Atomic Structure Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice
... d. either greater than or less than ____ 12. According to Dalton's atomic theory, atoms a. are destroyed in chemical reactions. b. can be divided. c. of each element are identical in size, mass, and other properties. d. of different elements cannot combine. ____ 13. Which of the following statements ...
... d. either greater than or less than ____ 12. According to Dalton's atomic theory, atoms a. are destroyed in chemical reactions. b. can be divided. c. of each element are identical in size, mass, and other properties. d. of different elements cannot combine. ____ 13. Which of the following statements ...
Atomic Structure Practice Test
... d. either greater than or less than ____ 12. According to Dalton's atomic theory, atoms a. are destroyed in chemical reactions. b. can be divided. c. of each element are identical in size, mass, and other properties. d. of different elements cannot combine. ____ 13. Which of the following statements ...
... d. either greater than or less than ____ 12. According to Dalton's atomic theory, atoms a. are destroyed in chemical reactions. b. can be divided. c. of each element are identical in size, mass, and other properties. d. of different elements cannot combine. ____ 13. Which of the following statements ...
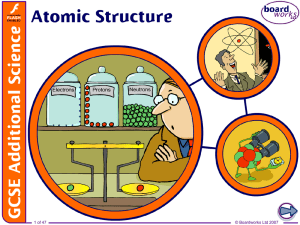
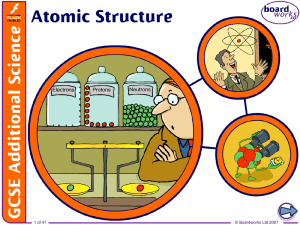
1. Atomic Structure
... positively charged because of the protons dense – it contains nearly all the mass of the atom in a tiny space. Electrons are: very small and light, and negatively charged able to be lost or gained in chemical reactions found thinly spread around the outside of the nucleus, orbiting in laye ...
... positively charged because of the protons dense – it contains nearly all the mass of the atom in a tiny space. Electrons are: very small and light, and negatively charged able to be lost or gained in chemical reactions found thinly spread around the outside of the nucleus, orbiting in laye ...
File
... 20. Element whose atoms lose electrons in chemical reactions to become positive ions. 21. Groups 3-12 on the periodic table. 22. Scientist who performed the gold foil experiment, and concluded that an atom must be composed of mostly empty space with a small, dense, positively-charged nucleus. 23. An ...
... 20. Element whose atoms lose electrons in chemical reactions to become positive ions. 21. Groups 3-12 on the periodic table. 22. Scientist who performed the gold foil experiment, and concluded that an atom must be composed of mostly empty space with a small, dense, positively-charged nucleus. 23. An ...
Electrons - biospaces
... • Matter is anything that takes up space and has mass • Matter is made up of elements • An element is a substance that cannot be broken down to other substances by chemical reactions • A compound is a substance consisting of two or more elements in a fixed ratio • A compound has characteristics diff ...
... • Matter is anything that takes up space and has mass • Matter is made up of elements • An element is a substance that cannot be broken down to other substances by chemical reactions • A compound is a substance consisting of two or more elements in a fixed ratio • A compound has characteristics diff ...
Click here to Ch 3.2_ Atoms_Structure
... • A proton has a positive charge equal in magnitude to the negative charge of an electron. • Atoms are electrically neutral because they contain equal numbers of protons and electrons. • A neutron is electrically neutral. ...
... • A proton has a positive charge equal in magnitude to the negative charge of an electron. • Atoms are electrically neutral because they contain equal numbers of protons and electrons. • A neutron is electrically neutral. ...
Slide 1
... number of protons in each atom of a particular element. ☺The atomic number _________ the element! ...
... number of protons in each atom of a particular element. ☺The atomic number _________ the element! ...
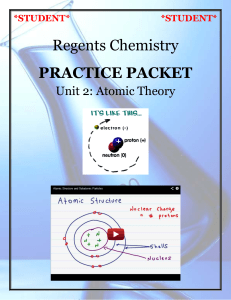
Practice Packet
... the nucleus in welldefined paths called orbits (like planets in a solar system) ...
... the nucleus in welldefined paths called orbits (like planets in a solar system) ...
Energy and Matter in Chemical Change Science 10
... • Have properties of metals and non-metals • Eight metalloids are: B, Si, Ge, As, Sb, Te, Po At border the staircase line of the periodic table • Important in semi-conductor industry ...
... • Have properties of metals and non-metals • Eight metalloids are: B, Si, Ge, As, Sb, Te, Po At border the staircase line of the periodic table • Important in semi-conductor industry ...
2.1 The Atomic Theory of Matter: The Early History
... Similar results with other substances led to the formulation of the Law of Definite Proportions: Compounds always contain elements in certain definite proportions by mass. Dalton's Atomic Theory In 1803, John Dalton published the first modern atomic theory to explain the unique identity of elements, ...
... Similar results with other substances led to the formulation of the Law of Definite Proportions: Compounds always contain elements in certain definite proportions by mass. Dalton's Atomic Theory In 1803, John Dalton published the first modern atomic theory to explain the unique identity of elements, ...
Atomic structure
... which was only a few atoms thick. they found that although most of them passed through. About 1 in 10,000 hit ...
... which was only a few atoms thick. they found that although most of them passed through. About 1 in 10,000 hit ...
Atomic Structure Note Packet
... 2) SUBATOMIC PARTICLES OF AN ATOM a) __________________________________________= a particle smaller than an atom • Ex: proton, neutron, electron b) An atom is composed of subatomic particles including protons, neutrons, and electrons (plus scientists have determined that protons and neutrons have th ...
... 2) SUBATOMIC PARTICLES OF AN ATOM a) __________________________________________= a particle smaller than an atom • Ex: proton, neutron, electron b) An atom is composed of subatomic particles including protons, neutrons, and electrons (plus scientists have determined that protons and neutrons have th ...
wahideh chemistry eportfolio hw
... compounds. Sodium metal itself has relatively few uses. It reacts with other substances easily, sometimes explosively. However, many sodium compounds have a variety of uses in industry, medicine, and everyday life. Physical Properties: Sodium is a silvery-white metal with a waxy appearance. It is so ...
... compounds. Sodium metal itself has relatively few uses. It reacts with other substances easily, sometimes explosively. However, many sodium compounds have a variety of uses in industry, medicine, and everyday life. Physical Properties: Sodium is a silvery-white metal with a waxy appearance. It is so ...
Intro to Nuclear Physics (Science 10 Review... Yes I know...)
... AP Physics – Nuclear Physics – the intersection of Physics and Chemistry Nuclear physics takes in a lot of territory and the range of things it effects is enormous – from saving the lives of cancer victims to its use in weapons of mass destruction. There’s a lot to love and hate in the nuke world. R ...
... AP Physics – Nuclear Physics – the intersection of Physics and Chemistry Nuclear physics takes in a lot of territory and the range of things it effects is enormous – from saving the lives of cancer victims to its use in weapons of mass destruction. There’s a lot to love and hate in the nuke world. R ...
Unit #3: ATOMIC STRUCTURE - Miss Virga`s Chemistry Class
... (1) They are positive subatomic particles and are found in the nucleus. (2) They are positive subatomic particles and are found surrounding the nucleus. (3) They are negative subatomic particles and are found in the nucleus. (4) They are negative subatomic particles and are found surrounding the nuc ...
... (1) They are positive subatomic particles and are found in the nucleus. (2) They are positive subatomic particles and are found surrounding the nucleus. (3) They are negative subatomic particles and are found in the nucleus. (4) They are negative subatomic particles and are found surrounding the nuc ...
Simple View of Atomic Structure - Chemwiki
... The atomic number is the number of protons (9); the mass number counts protons + neutrons (19). If there are 9 protons, there must be 10 neutrons adding up to a total of 19 nucleons in the atom. The atomic number is tied to the position of the element in the periodic table; the number of protons the ...
... The atomic number is the number of protons (9); the mass number counts protons + neutrons (19). If there are 9 protons, there must be 10 neutrons adding up to a total of 19 nucleons in the atom. The atomic number is tied to the position of the element in the periodic table; the number of protons the ...
Study Guide –Chapter 4 Atomic Theory and The Atom
... Read the words in the box. Read the sentences. Fill in each blank with the word or phrase that best completes the sentence. ...
... Read the words in the box. Read the sentences. Fill in each blank with the word or phrase that best completes the sentence. ...
Powerpoint covering atomic structure and isotopes
... positively charged because of the protons dense – it contains nearly all the mass of the atom in a tiny space. Electrons are: very small and light, and negatively charged able to be lost or gained in chemical reactions found thinly spread around the outside of the nucleus, orbiting in laye ...
... positively charged because of the protons dense – it contains nearly all the mass of the atom in a tiny space. Electrons are: very small and light, and negatively charged able to be lost or gained in chemical reactions found thinly spread around the outside of the nucleus, orbiting in laye ...
Chapter 7. Atomic Structure - The University of New Mexico
... 1.6021773 x 10−19 C (SI charge units, or Coulombs), equal to 1.5189073 x 10−14 (Jm)1/2 . At still lower temperatures (such as that of planets), atoms combine to form stable collections called molecules. Molecules, in turn, accumulate into ponderable amounts of matter. In an atom, the protons and neu ...
... 1.6021773 x 10−19 C (SI charge units, or Coulombs), equal to 1.5189073 x 10−14 (Jm)1/2 . At still lower temperatures (such as that of planets), atoms combine to form stable collections called molecules. Molecules, in turn, accumulate into ponderable amounts of matter. In an atom, the protons and neu ...
Atomic Structure
... Below you will practice figuring out the different protons, electrons, and neutrons for the table. I have left some open to help you out, but once you have an answer click on the cell shade to reveal the answers. If you need the periodic table click on the animal below to go to the periodic table. ...
... Below you will practice figuring out the different protons, electrons, and neutrons for the table. I have left some open to help you out, but once you have an answer click on the cell shade to reveal the answers. If you need the periodic table click on the animal below to go to the periodic table. ...
Lectures on Chapter 2, Part 1 Powerpoint 97 Document
... chemical properties. An element consists of only one type of atom. It cannot be broken down into any simpler substances by physical or chemical means. Molecule - Is a structure that is consisting of two or more atoms that are chemically bound together and thus behaves as an independent unit. Compoun ...
... chemical properties. An element consists of only one type of atom. It cannot be broken down into any simpler substances by physical or chemical means. Molecule - Is a structure that is consisting of two or more atoms that are chemically bound together and thus behaves as an independent unit. Compoun ...
Atoms, Molecules and Ions Chapter 2
... You should be able to … • understand the concept of the atom. • differentiate elements according to mass number. • use the periodic table to determine the number of protons, electrons and neutrons an element has. • explain what an isotope is. • calculate the average atomic mass of an element. • ide ...
... You should be able to … • understand the concept of the atom. • differentiate elements according to mass number. • use the periodic table to determine the number of protons, electrons and neutrons an element has. • explain what an isotope is. • calculate the average atomic mass of an element. • ide ...
Unit_1_The_Atom
... • Electrons and protons attract because of opposite electrical charges, but protons and protons repel since they have the same charge. • The nucleus is held together by a mysterious force called the strong nuclear force which only exists between nucleons (protons and neutrons) which are very close t ...
... • Electrons and protons attract because of opposite electrical charges, but protons and protons repel since they have the same charge. • The nucleus is held together by a mysterious force called the strong nuclear force which only exists between nucleons (protons and neutrons) which are very close t ...
Powerpoint
... • Electrons and protons attract because of opposite electrical charges, but protons and protons repel since they have the same charge. • The nucleus is held together by a mysterious force called the strong nuclear force which only exists between nucleons (protons and neutrons) which are very close t ...
... • Electrons and protons attract because of opposite electrical charges, but protons and protons repel since they have the same charge. • The nucleus is held together by a mysterious force called the strong nuclear force which only exists between nucleons (protons and neutrons) which are very close t ...
Unit 1 Powerpoint Notes
... • Electrons and protons attract because of opposite electrical charges, but protons and protons repel since they have the same charge. • The nucleus is held together by a mysterious force called the strong nuclear force which only exists between nucleons (protons and neutrons) which are very close t ...
... • Electrons and protons attract because of opposite electrical charges, but protons and protons repel since they have the same charge. • The nucleus is held together by a mysterious force called the strong nuclear force which only exists between nucleons (protons and neutrons) which are very close t ...
Chemical element
A chemical element (or element) is a chemical substance consisting of atoms having the same number of protons in their atomic nuclei (i.e. the same atomic number, Z). There are 118 elements that have been identified, of which the first 94 occur naturally on Earth with the remaining 24 being synthetic elements. There are 80 elements that have at least one stable isotope and 38 that have exclusively radioactive isotopes, which decay over time into other elements. Iron is the most abundant element (by mass) making up the Earth, while oxygen is the most common element in the crust of the earth.Chemical elements constitute approximately 15% of the matter in the universe: the remainder is dark matter, the composition of it is unknown, but it is not composed of chemical elements.The two lightest elements, hydrogen and helium were mostly formed in the Big Bang and are the most common elements in the universe. The next three elements (lithium, beryllium and boron) were formed mostly by cosmic ray spallation, and are thus more rare than those that follow. Formation of elements with from six to twenty six protons occurred and continues to occur in main sequence stars via stellar nucleosynthesis. The high abundance of oxygen, silicon, and iron on Earth reflects their common production in such stars. Elements with greater than twenty six protons are formed by supernova nucleosynthesis in supernovae, which, when they explode, blast these elements far into space as planetary nebulae, where they may become incorporated into planets when they are formed.When different elements are chemically combined, with the atoms held together by chemical bonds, they form chemical compounds. Only a minority of elements are found uncombined as relatively pure minerals. Among the more common of such ""native elements"" are copper, silver, gold, carbon (as coal, graphite, or diamonds), and sulfur. All but a few of the most inert elements, such as noble gases and noble metals, are usually found on Earth in chemically combined form, as chemical compounds. While about 32 of the chemical elements occur on Earth in native uncombined forms, most of these occur as mixtures. For example, atmospheric air is primarily a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, and argon, and native solid elements occur in alloys, such as that of iron and nickel.The history of the discovery and use of the elements began with primitive human societies that found native elements like carbon, sulfur, copper and gold. Later civilizations extracted elemental copper, tin, lead and iron from their ores by smelting, using charcoal. Alchemists and chemists subsequently identified many more, with almost all of the naturally-occurring elements becoming known by 1900. The properties of the chemical elements are summarized on the periodic table, which organizes the elements by increasing atomic number into rows (""periods"") in which the columns (""groups"") share recurring (""periodic"") physical and chemical properties. Save for unstable radioactive elements with short half-lives, all of the elements are available industrially, most of them in high degrees of purity.