Atomic Theory
... • In 1913, Niels Bohr proposed an improvement to Rutherford’s Model: • Electron’s move in definite orbits around the nucleus, like planets around the sun. ...
... • In 1913, Niels Bohr proposed an improvement to Rutherford’s Model: • Electron’s move in definite orbits around the nucleus, like planets around the sun. ...
black box - Waterford Public Schools
... called cathode rays, would travel from the negative electrode to the positive electrode The path of the cathode rays could be altered by the presence of a magnetic field ...
... called cathode rays, would travel from the negative electrode to the positive electrode The path of the cathode rays could be altered by the presence of a magnetic field ...
Chapter 3
... experiments measured the charge-to-mass ratio of an electron. Robert A. Millikan’s oil drop experiment measured the charge of an electron. With this information, scientists were able to determine the mass of an electron. ...
... experiments measured the charge-to-mass ratio of an electron. Robert A. Millikan’s oil drop experiment measured the charge of an electron. With this information, scientists were able to determine the mass of an electron. ...
The Atom and the Periodic Table
... 2. Identify each element as a metal, nonmetal, or metalloid using the zigzag line as a reference. 3. Identify an element by its chemical symbol. 4. Identify the groups and periods of the periodic table. 5. Describe how chemical properties of elements are similar in the same group. 6. Label each grou ...
... 2. Identify each element as a metal, nonmetal, or metalloid using the zigzag line as a reference. 3. Identify an element by its chemical symbol. 4. Identify the groups and periods of the periodic table. 5. Describe how chemical properties of elements are similar in the same group. 6. Label each grou ...
Step 1 Lesson Plan
... The extremely small size of atoms makes it impossible to count them or determine their individual masses using direct means. The average atomic masses depend on the number and masses of the isotopes of an element. Isotopes are atoms of the same atomic number having different masses due to different ...
... The extremely small size of atoms makes it impossible to count them or determine their individual masses using direct means. The average atomic masses depend on the number and masses of the isotopes of an element. Isotopes are atoms of the same atomic number having different masses due to different ...
Ch 3 Sec 3 Highlighted
... Mass Number: the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an isotope. From the periodic table the Mass Number is the atomic mass rounded to the nearest whole number. SECTION 3-3 OBJECTIVE 3 Given the identity of a nuclide, determine its number of protons, neutrons, and electrons. ...
... Mass Number: the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an isotope. From the periodic table the Mass Number is the atomic mass rounded to the nearest whole number. SECTION 3-3 OBJECTIVE 3 Given the identity of a nuclide, determine its number of protons, neutrons, and electrons. ...
Ch. 4 PPT
... Mass of Atoms (cont.) • The _________________________of an element is the weighted average mass of the isotopes of that element. Weighted average of the isotopes of an element Copper-63, 69.17%, 62.939 a.m.u Copper-65, 30.83%, 64.927 a.m.u ...
... Mass of Atoms (cont.) • The _________________________of an element is the weighted average mass of the isotopes of that element. Weighted average of the isotopes of an element Copper-63, 69.17%, 62.939 a.m.u Copper-65, 30.83%, 64.927 a.m.u ...
C:\Users\Jim\Documents\school stuff\atomic structure.wpd
... It turns out that atoms of the same element do not all have the same mass, thus also must have differing numbers of neutrons. The atoms of an element with the same number of neutrons are said to belong to the same isotope. Most elements have a number of stable isotopes, as well as a number of unstab ...
... It turns out that atoms of the same element do not all have the same mass, thus also must have differing numbers of neutrons. The atoms of an element with the same number of neutrons are said to belong to the same isotope. Most elements have a number of stable isotopes, as well as a number of unstab ...
Atomic Structure and Periodic Trend Review
... Our model of the atom continues to evolve as new discoveries are made. The first atomic model that was based on scientific experiments came from John Dalton. He believed that each element had a smallest subunit which he called the atom. He believed the atom could not be subdivided into smaller parts ...
... Our model of the atom continues to evolve as new discoveries are made. The first atomic model that was based on scientific experiments came from John Dalton. He believed that each element had a smallest subunit which he called the atom. He believed the atom could not be subdivided into smaller parts ...
Atomic Structure and Periodic Trend Review
... Our model of the atom continues to evolve as new discoveries are made. The first atomic model that was based on scientific experiments came from John Dalton. He believed that each element had a smallest subunit which he called the atom. He believed the atom could not be subdivided into smaller parts ...
... Our model of the atom continues to evolve as new discoveries are made. The first atomic model that was based on scientific experiments came from John Dalton. He believed that each element had a smallest subunit which he called the atom. He believed the atom could not be subdivided into smaller parts ...
File
... The three phases of matter (solids, liquids, and gases) have different properties. (3.1kk) A pure substance (element or compound) has a constant composition and constant properties throughout a given sample, and from sample to sample. (3.1r) Elements cannot be broken down by chemical change. (3.1u) ...
... The three phases of matter (solids, liquids, and gases) have different properties. (3.1kk) A pure substance (element or compound) has a constant composition and constant properties throughout a given sample, and from sample to sample. (3.1r) Elements cannot be broken down by chemical change. (3.1u) ...
C. - Taylor County Schools
... • Almost all of the atom's positive charge and almost all of its mass is contained in a dense region in the center of the atom called the nucleus. • Electrons are held within the atom by their attraction to the positively charged nucleus. ...
... • Almost all of the atom's positive charge and almost all of its mass is contained in a dense region in the center of the atom called the nucleus. • Electrons are held within the atom by their attraction to the positively charged nucleus. ...
Ch 30 Nuclear Physics
... The Atomic Mass is measured in unified atomic mass units (u) – basically the weight of a proton or neutron. The 12C atom is used as the standard, and is assigned the Atomic Mass of exactly 12 u. The weighted average mass of all carbon is slightly higher than 12 (12.011) because some is 13C and ...
... The Atomic Mass is measured in unified atomic mass units (u) – basically the weight of a proton or neutron. The 12C atom is used as the standard, and is assigned the Atomic Mass of exactly 12 u. The weighted average mass of all carbon is slightly higher than 12 (12.011) because some is 13C and ...
Early Atomic History
... protons). The atomic number, represented by the letter Z, is linked with the atomic symbol. For example, oxygen is atomic number 8, and any atom containing 8 protons, regardless of the number of neutrons or electrons, is represented by the ...
... protons). The atomic number, represented by the letter Z, is linked with the atomic symbol. For example, oxygen is atomic number 8, and any atom containing 8 protons, regardless of the number of neutrons or electrons, is represented by the ...
Atomic Structure
... John Dalton’s Atomic Theory (1808) 1. Elements are made of indivisible particles called atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are exactly alike; in particular, they have the same mass. 3. Compounds are formed by the joining of atoms of two or more elements in fixed, whole number ratios. e.g., 1:1, 2:1 ...
... John Dalton’s Atomic Theory (1808) 1. Elements are made of indivisible particles called atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are exactly alike; in particular, they have the same mass. 3. Compounds are formed by the joining of atoms of two or more elements in fixed, whole number ratios. e.g., 1:1, 2:1 ...
DAY
... Millions of dollars worth of equipment, a four-mile ring buried in a maze of tangled wire, particles hurtling at one another, and scientists monitoring it all from their computer screens...What's all the commotion about? The answer to this question is simple: particles. Particles are the building bl ...
... Millions of dollars worth of equipment, a four-mile ring buried in a maze of tangled wire, particles hurtling at one another, and scientists monitoring it all from their computer screens...What's all the commotion about? The answer to this question is simple: particles. Particles are the building bl ...
When forming IONS, ONLY (protons/electrons) are gained or lost
... ___________ determine the chemistry of an atom. o Both have ________ number of electrons, therefore both are chemically (alike/different). ...
... ___________ determine the chemistry of an atom. o Both have ________ number of electrons, therefore both are chemically (alike/different). ...
04_Lecture Atoms and Elements
... • Protons and neutrons have similar masses (1 amu), while electrons have a much smaller mass. ...
... • Protons and neutrons have similar masses (1 amu), while electrons have a much smaller mass. ...
04_Lecture Atoms and Elements
... • Protons and neutrons have similar masses (1 amu), while electrons have a much smaller mass. © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... • Protons and neutrons have similar masses (1 amu), while electrons have a much smaller mass. © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Atoms
... Atoms of an element always have the same Atomic number, but not always the same mass number How can that be? If protons change…you change the element. However, the number of electrons can change and the number of neutrons can change. If neutrons change…then an isotope is formed. ...
... Atoms of an element always have the same Atomic number, but not always the same mass number How can that be? If protons change…you change the element. However, the number of electrons can change and the number of neutrons can change. If neutrons change…then an isotope is formed. ...
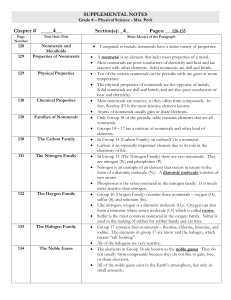
element connections
... • This is the most reactive, (but non-radioactive), member of the alkali metals. (cesium) • This element has 44 protons. (ruthenium) • The Latin name for this element is natrium. (sodium) • The average weight of an atom of this element is about 190. (osmium) • This is the lightest member of the true ...
... • This is the most reactive, (but non-radioactive), member of the alkali metals. (cesium) • This element has 44 protons. (ruthenium) • The Latin name for this element is natrium. (sodium) • The average weight of an atom of this element is about 190. (osmium) • This is the lightest member of the true ...
Chapter 4
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory 2) Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties. 3) Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. 4) Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to ...
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory 2) Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties. 3) Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. 4) Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to ...
Name - TeacherWeb
... The elements in Group 18 are known as the noble gases. They do not usually form compounds because they do not like to gain, lose, or share electrons. All of the noble gases exist in the Earth’s atmosphere, but only in small amounts. ...
... The elements in Group 18 are known as the noble gases. They do not usually form compounds because they do not like to gain, lose, or share electrons. All of the noble gases exist in the Earth’s atmosphere, but only in small amounts. ...
Chemical element
A chemical element (or element) is a chemical substance consisting of atoms having the same number of protons in their atomic nuclei (i.e. the same atomic number, Z). There are 118 elements that have been identified, of which the first 94 occur naturally on Earth with the remaining 24 being synthetic elements. There are 80 elements that have at least one stable isotope and 38 that have exclusively radioactive isotopes, which decay over time into other elements. Iron is the most abundant element (by mass) making up the Earth, while oxygen is the most common element in the crust of the earth.Chemical elements constitute approximately 15% of the matter in the universe: the remainder is dark matter, the composition of it is unknown, but it is not composed of chemical elements.The two lightest elements, hydrogen and helium were mostly formed in the Big Bang and are the most common elements in the universe. The next three elements (lithium, beryllium and boron) were formed mostly by cosmic ray spallation, and are thus more rare than those that follow. Formation of elements with from six to twenty six protons occurred and continues to occur in main sequence stars via stellar nucleosynthesis. The high abundance of oxygen, silicon, and iron on Earth reflects their common production in such stars. Elements with greater than twenty six protons are formed by supernova nucleosynthesis in supernovae, which, when they explode, blast these elements far into space as planetary nebulae, where they may become incorporated into planets when they are formed.When different elements are chemically combined, with the atoms held together by chemical bonds, they form chemical compounds. Only a minority of elements are found uncombined as relatively pure minerals. Among the more common of such ""native elements"" are copper, silver, gold, carbon (as coal, graphite, or diamonds), and sulfur. All but a few of the most inert elements, such as noble gases and noble metals, are usually found on Earth in chemically combined form, as chemical compounds. While about 32 of the chemical elements occur on Earth in native uncombined forms, most of these occur as mixtures. For example, atmospheric air is primarily a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, and argon, and native solid elements occur in alloys, such as that of iron and nickel.The history of the discovery and use of the elements began with primitive human societies that found native elements like carbon, sulfur, copper and gold. Later civilizations extracted elemental copper, tin, lead and iron from their ores by smelting, using charcoal. Alchemists and chemists subsequently identified many more, with almost all of the naturally-occurring elements becoming known by 1900. The properties of the chemical elements are summarized on the periodic table, which organizes the elements by increasing atomic number into rows (""periods"") in which the columns (""groups"") share recurring (""periodic"") physical and chemical properties. Save for unstable radioactive elements with short half-lives, all of the elements are available industrially, most of them in high degrees of purity.