notes 4.1 & 4.2
... Do we have to know this? • But you’ll hear more about that in chemistry. For now realize that each energy level is made up of sublevels that hold specific amounts of electrons. • The sublevels are called orbitals and are named s, p, d, f • You can see these patterns in the periodic table. ...
... Do we have to know this? • But you’ll hear more about that in chemistry. For now realize that each energy level is made up of sublevels that hold specific amounts of electrons. • The sublevels are called orbitals and are named s, p, d, f • You can see these patterns in the periodic table. ...
AP Projectile Motion
... approximate mass of a single proton or neutron is 1 amu mass of an atom in atomic mass units is simply the sum of its protons and neutrons and is known as the atomic mass number mass of an electron is so small that it's disregarded ...
... approximate mass of a single proton or neutron is 1 amu mass of an atom in atomic mass units is simply the sum of its protons and neutrons and is known as the atomic mass number mass of an electron is so small that it's disregarded ...
Define:
... 79. Chlorine has two naturally occurring isotopes, Cl-35 and Cl-37. The atomic mass of chlorine is 35.45. Which of these two isotopes of chlorine is more abundant? 80. Consider an element Z that has two naturally occurring isotopes with the following percent abundances: the isotope with a mass numbe ...
... 79. Chlorine has two naturally occurring isotopes, Cl-35 and Cl-37. The atomic mass of chlorine is 35.45. Which of these two isotopes of chlorine is more abundant? 80. Consider an element Z that has two naturally occurring isotopes with the following percent abundances: the isotope with a mass numbe ...
Grade 11 Chemistry E.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 23. Describe the different types of intermolecular forces. 24. Balance the following equations. a. CF4(l) → C(s) + F2(g) b. H2SO4(aq) + KOH(aq) → KHSO4(aq) + H2O(l) c. ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g) → Zn(s) + HCl(aq) d. SO2(g) + H2O(l) + O2(g) → H2SO4(aq) e. Li(s) + H2O(l) → LiOH(aq) + H2(g) f. H2CO3(aq) → H2O(l ...
... 23. Describe the different types of intermolecular forces. 24. Balance the following equations. a. CF4(l) → C(s) + F2(g) b. H2SO4(aq) + KOH(aq) → KHSO4(aq) + H2O(l) c. ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g) → Zn(s) + HCl(aq) d. SO2(g) + H2O(l) + O2(g) → H2SO4(aq) e. Li(s) + H2O(l) → LiOH(aq) + H2(g) f. H2CO3(aq) → H2O(l ...
(Questions 1-10) Write the letter of the answer that best complet
... Which of the following statements in Dalton’s atomic theory was shown to be incorrect by the results of Thomson’s cathode-ray tube experiment? A. All substances are made of atoms. B. Atoms are small particles that cannot be created, divided, or destroyed. C. Atoms of the same element are exactly ali ...
... Which of the following statements in Dalton’s atomic theory was shown to be incorrect by the results of Thomson’s cathode-ray tube experiment? A. All substances are made of atoms. B. Atoms are small particles that cannot be created, divided, or destroyed. C. Atoms of the same element are exactly ali ...
Unit2StudyGuide
... 17. What is a cation? Which particles does it have more of: electrons or protons? Average Atomic Mass 1. How do you calculate the average atomic mass of an element? 2. Example: The Carbon atom has three isotopes: Carbon-12 at 98.2%, Carbon-13 at 1.2%, and Carbon-14 at 0.6%. What is the average atomi ...
... 17. What is a cation? Which particles does it have more of: electrons or protons? Average Atomic Mass 1. How do you calculate the average atomic mass of an element? 2. Example: The Carbon atom has three isotopes: Carbon-12 at 98.2%, Carbon-13 at 1.2%, and Carbon-14 at 0.6%. What is the average atomi ...
Unit 1 Test Study Guide KEY
... Why does the atom have an overall neutral charge? Because for every proton (positive charge) there is one electron (negative charge). 9. Name the three main parts of an atom, give their location, and their charge. Proton – found in the nucleus of the atom – positive charge Neutron – found in the nuc ...
... Why does the atom have an overall neutral charge? Because for every proton (positive charge) there is one electron (negative charge). 9. Name the three main parts of an atom, give their location, and their charge. Proton – found in the nucleus of the atom – positive charge Neutron – found in the nuc ...
Chapter 2 Test Review - Mercer Island School District
... 14. An atom emits 3 colors of light, Red, Yellow and Violet when excited by an E.M. wave. Draw the Bohr Model of an atom that shows these colors of light being emitted. See the “Electron: How does it behave” Notes. This packet covers EM Waves and the Bohr Model. ...
... 14. An atom emits 3 colors of light, Red, Yellow and Violet when excited by an E.M. wave. Draw the Bohr Model of an atom that shows these colors of light being emitted. See the “Electron: How does it behave” Notes. This packet covers EM Waves and the Bohr Model. ...
PowerPoint - Models of the Atom
... • Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. • Due to isotopes, mass #s are not round #s. • Li (6.9) is made up of both 6Li and 7Li. • Often, at least one isotope is unstable. • It breaks down, releasing radioactivity. • These types of isotopes are called ...
... • Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. • Due to isotopes, mass #s are not round #s. • Li (6.9) is made up of both 6Li and 7Li. • Often, at least one isotope is unstable. • It breaks down, releasing radioactivity. • These types of isotopes are called ...
PowerPoint - Models of the Atom
... • Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. • Due to isotopes, mass #s are not round #s. • Li (6.9) is made up of both 6Li and 7Li. • Often, at least one isotope is unstable. • It breaks down, releasing radioactivity. • These types of isotopes are called ...
... • Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. • Due to isotopes, mass #s are not round #s. • Li (6.9) is made up of both 6Li and 7Li. • Often, at least one isotope is unstable. • It breaks down, releasing radioactivity. • These types of isotopes are called ...
Structure - Mole Cafe
... Changes in matter result from changes in the groupings of atoms and not the atoms themselves ...
... Changes in matter result from changes in the groupings of atoms and not the atoms themselves ...
electron
... abundance of 19.91%. The isotope with mass 11.009 amu has a relative abundance of 80.09%. 1. Calculate the atomic mass of this element (show all work) and then name this element. ...
... abundance of 19.91%. The isotope with mass 11.009 amu has a relative abundance of 80.09%. 1. Calculate the atomic mass of this element (show all work) and then name this element. ...
Atomic Structure
... Atomic Mass •It is useful to compare the relative masses of atoms to a standard reference isotope. Carbon-12 is the standard reference isotope. Cabon12 has a mass of exactly 12 atomic mass units. •An atomic mass unit (amu) is defined as one twelfth of the mass of a carbon-12 atom. ...
... Atomic Mass •It is useful to compare the relative masses of atoms to a standard reference isotope. Carbon-12 is the standard reference isotope. Cabon12 has a mass of exactly 12 atomic mass units. •An atomic mass unit (amu) is defined as one twelfth of the mass of a carbon-12 atom. ...
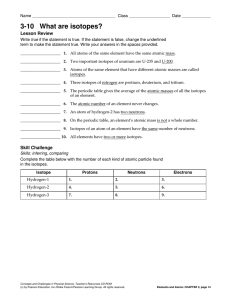
3-10 What are isotopes?
... reason for this? ____________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. According to the table, how are isotopes named? ______________________________________________ 6. What is true a ...
... reason for this? ____________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. According to the table, how are isotopes named? ______________________________________________ 6. What is true a ...
Day 2 Guided Reading Chapter 4
... c) charge d) location in the atom 19. What is the mass of a neutron compared to that of a proton? Atomic Number and Mass Number (page 110) 20. T or F Two atoms of the same element can have different numbers of protons. 21. What is an atomic number? 22. Which of the following quantities are always eq ...
... c) charge d) location in the atom 19. What is the mass of a neutron compared to that of a proton? Atomic Number and Mass Number (page 110) 20. T or F Two atoms of the same element can have different numbers of protons. 21. What is an atomic number? 22. Which of the following quantities are always eq ...
Full Text PDF - Science and Education Publishing
... The answer to the aforementioned question is given by quantum electrodynamics (QED), a theory that combines quantum mechanics and special relativity, usually taught in Physics advanced courses. The basic idea is easy to grasp: electrons (especially the most internal ones) interacting with a heavy nu ...
... The answer to the aforementioned question is given by quantum electrodynamics (QED), a theory that combines quantum mechanics and special relativity, usually taught in Physics advanced courses. The basic idea is easy to grasp: electrons (especially the most internal ones) interacting with a heavy nu ...
The Basics of Atomic Structure
... the number of neutrons and electrons. An element can be identified by its Atomic Number. • Isotopes are atoms with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons; therefore, the mass number will be different but the atomic number will be the same. All atoms of an element are considere ...
... the number of neutrons and electrons. An element can be identified by its Atomic Number. • Isotopes are atoms with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons; therefore, the mass number will be different but the atomic number will be the same. All atoms of an element are considere ...
希臘 - 中正大學化生系
... modern experimental scientific method. 2. He endorsed the view of elements as the undecomposable constituents of material bodies; and made the distinction between mixtures and compounds. ...
... modern experimental scientific method. 2. He endorsed the view of elements as the undecomposable constituents of material bodies; and made the distinction between mixtures and compounds. ...