What is the smallest particle of an element that retains the properties
... 62. What is the valence configuration of At? 63. What element has the valence configuration 4s2 4p5? 64. What is the name of the particles that make up protons and neutrons? 65. In modern atomic theory, what does the term fundamental mean? 66. Which particles are fundamental? (choose more than one i ...
... 62. What is the valence configuration of At? 63. What element has the valence configuration 4s2 4p5? 64. What is the name of the particles that make up protons and neutrons? 65. In modern atomic theory, what does the term fundamental mean? 66. Which particles are fundamental? (choose more than one i ...
Physical Science EOCT Review Domain 1: Chemistry
... 3) Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds 4) In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged – but never changed into atoms of another element. ...
... 3) Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds 4) In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged – but never changed into atoms of another element. ...
ISOTOPES
... all atoms of each element were the same. According to the model of atomic structure we have been developing, this would mean that each atom of an element would have the same number of protons, electrons, and neutrons as every other atom of the element. Thus the atomic mass of every atom of an elemen ...
... all atoms of each element were the same. According to the model of atomic structure we have been developing, this would mean that each atom of an element would have the same number of protons, electrons, and neutrons as every other atom of the element. Thus the atomic mass of every atom of an elemen ...
Physical Science Chapter 3 Test
... their properties will emerge in a regular pattern. 12. Because atoms of elements in the same group of the periodic table have the same number of ____________________, they have similar properties. 13. Some elements are highly ____________________ because their outermost energy levels are only partia ...
... their properties will emerge in a regular pattern. 12. Because atoms of elements in the same group of the periodic table have the same number of ____________________, they have similar properties. 13. Some elements are highly ____________________ because their outermost energy levels are only partia ...
Phys Sci I, Quiz #3 - Electriciy and Magnetism, Atomic and Nuclear
... B) quark C) electromagnetic D) gravitational ...
... B) quark C) electromagnetic D) gravitational ...
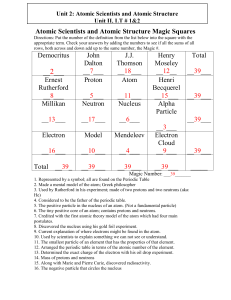
Atomic Scientists and Atomic Structure Magic Squares
... 5. The positive particle in the nucleus of an atom. (Not a fundamental particle) 6. The tiny positive core of an atom; contains protons and neutrons. 7. Credited with the first atomic theory model of the atom which had four main postulates. 8. Discovered the nucleus using his gold foil experiment. 9 ...
... 5. The positive particle in the nucleus of an atom. (Not a fundamental particle) 6. The tiny positive core of an atom; contains protons and neutrons. 7. Credited with the first atomic theory model of the atom which had four main postulates. 8. Discovered the nucleus using his gold foil experiment. 9 ...
Chapter 3 - Vocabulary and Notes
... element that have different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei (pg 83) Mass Number: Sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom (pg 83) ...
... element that have different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei (pg 83) Mass Number: Sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom (pg 83) ...
AP Unit 0: Chemical Foundations
... ◦ Compounds are formed by the combination of different atoms in the ratio of small whole numbers. ◦ A chemical reaction involves only the rearrangement of atoms; ◦ atoms are not created / destroyed ...
... ◦ Compounds are formed by the combination of different atoms in the ratio of small whole numbers. ◦ A chemical reaction involves only the rearrangement of atoms; ◦ atoms are not created / destroyed ...
VL: 0
... Bohr models of 14 elements in the correct place on the modified Periodic Table. 2. Answer the questions on RM 18. 3. Complete RM 19. ...
... Bohr models of 14 elements in the correct place on the modified Periodic Table. 2. Answer the questions on RM 18. 3. Complete RM 19. ...
Chapter 1 D Study Guide
... 3. Electrons move around the nucleus in electron rings or shells or energy levels. 4. Atomic number is equal to the number of protons, and is unique to each element 5. The number of protons is equal to the number of electrons in a balanced atom, but not in an ION 6. The atomic mass (rounded off) is ...
... 3. Electrons move around the nucleus in electron rings or shells or energy levels. 4. Atomic number is equal to the number of protons, and is unique to each element 5. The number of protons is equal to the number of electrons in a balanced atom, but not in an ION 6. The atomic mass (rounded off) is ...
Chapter 3
... by mass for example: NaCl is always 66.66% chlorine and 39.34% sodium • Law of Multiple Proportions: when two elements can form two compounds, the masses that combine are in simple whole number ratios, CO and CO2 ...
... by mass for example: NaCl is always 66.66% chlorine and 39.34% sodium • Law of Multiple Proportions: when two elements can form two compounds, the masses that combine are in simple whole number ratios, CO and CO2 ...
Elements and Atoms
... The reason different elements have different properties is because the atoms that make up different elements have different numbers of tiny particles that make them up. The particles that make up atoms are called subatomic particles. There are three types of subatomic particles: 1. protons (positive ...
... The reason different elements have different properties is because the atoms that make up different elements have different numbers of tiny particles that make them up. The particles that make up atoms are called subatomic particles. There are three types of subatomic particles: 1. protons (positive ...
Chapter 3
... by mass for example: NaCl is always 60.66% chlorine and 39.34% sodium • Law of Multiple Proportions: when two elements can form two compounds, the masses that combine are in simple whole number ratios, CO and CO2 ...
... by mass for example: NaCl is always 60.66% chlorine and 39.34% sodium • Law of Multiple Proportions: when two elements can form two compounds, the masses that combine are in simple whole number ratios, CO and CO2 ...
Name: Date: ______ Period: Unit 3 – Atomic Structure Review
... 1. Who was the ancient Greek philosopher who first proposed the notion of the atom? Democritus 2. What was Dalton’s atomic model called? Billard ball model 3. Who’s model first introduced the concept of energy levels? Bohr 4. What were the major problems of Dalton’s atomic theory? Did not have an in ...
... 1. Who was the ancient Greek philosopher who first proposed the notion of the atom? Democritus 2. What was Dalton’s atomic model called? Billard ball model 3. Who’s model first introduced the concept of energy levels? Bohr 4. What were the major problems of Dalton’s atomic theory? Did not have an in ...
PowerPoint_Atomic Structure
... Silicon has an Atomic Number of 14. This means it has 14 protons Silicon has an Atomic Mass of about 28, so that means it has 28 protons and neutrons. To find how many neutrons it has, we subtract the Atomic Number from the Atomic Mass. So, 28 – 14 = 14 neutrons. ...
... Silicon has an Atomic Number of 14. This means it has 14 protons Silicon has an Atomic Mass of about 28, so that means it has 28 protons and neutrons. To find how many neutrons it has, we subtract the Atomic Number from the Atomic Mass. So, 28 – 14 = 14 neutrons. ...
ANSWERS Using Key Terms Understanding Key Ideas
... exercise can be found at the back of this book. 16. Scientists must determine the atomic number, or the number of protons, in the newly formed nucleus. The nucleus is that of a new element only if the number of protons is different from all known elements. 17. Sample answer: Dalton’s atomic theory w ...
... exercise can be found at the back of this book. 16. Scientists must determine the atomic number, or the number of protons, in the newly formed nucleus. The nucleus is that of a new element only if the number of protons is different from all known elements. 17. Sample answer: Dalton’s atomic theory w ...
Chapter 11 and 12-2 Review/Study Guide for Test
... 1. List the major discovery or accomplishment associated with of each of the following scientists: a. Democritus – named the atom b. Dalton – said the atom was positively charged, had his atomic theory (all atoms of the same element are the same, atoms of different elements are different, everything ...
... 1. List the major discovery or accomplishment associated with of each of the following scientists: a. Democritus – named the atom b. Dalton – said the atom was positively charged, had his atomic theory (all atoms of the same element are the same, atoms of different elements are different, everything ...
Chapter 4
... - Man-made elements. They do not last but a few seconds in a lab. - The correct way to name them now is to use pre-fix symbols instead of fighting over a name. Bbp would be 225, Uns ...
... - Man-made elements. They do not last but a few seconds in a lab. - The correct way to name them now is to use pre-fix symbols instead of fighting over a name. Bbp would be 225, Uns ...
Summary: History of Models of the Atom
... regardless of the number of times you cut a form of matter in half, you would always have a smaller piece of that matter. This view held sway for 2000 years primarily because Aristotle was the tutor of Alexander the Great. John Dalton (1776-1844) proposed the theory that all matter is made up of ind ...
... regardless of the number of times you cut a form of matter in half, you would always have a smaller piece of that matter. This view held sway for 2000 years primarily because Aristotle was the tutor of Alexander the Great. John Dalton (1776-1844) proposed the theory that all matter is made up of ind ...
ppt
... 3)Gamma rays (γ) ● High energy electromagnetic radiation – more energetic than x-rays ● No rest mass or charge ● More dangerous than other radiation – may take several feet of concrete/lead to stop ● Breaks chemical bonds, damages DNA ● Gamma radiation accompanies other radioactive emissions. ...
... 3)Gamma rays (γ) ● High energy electromagnetic radiation – more energetic than x-rays ● No rest mass or charge ● More dangerous than other radiation – may take several feet of concrete/lead to stop ● Breaks chemical bonds, damages DNA ● Gamma radiation accompanies other radioactive emissions. ...
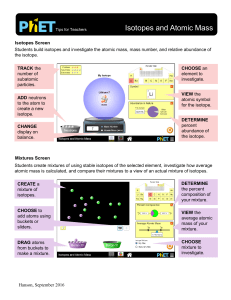
Isotopes and Atomic Mass
... • In college interviews, students wanted to select other common elements such as gold; investigation into other elements could be incorporated as part of an activity. • On the Mixtures screen, students attempted to match Nature’s Mix using My Mix view. This is not possible for all elements shown in ...
... • In college interviews, students wanted to select other common elements such as gold; investigation into other elements could be incorporated as part of an activity. • On the Mixtures screen, students attempted to match Nature’s Mix using My Mix view. This is not possible for all elements shown in ...