Atoms and the Periodic Table
... Isotopes & Avg. Atomic Mass • An isotope is an atom that has the ...
... Isotopes & Avg. Atomic Mass • An isotope is an atom that has the ...
Ch. 07 Notes ch7notes
... of particles is the same as the number of atoms of carbon in exactly 12 grams of carbon-12. • The mole is a counting unit used to count out a given number of particles. • Avogadro’s number- 6.022 x 1023, the number of atoms or molecules in ...
... of particles is the same as the number of atoms of carbon in exactly 12 grams of carbon-12. • The mole is a counting unit used to count out a given number of particles. • Avogadro’s number- 6.022 x 1023, the number of atoms or molecules in ...
atoms
... In a nuclear equation, the element symbols represent only the nuclei of atoms Rather than the entire neutral atoms, so the subscript represents only the number of nuclear charges (protons). An emitted electron is written as 0-1e , where the superscript o indicates that the mass of an electron is ess ...
... In a nuclear equation, the element symbols represent only the nuclei of atoms Rather than the entire neutral atoms, so the subscript represents only the number of nuclear charges (protons). An emitted electron is written as 0-1e , where the superscript o indicates that the mass of an electron is ess ...
Reactions and Equations
... How to Remember the Diatomic Elements • The elements ending with "-gen" including halogens form diatomic molecules. An easy-to-remember mnemonic for the diatomic elements is: Have No Fear Of Ice Cold Beverages ...
... How to Remember the Diatomic Elements • The elements ending with "-gen" including halogens form diatomic molecules. An easy-to-remember mnemonic for the diatomic elements is: Have No Fear Of Ice Cold Beverages ...
Unit 3 Notes, Practice, and Review
... 6. Because neutral atoms contain the same number of negative elections and positive protons, so they cancel out. 7. The number of protons in that atom. 8. a. 15, b. 42, c. 13, d. 48, e. 24, f. 82 ...
... 6. Because neutral atoms contain the same number of negative elections and positive protons, so they cancel out. 7. The number of protons in that atom. 8. a. 15, b. 42, c. 13, d. 48, e. 24, f. 82 ...
Catalyst (4 min) - Schurz High School
... Why do atoms have a neutral charge overall even though they are made of charged particles? #protons = # electrons Protons (+) and electrons (-) have opposite charges The charges cancel out! ...
... Why do atoms have a neutral charge overall even though they are made of charged particles? #protons = # electrons Protons (+) and electrons (-) have opposite charges The charges cancel out! ...
AP CHEMISTRY SUMMER ASSIGNMENT AP Chemistry is a
... compounds. The cations and anions switch partners. If an insoluble precipitate forms, the reaction occurs otherwise the result is an aqueous mixture of ions. In double replacement reactions, two compounds form two new product compounds. AgNO3(aq) + NaCl(aq) NaNO3(aq) + AgCl(s) Special case of a do ...
... compounds. The cations and anions switch partners. If an insoluble precipitate forms, the reaction occurs otherwise the result is an aqueous mixture of ions. In double replacement reactions, two compounds form two new product compounds. AgNO3(aq) + NaCl(aq) NaNO3(aq) + AgCl(s) Special case of a do ...
Meeting no
... P is the absolute pressure V is the volume of the vessel n is the number of moles of gas R is the ideal gas constant T is the absolute temperature Multiple Proportions When elements combine, they do so in the ratio of small whole numbers. The mass of one element combines with a fixed mass of another ...
... P is the absolute pressure V is the volume of the vessel n is the number of moles of gas R is the ideal gas constant T is the absolute temperature Multiple Proportions When elements combine, they do so in the ratio of small whole numbers. The mass of one element combines with a fixed mass of another ...
Atoms, Elements, and Compounds
... What are isotopes? In addition to its atomic number, every atom can also be described by its mass number: mass number = number of protons + number of neutrons Atoms of the same element always have the same number of protons, but can have different numbers of neutrons. These different forms of the sa ...
... What are isotopes? In addition to its atomic number, every atom can also be described by its mass number: mass number = number of protons + number of neutrons Atoms of the same element always have the same number of protons, but can have different numbers of neutrons. These different forms of the sa ...
PowerPoint Lecture Chapter 17-20
... A. compound– substance made of atoms of different elements in a fixed proportion 1. chemical formula– tells proportions of each kind of atom in compound 2. A compound may or may not be made of molecules ...
... A. compound– substance made of atoms of different elements in a fixed proportion 1. chemical formula– tells proportions of each kind of atom in compound 2. A compound may or may not be made of molecules ...
H 2 and H 2 + O 2 g H 2 O and H 2 O Hydrogen + Oxygen g Water
... Complete the following practical, ensuring you identify the mass of reactants and products (remember, we want to see if there was any change in mass)! Measure out 50ml of hydrochloric acid (HCl) into a beaker (find its mass) Measure out 50ml of copper sulfate (CuSO4) into a beaker (find its ma ...
... Complete the following practical, ensuring you identify the mass of reactants and products (remember, we want to see if there was any change in mass)! Measure out 50ml of hydrochloric acid (HCl) into a beaker (find its mass) Measure out 50ml of copper sulfate (CuSO4) into a beaker (find its ma ...
THE ATOM - McMaster Physics and Astronomy
... parts: First, there is a cloud of electrons (very light, negatively charged particles filling most of the volume), and second, there is a central nucleus, which is made up of a heavy ball of protons and neutrons. The proton has a positive electric charge equal and opposite to the electron, while the ...
... parts: First, there is a cloud of electrons (very light, negatively charged particles filling most of the volume), and second, there is a central nucleus, which is made up of a heavy ball of protons and neutrons. The proton has a positive electric charge equal and opposite to the electron, while the ...
Slide 1
... • Scaled-down models allow you to see either something too large to see all at once, or something that has not been built yet. • Scaled-up models are often used to visualize things that are too small to see. ...
... • Scaled-down models allow you to see either something too large to see all at once, or something that has not been built yet. • Scaled-up models are often used to visualize things that are too small to see. ...
Nuclear Chemistry - Solon City Schools
... 14N + 1 n ---> 14C + 1H o The C-14 is oxidized to CO2, which circulates through the biosphere. When a plant dies, the C-14 is not replenished. But the C-14 continues to decay with t1/2 = 5730 years. Activity of a sample can be used to date the sample. ...
... 14N + 1 n ---> 14C + 1H o The C-14 is oxidized to CO2, which circulates through the biosphere. When a plant dies, the C-14 is not replenished. But the C-14 continues to decay with t1/2 = 5730 years. Activity of a sample can be used to date the sample. ...
Teacher quality grant
... • At your groups, decide who is your ‘model’ and dress them up in a trash bag. • You will be assigned an element, decide how many valence electrons it has and inflate and attach the correct number of balloons • Determine your ion, and create a tag to wear ...
... • At your groups, decide who is your ‘model’ and dress them up in a trash bag. • You will be assigned an element, decide how many valence electrons it has and inflate and attach the correct number of balloons • Determine your ion, and create a tag to wear ...
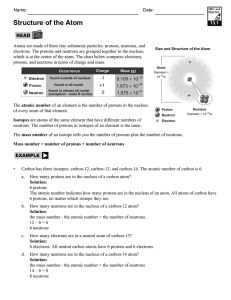
The Atom
... Describe the size of an atom. Name the parts of an atom. Describe the relationship between numbers of protons and neutrons and atomic number. State how isotopes differ. Calculate atomic masses. Describe the forces within an atom. ...
... Describe the size of an atom. Name the parts of an atom. Describe the relationship between numbers of protons and neutrons and atomic number. State how isotopes differ. Calculate atomic masses. Describe the forces within an atom. ...
Chapter 6 - Section 1-The Chemical Context of Life
... Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
... Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
Study Guide-Chemistry Of Life
... 10. Are the CHNOPS elements stable and unreactive? What are they and why? Why is this important for living things? ...
... 10. Are the CHNOPS elements stable and unreactive? What are they and why? Why is this important for living things? ...
3lou3atch - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
... What are some properties of metals? good conductors (poor insulators) of heat and electricity; ductile, malleable, lustrous, most are solids at room temp. nonmetals = second largest region right side What are some properties of nonmetals? good insulators (poor conductors) of heat and electricity, mo ...
... What are some properties of metals? good conductors (poor insulators) of heat and electricity; ductile, malleable, lustrous, most are solids at room temp. nonmetals = second largest region right side What are some properties of nonmetals? good insulators (poor conductors) of heat and electricity, mo ...
Teacher quality grant - Gulf Coast State College
... • At your groups, decide who is your ‘model’ and dress them up in a trash bag. • You will be assigned an element, decide how many valence electrons it has and inflate and attach the correct number of balloons • Determine your ion, and create a tag to wear ...
... • At your groups, decide who is your ‘model’ and dress them up in a trash bag. • You will be assigned an element, decide how many valence electrons it has and inflate and attach the correct number of balloons • Determine your ion, and create a tag to wear ...
Unit 3 PowerPoint
... • Noble Gases – stable, non-reactive non-metals in Family 8A • Periodic Trends – repeating patterns of chemical and physical properties of elements within the periodic table that correspond to the Law of Periodicity • Reactivity – chemical property describing the ability and speed with which element ...
... • Noble Gases – stable, non-reactive non-metals in Family 8A • Periodic Trends – repeating patterns of chemical and physical properties of elements within the periodic table that correspond to the Law of Periodicity • Reactivity – chemical property describing the ability and speed with which element ...
Chemical element
A chemical element (or element) is a chemical substance consisting of atoms having the same number of protons in their atomic nuclei (i.e. the same atomic number, Z). There are 118 elements that have been identified, of which the first 94 occur naturally on Earth with the remaining 24 being synthetic elements. There are 80 elements that have at least one stable isotope and 38 that have exclusively radioactive isotopes, which decay over time into other elements. Iron is the most abundant element (by mass) making up the Earth, while oxygen is the most common element in the crust of the earth.Chemical elements constitute approximately 15% of the matter in the universe: the remainder is dark matter, the composition of it is unknown, but it is not composed of chemical elements.The two lightest elements, hydrogen and helium were mostly formed in the Big Bang and are the most common elements in the universe. The next three elements (lithium, beryllium and boron) were formed mostly by cosmic ray spallation, and are thus more rare than those that follow. Formation of elements with from six to twenty six protons occurred and continues to occur in main sequence stars via stellar nucleosynthesis. The high abundance of oxygen, silicon, and iron on Earth reflects their common production in such stars. Elements with greater than twenty six protons are formed by supernova nucleosynthesis in supernovae, which, when they explode, blast these elements far into space as planetary nebulae, where they may become incorporated into planets when they are formed.When different elements are chemically combined, with the atoms held together by chemical bonds, they form chemical compounds. Only a minority of elements are found uncombined as relatively pure minerals. Among the more common of such ""native elements"" are copper, silver, gold, carbon (as coal, graphite, or diamonds), and sulfur. All but a few of the most inert elements, such as noble gases and noble metals, are usually found on Earth in chemically combined form, as chemical compounds. While about 32 of the chemical elements occur on Earth in native uncombined forms, most of these occur as mixtures. For example, atmospheric air is primarily a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, and argon, and native solid elements occur in alloys, such as that of iron and nickel.The history of the discovery and use of the elements began with primitive human societies that found native elements like carbon, sulfur, copper and gold. Later civilizations extracted elemental copper, tin, lead and iron from their ores by smelting, using charcoal. Alchemists and chemists subsequently identified many more, with almost all of the naturally-occurring elements becoming known by 1900. The properties of the chemical elements are summarized on the periodic table, which organizes the elements by increasing atomic number into rows (""periods"") in which the columns (""groups"") share recurring (""periodic"") physical and chemical properties. Save for unstable radioactive elements with short half-lives, all of the elements are available industrially, most of them in high degrees of purity.