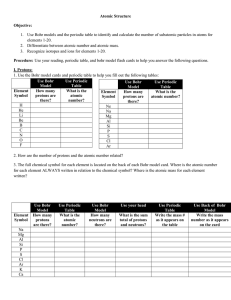
Name Date Period______________ DIRECTED READING
... 14. An element is composed of atoms with the same number of _______________________. (neutrons or protons) Are All Atoms of an Element the Same? (p. 290) 15. It is NOT true that isotopes of an element a. have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. b. are stable when radioactiv ...
... 14. An element is composed of atoms with the same number of _______________________. (neutrons or protons) Are All Atoms of an Element the Same? (p. 290) 15. It is NOT true that isotopes of an element a. have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. b. are stable when radioactiv ...
1.3 Biochemistry: Chemistry basics notes ppt
... Atomic Number and Atomic Mass • Atoms of the various elements differ in number of subatomic particles • An element’s atomic number is the number of protons in its nucleus • An element’s mass number is the sum of protons plus neutrons in the nucleus • Atomic mass, the atom’s total mass, can be appro ...
... Atomic Number and Atomic Mass • Atoms of the various elements differ in number of subatomic particles • An element’s atomic number is the number of protons in its nucleus • An element’s mass number is the sum of protons plus neutrons in the nucleus • Atomic mass, the atom’s total mass, can be appro ...
Atomic Structure_Bohr Flashcards
... 12. If protons are positively charged and electrons are negatively charged particles. What is the overall charge for each element listed above? 13. Suppose you do not have access to the Bohr models for the above elements. Describe how you can determine the number of electrons for a neutral element j ...
... 12. If protons are positively charged and electrons are negatively charged particles. What is the overall charge for each element listed above? 13. Suppose you do not have access to the Bohr models for the above elements. Describe how you can determine the number of electrons for a neutral element j ...
Unit 5: Atoms and the Periodic Table
... These electrons are the ones that are used to form chemical bonds with other atoms to form molecules or compounds. ...
... These electrons are the ones that are used to form chemical bonds with other atoms to form molecules or compounds. ...
Chapter 12 - MrsHenrikssoniClassroom
... opposite but equal in size (the atom is neutral). • If the number of electrons is different from the number of protons, the atom becomes a charged particle called an ion. • The mass of an electron is so small that it is usually considered to be zero. ...
... opposite but equal in size (the atom is neutral). • If the number of electrons is different from the number of protons, the atom becomes a charged particle called an ion. • The mass of an electron is so small that it is usually considered to be zero. ...
L41 - Atomic Structure
... they fired Helium nuclei at a piece of gold foil which was only a few atoms thick. they found that although most of them passed through. About 1 in 10,000 hit ...
... they fired Helium nuclei at a piece of gold foil which was only a few atoms thick. they found that although most of them passed through. About 1 in 10,000 hit ...
atom
... Atoms of same element have the same size, mass, and properties Atoms can’t be subdivided, created or destroyed Atoms of different elements combine in whole number ratios to make compounds In chemical reactions, atoms can be combined, separated, and rearranged. ...
... Atoms of same element have the same size, mass, and properties Atoms can’t be subdivided, created or destroyed Atoms of different elements combine in whole number ratios to make compounds In chemical reactions, atoms can be combined, separated, and rearranged. ...
File - Flipped Out Science with Mrs. Thomas!
... h. What are the products in the equation for photosynthesis? C6H12O6, ...
... h. What are the products in the equation for photosynthesis? C6H12O6, ...
Defining the Atom
... a. teaching that all matter is composed of tiny particles called atoms. b. theorizing that all atoms of the same element are identical. c. using experimental methods to establish a scientific theory. d. not relating atoms to chemical change. ...
... a. teaching that all matter is composed of tiny particles called atoms. b. theorizing that all atoms of the same element are identical. c. using experimental methods to establish a scientific theory. d. not relating atoms to chemical change. ...
Atoms Ions Valence Electrons Isotopes
... ▪ the number of valence electrons will either decrease to “0” or increase to 8, whichever requires less energy – an atom with 2 valence electrons will lose 2 electrons to reach 0 – an atom with 6 valence electrons will gain 2 electrons to reach 8 ...
... ▪ the number of valence electrons will either decrease to “0” or increase to 8, whichever requires less energy – an atom with 2 valence electrons will lose 2 electrons to reach 0 – an atom with 6 valence electrons will gain 2 electrons to reach 8 ...
History of the Atom
... In 1803, proposed an Atomic Theory which states: o All substances are made of atoms; atoms are small particles that cannot be created, divided, or destroyed. o Atoms of the same element are exactly alike, and atoms of different elements are different o Atoms join with other atoms to make new subst ...
... In 1803, proposed an Atomic Theory which states: o All substances are made of atoms; atoms are small particles that cannot be created, divided, or destroyed. o Atoms of the same element are exactly alike, and atoms of different elements are different o Atoms join with other atoms to make new subst ...
Chapter 3—Time and Geology
... hourglass in each unit of time, the graph would display an inclined straight line, indicating that the amount of original material lost from the top of the hourglass to the lower half is the same during each unit of time. Because the amount of original radioactive material that is lost diminishes wi ...
... hourglass in each unit of time, the graph would display an inclined straight line, indicating that the amount of original material lost from the top of the hourglass to the lower half is the same during each unit of time. Because the amount of original radioactive material that is lost diminishes wi ...
Key Concept Summary - Bellingham High School
... Dalton’s theory enables us to set up a scale of relative atomic masses. He cannot measure the exact mass of atoms but relative mass. E.g. Consider calcium sulfide, which consists of 55.6% calcium by mass and 44.4% sulfur by mass. Suppose there is one calcium atom for each sulfur atom in calcium sulf ...
... Dalton’s theory enables us to set up a scale of relative atomic masses. He cannot measure the exact mass of atoms but relative mass. E.g. Consider calcium sulfide, which consists of 55.6% calcium by mass and 44.4% sulfur by mass. Suppose there is one calcium atom for each sulfur atom in calcium sulf ...
Cosmetology Learning Module 12
... substances that contain carbon All living things are made up of compounds that contain carbon Organic compounds will burn ...
... substances that contain carbon All living things are made up of compounds that contain carbon Organic compounds will burn ...
Honors Chemistry Name_______________________________
... 5. Answer the following questions about a chlorine-37 atom. a) How many protons does the atom contain? _________________ b) How many neutrons does the atom contain? ________________ c) How many electrons does the atom contain? ________________ d) Draw the Bohr diagram for the atom. e) How many valen ...
... 5. Answer the following questions about a chlorine-37 atom. a) How many protons does the atom contain? _________________ b) How many neutrons does the atom contain? ________________ c) How many electrons does the atom contain? ________________ d) Draw the Bohr diagram for the atom. e) How many valen ...
chapter 2 - Scranton Prep Biology
... Chemistry is fundamental to an understandingof life, becauseliving organisms are made of matter. Matter: Anything that takes up spaceand has mass. Mass : A measure of the amount of matter an obiect contains. You might want to distinguish between mass and weight for your students. Mass is the measure ...
... Chemistry is fundamental to an understandingof life, becauseliving organisms are made of matter. Matter: Anything that takes up spaceand has mass. Mass : A measure of the amount of matter an obiect contains. You might want to distinguish between mass and weight for your students. Mass is the measure ...
Atomic Theory
... the periodic table. They are arranged in increasing order going from left to right. So Hydrogen has an atomic number of 1, Helium is 2 and so on. • The atomic number tells us how many protons an atom has. This also tells us how many electrons an atom has, because the number of protons and electrons ...
... the periodic table. They are arranged in increasing order going from left to right. So Hydrogen has an atomic number of 1, Helium is 2 and so on. • The atomic number tells us how many protons an atom has. This also tells us how many electrons an atom has, because the number of protons and electrons ...
Chem Midterm Review 2016
... Since these particles were smaller than atoms, but seemed to come from them, they must be subatomic parts. He concluded that electrons must be parts of atoms of all elements So, he discovered the first subatomic particle (electron), the atom is no longer indivisible, and developed the "plum pudding" ...
... Since these particles were smaller than atoms, but seemed to come from them, they must be subatomic parts. He concluded that electrons must be parts of atoms of all elements So, he discovered the first subatomic particle (electron), the atom is no longer indivisible, and developed the "plum pudding" ...
Document
... a) 16 protons and 18 neutrons b) 18 protons and 16neutrons c) 16 protons and 18 electrons d) 18 electrons and 32 neutrons e) 16 protons and 16 electrons ...
... a) 16 protons and 18 neutrons b) 18 protons and 16neutrons c) 16 protons and 18 electrons d) 18 electrons and 32 neutrons e) 16 protons and 16 electrons ...
Matching - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... a. Protons, electrons, and neutrons are evenly distributed throughout the volume of the atom. b. The nucleus is made of protons, electrons, and neutrons. c. Electrons are distributed around the nucleus and occupy almost all the volume of the atom. d. The nucleus is made of electrons and protons. ___ ...
... a. Protons, electrons, and neutrons are evenly distributed throughout the volume of the atom. b. The nucleus is made of protons, electrons, and neutrons. c. Electrons are distributed around the nucleus and occupy almost all the volume of the atom. d. The nucleus is made of electrons and protons. ___ ...
Periodic Table - personals.okan.edu.tr
... • - Chlorine react with water and hydrochloric acid and hypochlorous acid are produced : • Cl2(g) + H2O(l) HCl(aq) + HOCl(aq) • - Hypochlorous acid is an important desinfectant and used in swimming pools(Chlorine is added into the water). • - Halogenes react with plenty of metals to form metallic ...
... • - Chlorine react with water and hydrochloric acid and hypochlorous acid are produced : • Cl2(g) + H2O(l) HCl(aq) + HOCl(aq) • - Hypochlorous acid is an important desinfectant and used in swimming pools(Chlorine is added into the water). • - Halogenes react with plenty of metals to form metallic ...
Document
... • Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. • The atomic mass of an element is a weighted average of the masses of all of its naturally occurring isotopes. ...
... • Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. • The atomic mass of an element is a weighted average of the masses of all of its naturally occurring isotopes. ...
Atoms and the Periodic Table
... c. Unlike protons and electrons, neutrons have no charge. d. Protons and neutrons have the same charge. 32. This Group 2 element has fewer protons than bromine, but no more protons than sulfur. a. Potassium ...
... c. Unlike protons and electrons, neutrons have no charge. d. Protons and neutrons have the same charge. 32. This Group 2 element has fewer protons than bromine, but no more protons than sulfur. a. Potassium ...
2.3 Atomic Mass and Number
... Scientists can distinguish between different elements by counting the number of protons. If an atom has only one proton, we know it’s an atom of the element hydrogen. An atom with two protons is always an atom of the element helium. When scientists count four protons in an atom, they know it’s a ber ...
... Scientists can distinguish between different elements by counting the number of protons. If an atom has only one proton, we know it’s an atom of the element hydrogen. An atom with two protons is always an atom of the element helium. When scientists count four protons in an atom, they know it’s a ber ...
Chemical element
A chemical element (or element) is a chemical substance consisting of atoms having the same number of protons in their atomic nuclei (i.e. the same atomic number, Z). There are 118 elements that have been identified, of which the first 94 occur naturally on Earth with the remaining 24 being synthetic elements. There are 80 elements that have at least one stable isotope and 38 that have exclusively radioactive isotopes, which decay over time into other elements. Iron is the most abundant element (by mass) making up the Earth, while oxygen is the most common element in the crust of the earth.Chemical elements constitute approximately 15% of the matter in the universe: the remainder is dark matter, the composition of it is unknown, but it is not composed of chemical elements.The two lightest elements, hydrogen and helium were mostly formed in the Big Bang and are the most common elements in the universe. The next three elements (lithium, beryllium and boron) were formed mostly by cosmic ray spallation, and are thus more rare than those that follow. Formation of elements with from six to twenty six protons occurred and continues to occur in main sequence stars via stellar nucleosynthesis. The high abundance of oxygen, silicon, and iron on Earth reflects their common production in such stars. Elements with greater than twenty six protons are formed by supernova nucleosynthesis in supernovae, which, when they explode, blast these elements far into space as planetary nebulae, where they may become incorporated into planets when they are formed.When different elements are chemically combined, with the atoms held together by chemical bonds, they form chemical compounds. Only a minority of elements are found uncombined as relatively pure minerals. Among the more common of such ""native elements"" are copper, silver, gold, carbon (as coal, graphite, or diamonds), and sulfur. All but a few of the most inert elements, such as noble gases and noble metals, are usually found on Earth in chemically combined form, as chemical compounds. While about 32 of the chemical elements occur on Earth in native uncombined forms, most of these occur as mixtures. For example, atmospheric air is primarily a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, and argon, and native solid elements occur in alloys, such as that of iron and nickel.The history of the discovery and use of the elements began with primitive human societies that found native elements like carbon, sulfur, copper and gold. Later civilizations extracted elemental copper, tin, lead and iron from their ores by smelting, using charcoal. Alchemists and chemists subsequently identified many more, with almost all of the naturally-occurring elements becoming known by 1900. The properties of the chemical elements are summarized on the periodic table, which organizes the elements by increasing atomic number into rows (""periods"") in which the columns (""groups"") share recurring (""periodic"") physical and chemical properties. Save for unstable radioactive elements with short half-lives, all of the elements are available industrially, most of them in high degrees of purity.