Atoms
... Bohr – Said that electrons revolve around the nucleus in circular paths or orbits and that electrons could only exist in certain orbits and at certain energy levels. nitrogen ...
... Bohr – Said that electrons revolve around the nucleus in circular paths or orbits and that electrons could only exist in certain orbits and at certain energy levels. nitrogen ...
Chapter Two Atoms & The Periodic Table
... Democritus was the first to develop this idea of an atom in the 5th century John Dalton was the first to formalize the idea of an atom with Dalton’s atomic theory Known as the “father of atomic theory” ...
... Democritus was the first to develop this idea of an atom in the 5th century John Dalton was the first to formalize the idea of an atom with Dalton’s atomic theory Known as the “father of atomic theory” ...
CHE111-2 Atoms Molecules Ions
... Radiation is the study of the emission and transmission of energy through space in the form of waves. The cathode ray tube was used to study this phenomenon. It is a glass tube from which most of the air has been evacuated. Two metal plates are connected to a high voltage source and the negatively ...
... Radiation is the study of the emission and transmission of energy through space in the form of waves. The cathode ray tube was used to study this phenomenon. It is a glass tube from which most of the air has been evacuated. Two metal plates are connected to a high voltage source and the negatively ...
Unit 2 Notes Atomic Structures
... theory. He believed that different atoms or elements could be distinguished by their weight. While working on your theory you discovered the law of multiple proportions which states that when combining two or more elements to form a chemical compound, the elements are always in the smallest whole nu ...
... theory. He believed that different atoms or elements could be distinguished by their weight. While working on your theory you discovered the law of multiple proportions which states that when combining two or more elements to form a chemical compound, the elements are always in the smallest whole nu ...
Chap 03A-Atoms and Elements.pptx
... Ø explains the difference between an element and a compound. Ø explains two scientific laws, and Ø predicts a new scientific law. ...
... Ø explains the difference between an element and a compound. Ø explains two scientific laws, and Ø predicts a new scientific law. ...
Atoms - ChemistryatBiotech
... lost or gained with oxidation numbers (also known as charges) Ions are charged particles –when an atom has too many or too few electrons to be neutral No change to the nucleus Proton and neutrons stay the same number. ...
... lost or gained with oxidation numbers (also known as charges) Ions are charged particles –when an atom has too many or too few electrons to be neutral No change to the nucleus Proton and neutrons stay the same number. ...
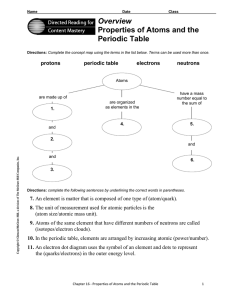
Overview Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table
... 8. The unit of measurement used for atomic particles is the (atom size/atomic mass unit). 9. Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called (isotopes/electron clouds). 10. In the periodic table, elements are arranged by increasing atomic (power/number). 11. An electron ...
... 8. The unit of measurement used for atomic particles is the (atom size/atomic mass unit). 9. Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called (isotopes/electron clouds). 10. In the periodic table, elements are arranged by increasing atomic (power/number). 11. An electron ...
03.03a Atomic Number, Mass Number, and Isotopes
... number is the total number of protons and neutrons that make up the nucleus of an isotope. For example, carbon-14, commonly used to date biological objects (up to approximately 50,000 years old), has six protons (Z=6) and eight neutrons. To determine the number of neutrons in an isotope: Mass Number ...
... number is the total number of protons and neutrons that make up the nucleus of an isotope. For example, carbon-14, commonly used to date biological objects (up to approximately 50,000 years old), has six protons (Z=6) and eight neutrons. To determine the number of neutrons in an isotope: Mass Number ...
Studying Atoms
... the protons and neutrons. To find neutrons: Mass number – Atomic number = # of neutrons ...
... the protons and neutrons. To find neutrons: Mass number – Atomic number = # of neutrons ...
Atoms and Atomic Theory
... This does not mean that there are 17 protons, 17 electrons and 18.5 neutrons in an atom of chlorine. It is not possible to have a fraction of a neutron, there can only be a whole number of neutrons in an atom. So what does it mean, and where does the 0.5 come from? Here is the explanation. The non i ...
... This does not mean that there are 17 protons, 17 electrons and 18.5 neutrons in an atom of chlorine. It is not possible to have a fraction of a neutron, there can only be a whole number of neutrons in an atom. So what does it mean, and where does the 0.5 come from? Here is the explanation. The non i ...
SL Topic 2 : Atomic structure
... 11. Which is correct for the mass and charge of the sub-atomic particle concerned? ...
... 11. Which is correct for the mass and charge of the sub-atomic particle concerned? ...
The Chemical Basis of Life
... – Other isotopes are radioactive, having unstable atoms that spontaneously break apart (decay) to form other atoms – When radioactive atoms decay, energy is released ...
... – Other isotopes are radioactive, having unstable atoms that spontaneously break apart (decay) to form other atoms – When radioactive atoms decay, energy is released ...
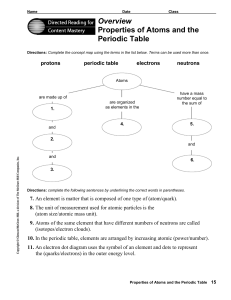
Overview Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table
... 8. The unit of measurement used for atomic particles is the (atom size/atomic mass unit). 9. Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called (isotopes/electron clouds). 10. In the periodic table, elements are arranged by increasing atomic (power/number). 11. An electron ...
... 8. The unit of measurement used for atomic particles is the (atom size/atomic mass unit). 9. Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called (isotopes/electron clouds). 10. In the periodic table, elements are arranged by increasing atomic (power/number). 11. An electron ...
8th-interlude-for-atoms - Epiphany Catholic School
... 1. A has 24 protons & 25 neutrons. B has 24 protons & 26 neutrons. Are A & B different elements or isotopes? 2. C has an atomic number of 12 & mass number of 24. D has an atomic number of 13 & a mass number of 26. Are C & D different elements or isotopes? ...
... 1. A has 24 protons & 25 neutrons. B has 24 protons & 26 neutrons. Are A & B different elements or isotopes? 2. C has an atomic number of 12 & mass number of 24. D has an atomic number of 13 & a mass number of 26. Are C & D different elements or isotopes? ...
Name Class Date Skills Worksheet Directed Reading B Section
... _____ 10. In 1911, Rutherford revised the atomic theory. Which of the following is NOT part of that theory? a. Atoms are mostly empty space. b. The nucleus is a tiny, dense, positively charged region. c. Positively charged particles that pass close by the nucleus are pushed away by the positive char ...
... _____ 10. In 1911, Rutherford revised the atomic theory. Which of the following is NOT part of that theory? a. Atoms are mostly empty space. b. The nucleus is a tiny, dense, positively charged region. c. Positively charged particles that pass close by the nucleus are pushed away by the positive char ...
Atom Unit Review Questions File
... 5. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that: a) have different numbers of electrons. b) have different numbers of protons. c) have different atomic numbers. d) have different numbers of neutrons. e) have different nuclear charges. ...
... 5. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that: a) have different numbers of electrons. b) have different numbers of protons. c) have different atomic numbers. d) have different numbers of neutrons. e) have different nuclear charges. ...
Kentucky newspapers 1949 look at the city, part 5
... (As published in The Oak Ridger’s Historically Speaking column on May 12, 2015) Reaction Controlled Some of these isotopes are “stable” and some are “radioactive.” The stable ones are all natural and just what the word stable indicates. The radioactive isotopes are in some cases natural, but in most ...
... (As published in The Oak Ridger’s Historically Speaking column on May 12, 2015) Reaction Controlled Some of these isotopes are “stable” and some are “radioactive.” The stable ones are all natural and just what the word stable indicates. The radioactive isotopes are in some cases natural, but in most ...
Atomic Structure - Madison County Schools
... He was a New Zealand physicist who came to be known as the father of nuclear physics. In early work he discovered the concept of radioactive half-life, proved that radioactivity involved the nuclear transmutation of one chemical element to another, and also differentiated and named alpha and beta ra ...
... He was a New Zealand physicist who came to be known as the father of nuclear physics. In early work he discovered the concept of radioactive half-life, proved that radioactivity involved the nuclear transmutation of one chemical element to another, and also differentiated and named alpha and beta ra ...
7th Grade Study Guide Test #1 – Jan. 28th Chapter 4.1: Introduction
... model of the atom. (Democritus, Dalton, Thompson, Rutherford and Bohr) 2. Identify the experiments the scientists above used to support their findings (Discharge cathode rays, gold foil experiment) 3. Determine who was responsible for: a. Determining that atoms are indivisible b. Atoms of the same e ...
... model of the atom. (Democritus, Dalton, Thompson, Rutherford and Bohr) 2. Identify the experiments the scientists above used to support their findings (Discharge cathode rays, gold foil experiment) 3. Determine who was responsible for: a. Determining that atoms are indivisible b. Atoms of the same e ...
Elements Elements (cont.) Elements (cont.)
... • Atoms of a given element are different from those of any other element. – C Carbon b atoms have h different diff chemical h i l andd physical h i l properties than sulfur atoms. ...
... • Atoms of a given element are different from those of any other element. – C Carbon b atoms have h different diff chemical h i l andd physical h i l properties than sulfur atoms. ...
atomic number
... • An isotope is often written with the element name followed by the mass number. ...
... • An isotope is often written with the element name followed by the mass number. ...