Reading Assignment Worksheet on Atoms - District 196 e
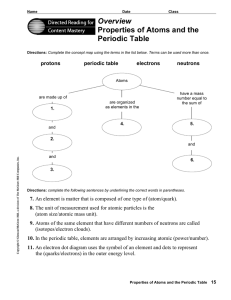
... Directions: Complete the concept map using the terms in the list below. Terms can be used more than once. ...
... Directions: Complete the concept map using the terms in the list below. Terms can be used more than once. ...
IE 1
... 1.2 Fundamental particles of an atom An atom is the smallest unit quantity of an element that is capable of existence, either alone or in chemical combination with other atoms of the same or another element. The fundamental particles of which atoms are composed are the proton , electron and neutron ...
... 1.2 Fundamental particles of an atom An atom is the smallest unit quantity of an element that is capable of existence, either alone or in chemical combination with other atoms of the same or another element. The fundamental particles of which atoms are composed are the proton , electron and neutron ...
chpt 11 and 12 notes with answers
... ◦ Right if the “zigzag” line on periodic table ◦ Almost complete electron shells ◦ Mostly gases at room temperature ◦ “semiconductors” ◦ Border left side of “zigzag” ◦ Varying number of electrons in outer shell ◦ Share properties of both metals and nonmetals ...
... ◦ Right if the “zigzag” line on periodic table ◦ Almost complete electron shells ◦ Mostly gases at room temperature ◦ “semiconductors” ◦ Border left side of “zigzag” ◦ Varying number of electrons in outer shell ◦ Share properties of both metals and nonmetals ...
TEST REVIEW S Valence Electrons TEST REVIEW SHEET 2017
... NOTE: If an element has <4 valence electrons it will give them away during an ionic bond and become a positive ion. If >4, it will take them and become a negative ion For the most part…. metals will give away their valence electrons and nonmetals will take enough valence electrons to fill their oute ...
... NOTE: If an element has <4 valence electrons it will give them away during an ionic bond and become a positive ion. If >4, it will take them and become a negative ion For the most part…. metals will give away their valence electrons and nonmetals will take enough valence electrons to fill their oute ...
Protons
... Laura works as a consultant at a software company. The amount of her annual bonus is based upon the number of hours she works. Over summer vacation, Debbie has to read a novel for English class. She has decided to spend the same amount of time reading every day. The number of hours she spends readin ...
... Laura works as a consultant at a software company. The amount of her annual bonus is based upon the number of hours she works. Over summer vacation, Debbie has to read a novel for English class. She has decided to spend the same amount of time reading every day. The number of hours she spends readin ...
2 C Atomic Number Mass Number Atomic Mass and Isotopes
... Atoms have no overall electrical charge so, an atom must have as many electrons as there are ...
... Atoms have no overall electrical charge so, an atom must have as many electrons as there are ...
Structures of Matter
... the Elements is a way of organizing all known elements by their physical and chemical properties. Each element has a unique name and a chemical symbol by which it can be identified. The symbol is either one capital letter or a capital letter followed by a single lowercase letter. ...
... the Elements is a way of organizing all known elements by their physical and chemical properties. Each element has a unique name and a chemical symbol by which it can be identified. The symbol is either one capital letter or a capital letter followed by a single lowercase letter. ...
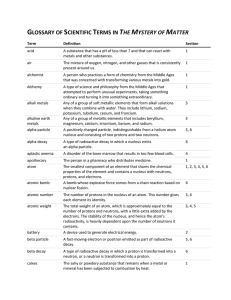
GLOSSARY OF SCIENTIFIC TERMS IN THE MYSTERY OF MATTER
... when they combine with water. They include lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, cesium, and francium. Any of a group of metallic elements that includes beryllium, magnesium, calcium, strontium, barium, and radium. A positively charged particle, indistinguishable from a helium atom nucleus and consi ...
... when they combine with water. They include lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, cesium, and francium. Any of a group of metallic elements that includes beryllium, magnesium, calcium, strontium, barium, and radium. A positively charged particle, indistinguishable from a helium atom nucleus and consi ...
Models of the Atom Intro
... Electrons have special rules…. • You can’t just shove all of the electrons into the first orbit of an electron. • Electrons live in something called shells or energy levels. ...
... Electrons have special rules…. • You can’t just shove all of the electrons into the first orbit of an electron. • Electrons live in something called shells or energy levels. ...
The atom
... SUBATOMIC PARTICLES • Atoms are made up of three subatomic particles • Neutron: neutral (no charge) particle in the nucleus • Proton: positively charged particle in the nucleus ...
... SUBATOMIC PARTICLES • Atoms are made up of three subatomic particles • Neutron: neutral (no charge) particle in the nucleus • Proton: positively charged particle in the nucleus ...
Chapter 2 - profpaz.com
... element identified by its unique atomic number, is represented by a unique chemical symbol, a one- or two-letter abbreviation. ...
... element identified by its unique atomic number, is represented by a unique chemical symbol, a one- or two-letter abbreviation. ...
Atoms, Elements, and Ions
... • The atom is extremely small. One teaspoon of water has 3 times as many atoms as the Atlantic Ocean has teaspoons of water. • If a large sports stadium were an atom, a marble would represent the nucleus. ...
... • The atom is extremely small. One teaspoon of water has 3 times as many atoms as the Atlantic Ocean has teaspoons of water. • If a large sports stadium were an atom, a marble would represent the nucleus. ...
review-basics-atomic-structure-and-electron-configurations-v1
... c.) The particle that can occur in different numbers in atoms of the same neutral element ______ d.) Held in energy levels around the nucleus. ______ e.) The negatively-charged particle. ______ f.) The particle with the negligible mass. ______ g.) The number of these particles is found by subtractin ...
... c.) The particle that can occur in different numbers in atoms of the same neutral element ______ d.) Held in energy levels around the nucleus. ______ e.) The negatively-charged particle. ______ f.) The particle with the negligible mass. ______ g.) The number of these particles is found by subtractin ...
Atoms and the Periodic Table
... The elements are arranged on the periodic table by the number of protons and then grouped by other properties, such as: ...
... The elements are arranged on the periodic table by the number of protons and then grouped by other properties, such as: ...
Isotope PPT - MrsPage.com
... Contain protons, neutrons, and electrons Protons & neutrons are found in the nucleus The nucleus contains most of the mass of an atom Electrons are distributed around the nucleus in energy levels/shells/orbitals (which make up the electron cloud) The outermost electrons in the shell farthest from th ...
... Contain protons, neutrons, and electrons Protons & neutrons are found in the nucleus The nucleus contains most of the mass of an atom Electrons are distributed around the nucleus in energy levels/shells/orbitals (which make up the electron cloud) The outermost electrons in the shell farthest from th ...
Inside the Atom
... • The orbital closest to the nucleus is the 1s orbital and it can hold 2 electrons • The 2s is next and can hold two more. Then there is a 2p orbital that can hold 6 more electrons. • Then comes a 3s (2), 3p (6) and a 3d (10), 4s (2), 4p(6), 4d (10), and 4f (14) • But this method is also screwed up. ...
... • The orbital closest to the nucleus is the 1s orbital and it can hold 2 electrons • The 2s is next and can hold two more. Then there is a 2p orbital that can hold 6 more electrons. • Then comes a 3s (2), 3p (6) and a 3d (10), 4s (2), 4p(6), 4d (10), and 4f (14) • But this method is also screwed up. ...
ATOMS, MOLECULES and IONS
... Recall that an element consists of atoms which have the same number of protons, and therefore, the same Atomic Number. Chemical properties of elements depend on the atomic number of the element. A complete Periodic Table lists the elements, their symbols and atomic numbers as well as atomic masses. ...
... Recall that an element consists of atoms which have the same number of protons, and therefore, the same Atomic Number. Chemical properties of elements depend on the atomic number of the element. A complete Periodic Table lists the elements, their symbols and atomic numbers as well as atomic masses. ...
Writing Formulas
... Writing Ionic Formulas When writing the chemical formula for ionic compounds put the cation first followed by the anion and use subscripts to indicate the number of each ion present. Remember the algebraic sum of the ions' oxidation numbers must equal zero. (Balance) Learn the polyatomic ions. ...
... Writing Ionic Formulas When writing the chemical formula for ionic compounds put the cation first followed by the anion and use subscripts to indicate the number of each ion present. Remember the algebraic sum of the ions' oxidation numbers must equal zero. (Balance) Learn the polyatomic ions. ...
Topic 13 – 14.1
... 14.1 How atoms of various elements are different The atoms of different elements contain different numbers of protons in the nucleus. Because the number of protons is so important, it is called the atomic number. ...
... 14.1 How atoms of various elements are different The atoms of different elements contain different numbers of protons in the nucleus. Because the number of protons is so important, it is called the atomic number. ...
Atomic Theories
... • Developed the first useful atomic theory • His theory was comprised of 4 postulates ...
... • Developed the first useful atomic theory • His theory was comprised of 4 postulates ...
Atomic Structure - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
... When e– falls back to a lower-energy, more stable orbital (it might be the orbital it started out in, but it might not), atom releases the “right” amount of energy as light. ...
... When e– falls back to a lower-energy, more stable orbital (it might be the orbital it started out in, but it might not), atom releases the “right” amount of energy as light. ...
Unit 2 Atomic Structure
... When e– falls back to a lower-energy, more stable orbital (it might be the orbital it started out in, but it might not), atom releases the “right” amount of energy as light. ...
... When e– falls back to a lower-energy, more stable orbital (it might be the orbital it started out in, but it might not), atom releases the “right” amount of energy as light. ...