The Atoms Family
... sound, or light (forms of energy) Matter generally exists in three different forms: Solids, Liquids and Gases (there are two others) We’ll talk about this later! ...
... sound, or light (forms of energy) Matter generally exists in three different forms: Solids, Liquids and Gases (there are two others) We’ll talk about this later! ...
2-1 The Nature of Matter
... that consists entirely of one type of atom. Elements are represented by a one- or two-letter symbol. ...
... that consists entirely of one type of atom. Elements are represented by a one- or two-letter symbol. ...
Mass # = Atomic # + # Neutrons
... John Dalton proposed a new atomic theory based on the three Laws we have been discussing and the ideas of Democritus. See page 64 for a discussion of Daltons ideas. Dalton’s Atomic Theory (1808 A.D.)-very similar to ideas of Democritus (~400 B.C.) ...
... John Dalton proposed a new atomic theory based on the three Laws we have been discussing and the ideas of Democritus. See page 64 for a discussion of Daltons ideas. Dalton’s Atomic Theory (1808 A.D.)-very similar to ideas of Democritus (~400 B.C.) ...
Understanding the Atom - Verona Public Schools
... believed that all matter is made of fire, water, air, and earth. • Because Aristotle was so influential, his ideas were accepted and Democritus’s ideas about atoms were not studied again for more than 2,000 years. ...
... believed that all matter is made of fire, water, air, and earth. • Because Aristotle was so influential, his ideas were accepted and Democritus’s ideas about atoms were not studied again for more than 2,000 years. ...
ATOMS AND MOLECULES
... oxygen atom is 16/12 = 4/3 times as heavy as an atom of carbon-12. This also means that the mass of one atom of oxygen is 16 times greater than 1/12 the mass of one atom of carbon-12. Gram Atomic Mass When the mass of an atom taken in grams is numerically equal to its atomic mass it is called gram a ...
... oxygen atom is 16/12 = 4/3 times as heavy as an atom of carbon-12. This also means that the mass of one atom of oxygen is 16 times greater than 1/12 the mass of one atom of carbon-12. Gram Atomic Mass When the mass of an atom taken in grams is numerically equal to its atomic mass it is called gram a ...
Period:______ Table Number
... 56. On the periodic table of elements those elements which have an atomic number of ____ (Hydrogen) to ________ (Uranium) are naturally occuring elements which can be found to exist somewhere in the earth’s land, water, or air. 57. On the periodic table of elements those elements which have an atomi ...
... 56. On the periodic table of elements those elements which have an atomic number of ____ (Hydrogen) to ________ (Uranium) are naturally occuring elements which can be found to exist somewhere in the earth’s land, water, or air. 57. On the periodic table of elements those elements which have an atomi ...
Atomic Structure Protons, neutrons and electrons
... The atom is very simple, it consists of a positively charged nucleus with negatively charged electrons whizzing all around it. The atom is held together by the electrostatic attraction between t ...
... The atom is very simple, it consists of a positively charged nucleus with negatively charged electrons whizzing all around it. The atom is held together by the electrostatic attraction between t ...
Question, hints, and answers. Look at hints if you need help. Look at
... between N and H. But the N "wants" the electrons more than the H does, so it pulls them closer to itself. You end up with a little more than half the negative charge from the bond on the N, and a little less than half on the H. That means N has a partial negative charge and H has a partial positive ...
... between N and H. But the N "wants" the electrons more than the H does, so it pulls them closer to itself. You end up with a little more than half the negative charge from the bond on the N, and a little less than half on the H. That means N has a partial negative charge and H has a partial positive ...
Class Notes KEY
... 1. Which elements have outer shells that are full of electrons? Where are they located on the periodic table? 2. Which elements have only 1 electron in their outer shell? Where are they located on the periodic table? 3. What do you notice about the number of valence electrons (electrons in the outer ...
... 1. Which elements have outer shells that are full of electrons? Where are they located on the periodic table? 2. Which elements have only 1 electron in their outer shell? Where are they located on the periodic table? 3. What do you notice about the number of valence electrons (electrons in the outer ...
CHAPTER 1
... Explaining what matter is involves finding properties that all matter has in common. That may seem difficult, given that matter takes so many different forms. For the moment, just consider one example of matter—a rock. The first thing you might notice is that the rock takes up space. In other words, ...
... Explaining what matter is involves finding properties that all matter has in common. That may seem difficult, given that matter takes so many different forms. For the moment, just consider one example of matter—a rock. The first thing you might notice is that the rock takes up space. In other words, ...
Atomic Structure Practice Test
... ____ 10. The smallest unit of an element that can exist either alone or in combination with other such particles of the same or different elements is the a. electron. b. proton. c. neutron. d. atom. ____ 11. The atomic number of oxygen, 8, indicates that there are eight a. protons in the nucleus. c. ...
... ____ 10. The smallest unit of an element that can exist either alone or in combination with other such particles of the same or different elements is the a. electron. b. proton. c. neutron. d. atom. ____ 11. The atomic number of oxygen, 8, indicates that there are eight a. protons in the nucleus. c. ...
Atomic Theory and Isotopes powerpoint
... Law of Multiple Proportions Mass of oxygen that combines with 1 g of Carbon ...
... Law of Multiple Proportions Mass of oxygen that combines with 1 g of Carbon ...
Chapter 2 PowerPoint
... Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
... Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
Ch.1-Matter and Change
... characteristic properties. Every sample of a given pure substance has exactly the same composition. Water is always 11.2% hydrogen and 88.8% oxygen by mass. ...
... characteristic properties. Every sample of a given pure substance has exactly the same composition. Water is always 11.2% hydrogen and 88.8% oxygen by mass. ...
Ch_6 L2 Packet - Mater Academy Lakes High School
... Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. ...
... Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. ...
Writing Chemical Formulas
... Use the oxidation number (without the plus or minus) for each half as the subscript for the other half. Do not write a subscript of 1. Reduce the subscripts, if needed. After doing this, be sure the subscripts will not reduce. If both subscripts are divisible by the same number, they must be reduced ...
... Use the oxidation number (without the plus or minus) for each half as the subscript for the other half. Do not write a subscript of 1. Reduce the subscripts, if needed. After doing this, be sure the subscripts will not reduce. If both subscripts are divisible by the same number, they must be reduced ...
CHAPTER 11 Introduction to Atoms
... d. All of the above 8. How many protons does an atom with an atomic number of 23 and a mass number of 51 have? a. 23 c. 51 b. 28 d. 74 9. An atom has no overall charge if it contains equal numbers of a. electrons and protons. b. neutrons and protons. c. neutrons and electrons. d. None of the above ...
... d. All of the above 8. How many protons does an atom with an atomic number of 23 and a mass number of 51 have? a. 23 c. 51 b. 28 d. 74 9. An atom has no overall charge if it contains equal numbers of a. electrons and protons. b. neutrons and protons. c. neutrons and electrons. d. None of the above ...
1st block atomic structure ppts.
... Calculating Atomic Mass of an Element Atomic mass: • It is an average mass calculated from all the isotopes of a particular element. • The average mass is weighted because there is NOT an equal amount of each isotope in a sample. • How do you calculate a weighted average mass? 1. For each isotope, ...
... Calculating Atomic Mass of an Element Atomic mass: • It is an average mass calculated from all the isotopes of a particular element. • The average mass is weighted because there is NOT an equal amount of each isotope in a sample. • How do you calculate a weighted average mass? 1. For each isotope, ...
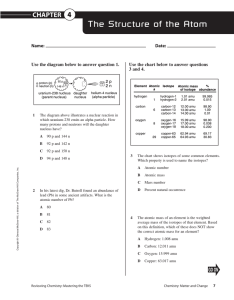
Reviewing Chemistry: Mastering the TEKS - Student
... The diagram above shows the results of Rutherford’s experiment in which he used a radioactive source to “shoot” alpha particles at a thin sheet of gold foil. Based on these results, what were Rutherford’s ...
... The diagram above shows the results of Rutherford’s experiment in which he used a radioactive source to “shoot” alpha particles at a thin sheet of gold foil. Based on these results, what were Rutherford’s ...
Classification of Matter
... Matter can be a gas, a liquid, or a solid. These are the three states of matter. Gases take the shape and volume of their container. Gases can be compressed to form liquids. Liquids take the shape of their container, but they do have their own volume. Solids are rigid and have a definite shape and v ...
... Matter can be a gas, a liquid, or a solid. These are the three states of matter. Gases take the shape and volume of their container. Gases can be compressed to form liquids. Liquids take the shape of their container, but they do have their own volume. Solids are rigid and have a definite shape and v ...
Chapter 3 Atoms and Elements
... In Dalton's atomic theory, atoms: • are tiny particles of matter • of an element are similar to each other and different from other elements • of two or more different elements combine to form compounds • are rearranged to form new combinations in a chemical reaction ...
... In Dalton's atomic theory, atoms: • are tiny particles of matter • of an element are similar to each other and different from other elements • of two or more different elements combine to form compounds • are rearranged to form new combinations in a chemical reaction ...
GCSE Chemistry Textbook sample
... From understanding and preparing to teach new specifications, through to developing subject expertise and moving leadership, AQA has a training offering for you. Continued professional development training is provided to over 30,000 teachers each year, either through face to face, online or in-schoo ...
... From understanding and preparing to teach new specifications, through to developing subject expertise and moving leadership, AQA has a training offering for you. Continued professional development training is provided to over 30,000 teachers each year, either through face to face, online or in-schoo ...
4.2 Discovering Parts of the Atom
... • Rutherford knew the mass of a proton, but could not account for the total mass of an atom. • Rutherford’s theory was later confirmed when the existence of the neutron—a neutral atomic particle with a mass similar to a proton but without a charge—was proved. ...
... • Rutherford knew the mass of a proton, but could not account for the total mass of an atom. • Rutherford’s theory was later confirmed when the existence of the neutron—a neutral atomic particle with a mass similar to a proton but without a charge—was proved. ...
File
... • Rutherford knew the mass of a proton, but could not account for the total mass of an atom. • Rutherford’s theory was later confirmed when the existence of the neutron—a neutral atomic particle with a mass similar to a proton but without a charge—was proved. ...
... • Rutherford knew the mass of a proton, but could not account for the total mass of an atom. • Rutherford’s theory was later confirmed when the existence of the neutron—a neutral atomic particle with a mass similar to a proton but without a charge—was proved. ...
Chemical element
A chemical element (or element) is a chemical substance consisting of atoms having the same number of protons in their atomic nuclei (i.e. the same atomic number, Z). There are 118 elements that have been identified, of which the first 94 occur naturally on Earth with the remaining 24 being synthetic elements. There are 80 elements that have at least one stable isotope and 38 that have exclusively radioactive isotopes, which decay over time into other elements. Iron is the most abundant element (by mass) making up the Earth, while oxygen is the most common element in the crust of the earth.Chemical elements constitute approximately 15% of the matter in the universe: the remainder is dark matter, the composition of it is unknown, but it is not composed of chemical elements.The two lightest elements, hydrogen and helium were mostly formed in the Big Bang and are the most common elements in the universe. The next three elements (lithium, beryllium and boron) were formed mostly by cosmic ray spallation, and are thus more rare than those that follow. Formation of elements with from six to twenty six protons occurred and continues to occur in main sequence stars via stellar nucleosynthesis. The high abundance of oxygen, silicon, and iron on Earth reflects their common production in such stars. Elements with greater than twenty six protons are formed by supernova nucleosynthesis in supernovae, which, when they explode, blast these elements far into space as planetary nebulae, where they may become incorporated into planets when they are formed.When different elements are chemically combined, with the atoms held together by chemical bonds, they form chemical compounds. Only a minority of elements are found uncombined as relatively pure minerals. Among the more common of such ""native elements"" are copper, silver, gold, carbon (as coal, graphite, or diamonds), and sulfur. All but a few of the most inert elements, such as noble gases and noble metals, are usually found on Earth in chemically combined form, as chemical compounds. While about 32 of the chemical elements occur on Earth in native uncombined forms, most of these occur as mixtures. For example, atmospheric air is primarily a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, and argon, and native solid elements occur in alloys, such as that of iron and nickel.The history of the discovery and use of the elements began with primitive human societies that found native elements like carbon, sulfur, copper and gold. Later civilizations extracted elemental copper, tin, lead and iron from their ores by smelting, using charcoal. Alchemists and chemists subsequently identified many more, with almost all of the naturally-occurring elements becoming known by 1900. The properties of the chemical elements are summarized on the periodic table, which organizes the elements by increasing atomic number into rows (""periods"") in which the columns (""groups"") share recurring (""periodic"") physical and chemical properties. Save for unstable radioactive elements with short half-lives, all of the elements are available industrially, most of them in high degrees of purity.