Matter_Quiz_Topics_2017
... Understand what is meant by the following terms: atom, proton, neutron and electron, isotope, atomic number, mass number, matter, families, period, charge, atomic mass, ion Discuss the structure of an atom. How many electrons can each of the first three energy levels hold? Where is most of the mass ...
... Understand what is meant by the following terms: atom, proton, neutron and electron, isotope, atomic number, mass number, matter, families, period, charge, atomic mass, ion Discuss the structure of an atom. How many electrons can each of the first three energy levels hold? Where is most of the mass ...
Unit 2 - Chapter 3 Elements, Atoms, Ions The elements Can we
... • how many protons does hydrogen have? ...
... • how many protons does hydrogen have? ...
and View
... atom. * Number never changes* b. Isotopes—atoms of same element that have different numbers of neutrons. Ex: carbon-12, carbon-13, carbon-14 c. Mass number—number of neutrons plus protons in an atom. i. Neutron number is found by--Mass number - Atomic number _______________ Number of neutrons ...
... atom. * Number never changes* b. Isotopes—atoms of same element that have different numbers of neutrons. Ex: carbon-12, carbon-13, carbon-14 c. Mass number—number of neutrons plus protons in an atom. i. Neutron number is found by--Mass number - Atomic number _______________ Number of neutrons ...
AP Chapter 2 Outline 2014
... (1) Each element is made of extremely small particles (atoms). (2) All atoms of a given element are identical to one another in mass and other properties, but the atoms of one element are different from the atoms of other elements. (3) Atoms of an element are not changed into atoms of a different el ...
... (1) Each element is made of extremely small particles (atoms). (2) All atoms of a given element are identical to one another in mass and other properties, but the atoms of one element are different from the atoms of other elements. (3) Atoms of an element are not changed into atoms of a different el ...
Chapter 14 Inside the Atom Notes
... B. Radioactive decay occurs when an atom releases nuclear particles and energy. 1. When a proton is released, one element changes into another, a process called transmutation. ...
... B. Radioactive decay occurs when an atom releases nuclear particles and energy. 1. When a proton is released, one element changes into another, a process called transmutation. ...
Atoms and Molecules
... Atoms are NOT indivisible – they can be broken apart into P+, neutrons, and e-. 2. Atoms can be changed from one element to another, but not by chemical means (chemical reactions). Can do it by nuclear reactions. 3. Atoms of the same element are NOT all exactly alike isotopes ...
... Atoms are NOT indivisible – they can be broken apart into P+, neutrons, and e-. 2. Atoms can be changed from one element to another, but not by chemical means (chemical reactions). Can do it by nuclear reactions. 3. Atoms of the same element are NOT all exactly alike isotopes ...
Regents Review Packet B2 Answer Key
... chemistry. Three elements, represented by D, E, and Q, are located in Period 3. Some properties of these elements are listed in the table below. A student's experimental result indicates that the density of element Q is , at room temperature and standard pressure. ...
... chemistry. Three elements, represented by D, E, and Q, are located in Period 3. Some properties of these elements are listed in the table below. A student's experimental result indicates that the density of element Q is , at room temperature and standard pressure. ...
Atomic Structure
... Reasoned that electrons could not be random Reasoned that they were in set orbits, set distances away from nucleus. Planetary orbital model ...
... Reasoned that electrons could not be random Reasoned that they were in set orbits, set distances away from nucleus. Planetary orbital model ...
Glencoe Chapter 4 Structure of the Atom for the Wiki
... Law of definite proportions • Joseph Proust specific substances always contain elements in the same ratio by mass. Law of Multiple Proportions Based on atomic theory but no experiment evidence at the time • The ratio of the masses of one element that combine with a constant mass of another element ...
... Law of definite proportions • Joseph Proust specific substances always contain elements in the same ratio by mass. Law of Multiple Proportions Based on atomic theory but no experiment evidence at the time • The ratio of the masses of one element that combine with a constant mass of another element ...
Big History Chemistry Study Guide File
... Isotopes: o While there are usually a similar number of neutrons and protons, they definitely do not have to be equal. As you progress through the periodic table, the ratio changes from roughly 1:1 (Helium has 2 neutrons and 2 protons) up to roughly 1.5 : 1 (Mercury has 121 neutrons holding its 80 p ...
... Isotopes: o While there are usually a similar number of neutrons and protons, they definitely do not have to be equal. As you progress through the periodic table, the ratio changes from roughly 1:1 (Helium has 2 neutrons and 2 protons) up to roughly 1.5 : 1 (Mercury has 121 neutrons holding its 80 p ...
Unit 3 Study Guide
... Is this still true today? Explain. No, it is not true. In Dalton’s time technology for splitting atoms was not yet developed. 2. According to Dalton’s theory all atoms of the same element are identical in mass, size and properties. Is this still true today? Explain. Part of it is true. Atoms of the ...
... Is this still true today? Explain. No, it is not true. In Dalton’s time technology for splitting atoms was not yet developed. 2. According to Dalton’s theory all atoms of the same element are identical in mass, size and properties. Is this still true today? Explain. Part of it is true. Atoms of the ...
Chemistry- History of the Atom Notes Democritus
... Daltons turned Democritus’s idea into scientific theory that could be tested by experiment. ...
... Daltons turned Democritus’s idea into scientific theory that could be tested by experiment. ...
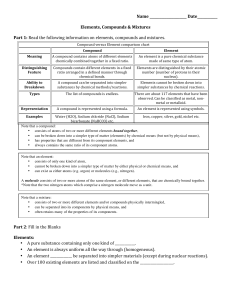
Compound vs Element chart
... • can be broken down into a simpler type of matter (elements) by chemical means (but not by physical means), • has properties that are different from its component elements, and • always contains the same ratio of its component atoms. Note that an element: • consists of only one kind of atom, • cann ...
... • can be broken down into a simpler type of matter (elements) by chemical means (but not by physical means), • has properties that are different from its component elements, and • always contains the same ratio of its component atoms. Note that an element: • consists of only one kind of atom, • cann ...
section_2_review_set
... 1. What is the claim to fame for the proton? 2. What is the claim to fame for the electron? 3. What is the claim to fame for the neutron? 4. What is the mass of each of the following particles?: proton; neutron; electron. 5. What is the charge for each of the following particles?: proton; neutron; e ...
... 1. What is the claim to fame for the proton? 2. What is the claim to fame for the electron? 3. What is the claim to fame for the neutron? 4. What is the mass of each of the following particles?: proton; neutron; electron. 5. What is the charge for each of the following particles?: proton; neutron; e ...
Document
... must contain the same number of protons. They may contain varying numbers of neutrons. Isotopes of an element have the same Z but differing N and A values. Example: 11 12 13 14 ...
... must contain the same number of protons. They may contain varying numbers of neutrons. Isotopes of an element have the same Z but differing N and A values. Example: 11 12 13 14 ...
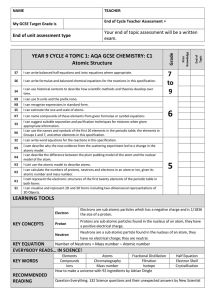
Cycle 4 Topic 1 C1 Atomic Structure Cycle Sheet
... I can use the atomic model to describe atoms. I can calculate the numbers of protons, neutrons and electrons in an atom or ion, given its atomic number and mass number. I can represent the electronic structures of the first twenty elements of the periodic table in both forms I can visualise and repr ...
... I can use the atomic model to describe atoms. I can calculate the numbers of protons, neutrons and electrons in an atom or ion, given its atomic number and mass number. I can represent the electronic structures of the first twenty elements of the periodic table in both forms I can visualise and repr ...
Unit 3 Notebook Notes
... o Could not be proven scientifically 350 BC - Greek philosopher Aristotle said all matter is made of Earth, Wind, Fire and Water. o He was wrong, but his theory persisted for 2000 years 1808 John Dalton developed the “Atomic Theory” based on Experiments 1. All matter is made of small particles c ...
... o Could not be proven scientifically 350 BC - Greek philosopher Aristotle said all matter is made of Earth, Wind, Fire and Water. o He was wrong, but his theory persisted for 2000 years 1808 John Dalton developed the “Atomic Theory” based on Experiments 1. All matter is made of small particles c ...
Year 11 Chemistry Balancing Equations
... Looking over your electron configurations, are there any elements above that have similar valence electron configurations to those of other elements? If so, list below the elements that are similar (in terms of valence electrons) and state the similarity for each of the groups. ...
... Looking over your electron configurations, are there any elements above that have similar valence electron configurations to those of other elements? If so, list below the elements that are similar (in terms of valence electrons) and state the similarity for each of the groups. ...
Chemistry 1 – Tollett Chapter 5 – Atomic Structure & The Periodic
... • He proposed that the ray was composed of negatively charged particles which he called electrons. • He also calculated the charge-to-mass ratio of the electron. ...
... • He proposed that the ray was composed of negatively charged particles which he called electrons. • He also calculated the charge-to-mass ratio of the electron. ...
CHAPTER 4 ATOMIC STRUCTURE
... When an atom does not have the same ________of neutrons Same atomic number but different mass #’s Ex. Oxygen-16, 17, and 18 All oxygen atoms have 8 protons, but some have 9 or 10 neutrons • Ques. 1-7 pg. 112 ...
... When an atom does not have the same ________of neutrons Same atomic number but different mass #’s Ex. Oxygen-16, 17, and 18 All oxygen atoms have 8 protons, but some have 9 or 10 neutrons • Ques. 1-7 pg. 112 ...
DALTON`S ATOMIC THEORY - 1808: Publication of Dalton`s "A New
... Matter is composed of small, chemically indivisible ATOMS ELEMENTS are kinds of matter that contain only a single kind of atom. All the atoms of an element have identical chemical properties. COMPOUNDS are kinds of matter that are composed of atoms of two or more ELEMENTS which are combined in simpl ...
... Matter is composed of small, chemically indivisible ATOMS ELEMENTS are kinds of matter that contain only a single kind of atom. All the atoms of an element have identical chemical properties. COMPOUNDS are kinds of matter that are composed of atoms of two or more ELEMENTS which are combined in simpl ...