rutherford proposed a more sophisticated model of the atom. 40. State one conclusion from Rutherford's experiment that contradicts one conc ...
... In the early 1900s, Ernest Rutherford bombarded a very thin sheet of gold foil with alpha particles. After interpreting the results of the gold foil experiment, Rutherford proposed a more sophisticated model of the atom. 40. State one conclusion from Rutherford's experiment that contradicts one conc ...
NSCC Chem 121 chapter2
... electrical charge and have a mass of 1 atomic mass unit (u). • Neutrons are located in the nucleus of an atom. They carry no electrical charge and have a mass of 1 atomic mass unit (u). • Electrons are located outside the nucleus of an atom. They carry a -1 electrical charge and have a mass of 1/183 ...
... electrical charge and have a mass of 1 atomic mass unit (u). • Neutrons are located in the nucleus of an atom. They carry no electrical charge and have a mass of 1 atomic mass unit (u). • Electrons are located outside the nucleus of an atom. They carry a -1 electrical charge and have a mass of 1/183 ...
Unit 2: Atomic Concepts and Periodic Table (Level 1)
... not all columns or groups qualify as “families.” In fact, the only groups that are considered to be families are Group I (Alkalai Metals), Group II (Alkaline Earth Metals), Group XVII (Halogens), and Group XVIII (Noble Gases). The behaviors of the transition metals are very difficult to predict, and ...
... not all columns or groups qualify as “families.” In fact, the only groups that are considered to be families are Group I (Alkalai Metals), Group II (Alkaline Earth Metals), Group XVII (Halogens), and Group XVIII (Noble Gases). The behaviors of the transition metals are very difficult to predict, and ...
Chapter 2 - HCC Learning Web
... (b) CoCl2 is a compound composed of a metal (left side of periodic table) and nonmetal (right side of the periodic table); therefore, it is an ionic compound. (c) Nitrogen is an element that is listed as diatomic in Table 5.2; therefore, it is a molecular element. (d) SO2 is a compound composed of t ...
... (b) CoCl2 is a compound composed of a metal (left side of periodic table) and nonmetal (right side of the periodic table); therefore, it is an ionic compound. (c) Nitrogen is an element that is listed as diatomic in Table 5.2; therefore, it is a molecular element. (d) SO2 is a compound composed of t ...
CHEM 1405 Practice Exam #2
... 4) How many valence electrons do atoms with the following electron configurations have? A) 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p4 B) 1s22s22p63s2 C) 1s22s22p63s23p64s1 D) 1s22s22p6 5) Fill in the chart below for each of the following isotopes. ...
... 4) How many valence electrons do atoms with the following electron configurations have? A) 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p4 B) 1s22s22p63s2 C) 1s22s22p63s23p64s1 D) 1s22s22p6 5) Fill in the chart below for each of the following isotopes. ...
CHEMISTRY 123-07 Midterm #1 – Answer key October 14, 2010
... 32. Ions that contain atoms of more than one element are called polyatomic ions. 33. Proton donors are known as Brønsted acids. 34. A compound that forms between a non-metal and a non-metal is a molecular compound. 35. Stoichiometric coefficients found in a balanced equation can be used to derive mo ...
... 32. Ions that contain atoms of more than one element are called polyatomic ions. 33. Proton donors are known as Brønsted acids. 34. A compound that forms between a non-metal and a non-metal is a molecular compound. 35. Stoichiometric coefficients found in a balanced equation can be used to derive mo ...
Unit 2 Review
... During the simulation, many alpha particles passed by the atom with little to no interaction. This is shown in the screenshot above. Which statement is consistent with this observation? a. Orbiting electrons attract alpha particles; this influence makes the path more straight. b. The affect of the n ...
... During the simulation, many alpha particles passed by the atom with little to no interaction. This is shown in the screenshot above. Which statement is consistent with this observation? a. Orbiting electrons attract alpha particles; this influence makes the path more straight. b. The affect of the n ...
Review - gbschemphys
... During the simulation, many alpha particles passed by the atom with little to no interaction. This is shown in the screenshot above. Which statement is consistent with this observation? a. Orbiting electrons attract alpha particles; this influence makes the path more straight. b. The affect of the n ...
... During the simulation, many alpha particles passed by the atom with little to no interaction. This is shown in the screenshot above. Which statement is consistent with this observation? a. Orbiting electrons attract alpha particles; this influence makes the path more straight. b. The affect of the n ...
Chapter 20 Resource: Chemical Bonds
... 1. When an atom ______________ an electron, it becomes a positively charged ion; a superscript indicates the charge. 2. When an atom ______________ an electron, it becomes a negatively charged ion. B. An ionic compound is held together by the ___________________—the force of attraction between oppos ...
... 1. When an atom ______________ an electron, it becomes a positively charged ion; a superscript indicates the charge. 2. When an atom ______________ an electron, it becomes a negatively charged ion. B. An ionic compound is held together by the ___________________—the force of attraction between oppos ...
Atomic Theory Quiz A
... That’s the most common isotope, Sr-88. Watch your rounding to the nearest whole number work. 6. Name all seven metalloids and write their symbols next to their names (size order, small to large) Boron (B), Silicon (Si), Germanium (Ge), Arsenic (As), Antimony (Sb), Tellurium (Te), and Astatine (At). ...
... That’s the most common isotope, Sr-88. Watch your rounding to the nearest whole number work. 6. Name all seven metalloids and write their symbols next to their names (size order, small to large) Boron (B), Silicon (Si), Germanium (Ge), Arsenic (As), Antimony (Sb), Tellurium (Te), and Astatine (At). ...
Atoms and the Periodic Table
... of Triads stated there were groups of “3” ELEMENTS where the middle ELEMENT’S atomic MASS was the average of the other “2” ELEMENTS *a. (e.g.) calcium [Ca] = 40.08; strontium [Sr] = 87.62; barium [Ba] = 137.33 *2. In 1856, Newlands proposed the Law of Octaves stated that some of the 56 ELEMENTS ...
... of Triads stated there were groups of “3” ELEMENTS where the middle ELEMENT’S atomic MASS was the average of the other “2” ELEMENTS *a. (e.g.) calcium [Ca] = 40.08; strontium [Sr] = 87.62; barium [Ba] = 137.33 *2. In 1856, Newlands proposed the Law of Octaves stated that some of the 56 ELEMENTS ...
Chapter 2 Atoms and the Atomic Theory
... Dalton’s theory enables us to set up a scale of relative atomic masses. He cannot measure the exact mass of atoms but relative mass. E.g. Consider calcium sulfide, which consists of 55.6% calcium by mass and 44.4% sulfur by mass. Suppose there is one calcium atom for each sulfur atom in calcium sulf ...
... Dalton’s theory enables us to set up a scale of relative atomic masses. He cannot measure the exact mass of atoms but relative mass. E.g. Consider calcium sulfide, which consists of 55.6% calcium by mass and 44.4% sulfur by mass. Suppose there is one calcium atom for each sulfur atom in calcium sulf ...
Chapter 1 (Matter and Measurement) Objectives
... The following California State Standards for Chemistry are met by the objectives above: 1. The periodic table displays the elements in increasing atomic number and shows how periodicity of the physical and chemical properties of the elements relates to atomic structure. As a basis for understanding ...
... The following California State Standards for Chemistry are met by the objectives above: 1. The periodic table displays the elements in increasing atomic number and shows how periodicity of the physical and chemical properties of the elements relates to atomic structure. As a basis for understanding ...
4.1 Introduction to Atoms
... Niels Bohr • In 1913, Niels Bohr, a Danish scientist, showed that electrons could have only specific amounts of energy causing them to move in certain orbits (similar to how the planets orbit the sun). ...
... Niels Bohr • In 1913, Niels Bohr, a Danish scientist, showed that electrons could have only specific amounts of energy causing them to move in certain orbits (similar to how the planets orbit the sun). ...
ch 4 notes sept 30 oct 1.notebook
... periodic table: a chart that organizes all known elements into a grid of horizontal rows (periods) and vertical columns (groups or families) arranged by increasing atomic number ...
... periodic table: a chart that organizes all known elements into a grid of horizontal rows (periods) and vertical columns (groups or families) arranged by increasing atomic number ...
Elements and the Periodic Table
... nonmetals. Atoms of these elements easily form compounds by sharing or gaining one electron when reacting with atoms of other elements. ...
... nonmetals. Atoms of these elements easily form compounds by sharing or gaining one electron when reacting with atoms of other elements. ...
Lesson 2 | The Structure of Atoms
... Content Practice B (page 31) 1. protons 2. positive charge, most mass 3. negatively charged 4. electron-cloud 5. less energy 6. protons 7. neutrons 8. electrons 9. positive 10. proton School to Home (page 35) 1. The nucleus contains protons and neutrons. It has an overall neutral charge, and it con ...
... Content Practice B (page 31) 1. protons 2. positive charge, most mass 3. negatively charged 4. electron-cloud 5. less energy 6. protons 7. neutrons 8. electrons 9. positive 10. proton School to Home (page 35) 1. The nucleus contains protons and neutrons. It has an overall neutral charge, and it con ...
O usually has oxidation number of -2, except in peroxides where it is
... O usually has oxidation number of -2, except in peroxides where it is assigned -1, and in OF2 where it is assigned a +2 due to the higher electro negativity of F. -In calcium oxide, CaO, oxide ion has a 2- charge. Its oxidation number is -2 -In H2O2, Each O is assigned the oxidation number of -1 5. ...
... O usually has oxidation number of -2, except in peroxides where it is assigned -1, and in OF2 where it is assigned a +2 due to the higher electro negativity of F. -In calcium oxide, CaO, oxide ion has a 2- charge. Its oxidation number is -2 -In H2O2, Each O is assigned the oxidation number of -1 5. ...
Matter and Atoms
... each day. You might see pure elements, such as copper and iron. You also might see many compounds, such as table salt. Table salt is a compound because it contains the atoms of two different elements in a specific combination. These elements are sodium and chlorine. You also probably see many mixtur ...
... each day. You might see pure elements, such as copper and iron. You also might see many compounds, such as table salt. Table salt is a compound because it contains the atoms of two different elements in a specific combination. These elements are sodium and chlorine. You also probably see many mixtur ...
© NCERT not to be republished
... 33. Why E values for Mn, Ni and Zn are more negative than expected? 34. Why first ionisation enthalpy of Cr is lower than that of Zn ? 35. Transition elements show high melting points. Why? 36. When Cu2+ ion is treated with KI, a white precipitate is formed. Explain the reaction with the help of che ...
... 33. Why E values for Mn, Ni and Zn are more negative than expected? 34. Why first ionisation enthalpy of Cr is lower than that of Zn ? 35. Transition elements show high melting points. Why? 36. When Cu2+ ion is treated with KI, a white precipitate is formed. Explain the reaction with the help of che ...
Atomic Mass - Warren County Schools
... • I can determine the atomic composition of atoms when I know the atomic mass and atomic #. • I can recognize that the periodic table is organized by an element’s atomic number. • I can divide the elements in the periodic table into periods and groups. • I can identify and distinguish between metals ...
... • I can determine the atomic composition of atoms when I know the atomic mass and atomic #. • I can recognize that the periodic table is organized by an element’s atomic number. • I can divide the elements in the periodic table into periods and groups. • I can identify and distinguish between metals ...
Chapter 4 Chemical Foundations: Elements, Atoms, and Ions
... Introduction to the Modern Concept of Atomic Structure Why do different atoms have different chemical properties? ...
... Introduction to the Modern Concept of Atomic Structure Why do different atoms have different chemical properties? ...
Practice Packet Level 3: Atomics - Mr. Palermo`s Flipped Chemistry
... field. This suggested that cathode rays were composed of negatively charged particles found in all atoms. Thomson concluded that the atom was a positively charged sphere of almost uniform density in which ...
... field. This suggested that cathode rays were composed of negatively charged particles found in all atoms. Thomson concluded that the atom was a positively charged sphere of almost uniform density in which ...