ATOMIC THEORY
... ATOMS CANNOT BE BROKEN DOWN INTO SMALLER PARTICLES. ALL ATOMS OF AN ELEMENT WERE EXACTLY ALIKE AND ATOMS ...
... ATOMS CANNOT BE BROKEN DOWN INTO SMALLER PARTICLES. ALL ATOMS OF AN ELEMENT WERE EXACTLY ALIKE AND ATOMS ...
Chapter 4 Notes
... ____________________ - smallest particle of an element that retains the ____________________ of that element. ____________________ is the man credited with the discovery of the electrons in the late _____, using cathode ray tubes. ____________________ discovered the mass of the electron. Knowledge o ...
... ____________________ - smallest particle of an element that retains the ____________________ of that element. ____________________ is the man credited with the discovery of the electrons in the late _____, using cathode ray tubes. ____________________ discovered the mass of the electron. Knowledge o ...
atoms - My CCSD
... identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
... identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
Chapter 4
... identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
... identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
GY 111 Lecture Note Series Elemental Chemistry
... Many of the man-made elements and even some of the naturally occurring ones are unstable. They tend to break apart over time through a process called or radioactivity. This must mean that there is something smaller than an atom (i.e. atoms and ions are not the smallest particles). It has been known ...
... Many of the man-made elements and even some of the naturally occurring ones are unstable. They tend to break apart over time through a process called or radioactivity. This must mean that there is something smaller than an atom (i.e. atoms and ions are not the smallest particles). It has been known ...
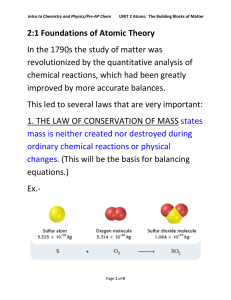
2:1 Foundations of Atomic Theory In the 1790s the study of matter
... of atoms in an element in a sample with a known mass. Atoms of different elements have different numbers of protons; Atoms of the same element have the same number of protons. The ATOMIC NUMBER (Z) of an element is the number of protons of each atom of that element, so it identifies an element. The ...
... of atoms in an element in a sample with a known mass. Atoms of different elements have different numbers of protons; Atoms of the same element have the same number of protons. The ATOMIC NUMBER (Z) of an element is the number of protons of each atom of that element, so it identifies an element. The ...
200
... •Q How are the number of electrons in an atom determined? •A The number of electrons is equal to the number of protons ...
... •Q How are the number of electrons in an atom determined? •A The number of electrons is equal to the number of protons ...
Jeopardy
... •Q How are the number of electrons in an atom determined? •A The number of electrons is equal to the number of protons ...
... •Q How are the number of electrons in an atom determined? •A The number of electrons is equal to the number of protons ...
The Modern Theory of Atomic Structure
... the SAME # of Protons but with DIFFERENT #’s of Neutrons ...
... the SAME # of Protons but with DIFFERENT #’s of Neutrons ...
Packet 5
... Protons – Positive charge, found in the nucleus and have a mass of 1 amu. ( Identify) Neutrons- No charge, found in the nucleus, and have a mass of 1 amu ( Isotopes) Electrons- Negative charge, found in the energy levels outside of the nucleus, have relatively no mass ( Ions) ...
... Protons – Positive charge, found in the nucleus and have a mass of 1 amu. ( Identify) Neutrons- No charge, found in the nucleus, and have a mass of 1 amu ( Isotopes) Electrons- Negative charge, found in the energy levels outside of the nucleus, have relatively no mass ( Ions) ...
Notepack - Hood River County School District
... 4.1 Atoms: Smallest particle of matter that retains it’s identity in a _______________ A. ______________ Atomic Theory. 1. All _________________ are composed of _____ ______________________ particles called ___________ 2. Atoms of the same element are __________________. Atoms of any one element ar ...
... 4.1 Atoms: Smallest particle of matter that retains it’s identity in a _______________ A. ______________ Atomic Theory. 1. All _________________ are composed of _____ ______________________ particles called ___________ 2. Atoms of the same element are __________________. Atoms of any one element ar ...
Topic one midterm review
... – If the “Plum Pudding” model was correct then the α particles would pass through the foil with just a few being slightly ...
... – If the “Plum Pudding” model was correct then the α particles would pass through the foil with just a few being slightly ...
atom
... --Matter is made of small, indivisible particles – “atomos” In the 1700’s, scientists making accurate measurements discovered several new laws -- ...
... --Matter is made of small, indivisible particles – “atomos” In the 1700’s, scientists making accurate measurements discovered several new laws -- ...
ppt - Faculty
... • The nucleus depicted is understood to be a quantum system composed of protons and neutrons, particles of nearly equal mass and the same intrinsic angular momentum (spin) of 1/2. • The proton carries one unit of positive electric charge while the neutron has no electric charge. • The simplest nuc ...
... • The nucleus depicted is understood to be a quantum system composed of protons and neutrons, particles of nearly equal mass and the same intrinsic angular momentum (spin) of 1/2. • The proton carries one unit of positive electric charge while the neutron has no electric charge. • The simplest nuc ...
What do atoms look like?
... mass number and atomic mass? • Atomic Mass= weighted average of the masses of all known isotopes of an element. • Mass Number = protons + neutrons for a particular isotope of an element ***Round atomic mass to the nearest whole number to get the mass number for the most common isotope of that elemen ...
... mass number and atomic mass? • Atomic Mass= weighted average of the masses of all known isotopes of an element. • Mass Number = protons + neutrons for a particular isotope of an element ***Round atomic mass to the nearest whole number to get the mass number for the most common isotope of that elemen ...
Chapter 4: The Structure of the Atom
... In a neutral atom, the number of protons = the number of electrons. ...
... In a neutral atom, the number of protons = the number of electrons. ...
Section 4.2 The Structure of an Atom
... 4. Circle the letter of the expression that accurately compares the masses of neutrons and protons. a. mass of 1 neutron = mass of 1 proton b. mass of 2000 neutrons = mass of 1 proton c. mass of 1 electron = mass of 1 proton Physical Science Reading and Study Workbook Level B ...
... 4. Circle the letter of the expression that accurately compares the masses of neutrons and protons. a. mass of 1 neutron = mass of 1 proton b. mass of 2000 neutrons = mass of 1 proton c. mass of 1 electron = mass of 1 proton Physical Science Reading and Study Workbook Level B ...
What is an isotope?
... What is an isotope? Number of protons for an atom of a specific element never changes. Number of neutrons can change. Two atoms with equal protons but different neutrons are called isotopes of each other. All atoms in existence are isotopes! Some isotopes are just more common than others. ...
... What is an isotope? Number of protons for an atom of a specific element never changes. Number of neutrons can change. Two atoms with equal protons but different neutrons are called isotopes of each other. All atoms in existence are isotopes! Some isotopes are just more common than others. ...
投影片 - 中正大學化生系
... modern experimental scientific method. 2. He endorsed the view of elements as the undecomposable constituents of material bodies; and made the distinction between mixtures and compounds. ...
... modern experimental scientific method. 2. He endorsed the view of elements as the undecomposable constituents of material bodies; and made the distinction between mixtures and compounds. ...
The Atom
... Atoms of the same element can have different number of neutrons. Atoms of the same element that has different number of neutrons have different masses. ...
... Atoms of the same element can have different number of neutrons. Atoms of the same element that has different number of neutrons have different masses. ...
Atoms and the Periodic Table
... table by increasing atomic number. 1. In the late 1800’s, Dmitri Mendeleev devised the first periodic table based on atomic mass. 2. In 1913, Henry G.J. Moseley arranged the elements by atomic number rather than atomic mass. ...
... table by increasing atomic number. 1. In the late 1800’s, Dmitri Mendeleev devised the first periodic table based on atomic mass. 2. In 1913, Henry G.J. Moseley arranged the elements by atomic number rather than atomic mass. ...
Posttest answers - Aurora City Schools
... electrons, so it has a charge (happens during chemical reactions). It’s written with the charge in the upper right hand corner 59. - 60. What is an isotope and how is the symbol written differently? ...
... electrons, so it has a charge (happens during chemical reactions). It’s written with the charge in the upper right hand corner 59. - 60. What is an isotope and how is the symbol written differently? ...