Lecture 3
... Balancing a chemical equation that describes a reaction involves inserting coefficients before the chemical formulas so that the same number of each type of atom is shown on each side of the equation. Chemical equations may be balances “by inspection” or algebraically (Section 2.1, pages 55-57). Ins ...
... Balancing a chemical equation that describes a reaction involves inserting coefficients before the chemical formulas so that the same number of each type of atom is shown on each side of the equation. Chemical equations may be balances “by inspection” or algebraically (Section 2.1, pages 55-57). Ins ...
Atoms, Elements, and
... below on your worksheet or on a numbered sheet of paper. • Write an A if you agree with the statement. • Write a D if you disagree with the statement. ...
... below on your worksheet or on a numbered sheet of paper. • Write an A if you agree with the statement. • Write a D if you disagree with the statement. ...
Chemistry Academic v. 2016
... Explain the law of definite proportions to classify elements and compounds as pure substances. Explain why compounds are composed of integer ratios of elements. Interpret and apply the law of conservation of energy, law of conservation of mass, constant composition (definite proportions), and multip ...
... Explain the law of definite proportions to classify elements and compounds as pure substances. Explain why compounds are composed of integer ratios of elements. Interpret and apply the law of conservation of energy, law of conservation of mass, constant composition (definite proportions), and multip ...
atomic number - iGCSE Science Courses
... only one or two stable ones. The other isotopes tend to be radioactive, which means that they decay into other elements and give out radiation. This is where all radioactivity comes from – unstable radioactive isotopes undergoing nuclear decay and spitting out high energy particles. ...
... only one or two stable ones. The other isotopes tend to be radioactive, which means that they decay into other elements and give out radiation. This is where all radioactivity comes from – unstable radioactive isotopes undergoing nuclear decay and spitting out high energy particles. ...
Answers - Dr Terry Dwyer National Curriculum mathematics and
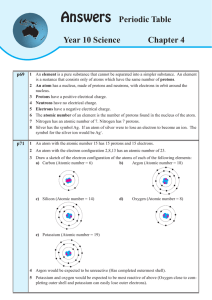
... 1 Briefly describe the chemical properties of group 17 - the halogens. The group 17 halogens are reactive and dangerous (Chlorine was used as a poisonous gas during World War I). The halogens react with metals to form salts. The halogens become less reactive the further down the group. 2 Briefly ...
... 1 Briefly describe the chemical properties of group 17 - the halogens. The group 17 halogens are reactive and dangerous (Chlorine was used as a poisonous gas during World War I). The halogens react with metals to form salts. The halogens become less reactive the further down the group. 2 Briefly ...
TEST on Atomic Structure
... _A__ 44) Which of the following pairs of elements is most likely to form an ionic compound? a. magnesium and fluorine c. oxygen and chlorine (ionic = metal and nonmetal) b. nitrogen and sulfur d. sodium and aluminum _A__ 45) A bond formed between a calcium atom and an oxygen atom is likely to be ___ ...
... _A__ 44) Which of the following pairs of elements is most likely to form an ionic compound? a. magnesium and fluorine c. oxygen and chlorine (ionic = metal and nonmetal) b. nitrogen and sulfur d. sodium and aluminum _A__ 45) A bond formed between a calcium atom and an oxygen atom is likely to be ___ ...
MID-COURSE REVISION QUESTIONS The following questions are
... The empirical formula gives the number of atoms of each of the component elements in any compound, expressed as the simplest whole-number ratio. Every compound, be it ionic or covalent, has an empirical formula. Compounds that exist as molecules also have a molecular formula which gives the actual n ...
... The empirical formula gives the number of atoms of each of the component elements in any compound, expressed as the simplest whole-number ratio. Every compound, be it ionic or covalent, has an empirical formula. Compounds that exist as molecules also have a molecular formula which gives the actual n ...
MID-COURSE REVISION QUESTIONS The following questions are
... doing, emit energy equivalent to the energy difference between the orbits used. The emitted energy is in the form of electromagnetic radiation and often occurs at frequencies corresponding to the visible part of the spectrum. A pattern of spectral lines is observed, called the atomic emission spectr ...
... doing, emit energy equivalent to the energy difference between the orbits used. The emitted energy is in the form of electromagnetic radiation and often occurs at frequencies corresponding to the visible part of the spectrum. A pattern of spectral lines is observed, called the atomic emission spectr ...
Atoms – Building Blocks of Matter Notes
... 4. Isotopes – atoms with the same number of protons (atomic number is the same) but different numbers of neutrons (mass number is different). Usually isotopes are referred to by their name (of symbol) and their mass number. Every element on the chart has at least 2 isotopes and some elements have as ...
... 4. Isotopes – atoms with the same number of protons (atomic number is the same) but different numbers of neutrons (mass number is different). Usually isotopes are referred to by their name (of symbol) and their mass number. Every element on the chart has at least 2 isotopes and some elements have as ...
Chapter 3 - SaddleSpace/Haiku
... II. Development of Atomic Models: Other particles must account for most of the mass of the atom Millikan determine the size of the charge on the electron (oil drop ...
... II. Development of Atomic Models: Other particles must account for most of the mass of the atom Millikan determine the size of the charge on the electron (oil drop ...
Unit 2 - Solon City Schools
... 1) Set one of the isotope’s relative abundance equal to X. 2) The relative abundances must add up to 1; therefore, the other isotope’s relative abundance would be equal to 1-X. 3) Remember, the relative mass is equal to the relative abundance times the mass number. Remember, the relative masses must ...
... 1) Set one of the isotope’s relative abundance equal to X. 2) The relative abundances must add up to 1; therefore, the other isotope’s relative abundance would be equal to 1-X. 3) Remember, the relative mass is equal to the relative abundance times the mass number. Remember, the relative masses must ...
atoms
... O Although the atoms that make up an element may have different mass numbers, the atoms all react the same way chemically. ...
... O Although the atoms that make up an element may have different mass numbers, the atoms all react the same way chemically. ...
Chapter 1 Student Notes
... All matter is composed of about 118 different kinds of atoms. These atoms can be physically mixed or chemically joined together to make up all kinds of matter. Atom the smallest unit of an element that maintains the properties of that element. Since matter exists in so many different forms, having ...
... All matter is composed of about 118 different kinds of atoms. These atoms can be physically mixed or chemically joined together to make up all kinds of matter. Atom the smallest unit of an element that maintains the properties of that element. Since matter exists in so many different forms, having ...
Chapter 18 - Houston ISD
... add one proton at a time for each element. The atomic masses however, increase by amounts greater than one (figure 18.10). This difference is due to the neutrons in the nucleus. Neutrons add mass to the atom, but do not change its charge. Mass number and The total number of protons and neutrons in t ...
... add one proton at a time for each element. The atomic masses however, increase by amounts greater than one (figure 18.10). This difference is due to the neutrons in the nucleus. Neutrons add mass to the atom, but do not change its charge. Mass number and The total number of protons and neutrons in t ...
Unit 1 Notes
... Since ancient times, people have known of seven metallic elements (gold, silver, copper, tin, lead, mercury, iron) – each was associated with a symbol of a different celestial body. e.g. gold - sun, copper – Venus, lead – Saturn, etc. Early 1800’s - alchemists had discovered new elements and nee ...
... Since ancient times, people have known of seven metallic elements (gold, silver, copper, tin, lead, mercury, iron) – each was associated with a symbol of a different celestial body. e.g. gold - sun, copper – Venus, lead – Saturn, etc. Early 1800’s - alchemists had discovered new elements and nee ...
File
... shell. Each of the elements has a different number of the tiny electrons, and a corresponding number of protons. Hydrogen is the smallest, with only one electron. Carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen, are also small, light atoms. These electron shells are filled one by one from the inner shell going outward ...
... shell. Each of the elements has a different number of the tiny electrons, and a corresponding number of protons. Hydrogen is the smallest, with only one electron. Carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen, are also small, light atoms. These electron shells are filled one by one from the inner shell going outward ...
chapter 2: atoms, ions, and molecules
... compound (eg. NaCl, Al2O3, etc.) – The formula gives the ratio of ions (not actual #). – The 3D representation of NaCl at the right shows a network of Na+ (purple) and Cl– ions (green). – The formula, NaCl, indicates a 1-to-1 ratio of Na+ ions and Cl– ions present, not the presence of only one ion o ...
... compound (eg. NaCl, Al2O3, etc.) – The formula gives the ratio of ions (not actual #). – The 3D representation of NaCl at the right shows a network of Na+ (purple) and Cl– ions (green). – The formula, NaCl, indicates a 1-to-1 ratio of Na+ ions and Cl– ions present, not the presence of only one ion o ...
Activity 9 What Determines and Limits an Atom`s Mass?
... The key word in this statement is “stable.” There are other isotopes of chlorine, both heavier and lighter than chlorine-35 and chlorine-37, but they are not stable.The unstable isotopes can convert to a more stable combination of neutrons and protons, and they do so according to a systematic patter ...
... The key word in this statement is “stable.” There are other isotopes of chlorine, both heavier and lighter than chlorine-35 and chlorine-37, but they are not stable.The unstable isotopes can convert to a more stable combination of neutrons and protons, and they do so according to a systematic patter ...
Chapter 3 - Higher Education | Kendall Hunt Publishing
... melting point. A physical change is one that alters at least one of the physical properties of the substance without changing its chemical composition. Some examples of physical change are (1) altering the physical state of matter, such as what occurs when an ice cube is melted; (2) dissolving or mi ...
... melting point. A physical change is one that alters at least one of the physical properties of the substance without changing its chemical composition. Some examples of physical change are (1) altering the physical state of matter, such as what occurs when an ice cube is melted; (2) dissolving or mi ...
atomic number
... Neutron numbers are able to change the mass of atoms, because they weigh about as much as a proton and electron together. If there are many atoms of an element that are isotopes, the average atomic mass for that element will change. We have spoken about carbon (C) having an average mass of 12.01. It ...
... Neutron numbers are able to change the mass of atoms, because they weigh about as much as a proton and electron together. If there are many atoms of an element that are isotopes, the average atomic mass for that element will change. We have spoken about carbon (C) having an average mass of 12.01. It ...
February Homework Packet
... 8. How do the energy and the most probable location of an electron in the third shell of an atom compare to the energy and the most probable location of an electron in the first shell of the same atom? (1) In the third shell, an electron has more energy and is closer to the nucleus. (2) In the third ...
... 8. How do the energy and the most probable location of an electron in the third shell of an atom compare to the energy and the most probable location of an electron in the first shell of the same atom? (1) In the third shell, an electron has more energy and is closer to the nucleus. (2) In the third ...
CH101 General Chemistry - 유룡
... - achieved by reversing the cathode-anode - ratio of q/m → highly dependent on the gas fill, highest value for the lightest element (H), 1836 times smaller than for the electron - For electrical neutrality, H ion carries an equal but opposite charge to that of electron with 1836 times heavier - Mode ...
... - achieved by reversing the cathode-anode - ratio of q/m → highly dependent on the gas fill, highest value for the lightest element (H), 1836 times smaller than for the electron - For electrical neutrality, H ion carries an equal but opposite charge to that of electron with 1836 times heavier - Mode ...
Dalton`s atomic theory
... Dalton estimated the atomic weights according to the mass ratios in which they combined, with hydrogen being the basic unit. However, Dalton did not conceive that with some elements atoms exist in molecules – e.g. pure oxygen exists as O2. He also mistakenly believed that the simplest compound betwe ...
... Dalton estimated the atomic weights according to the mass ratios in which they combined, with hydrogen being the basic unit. However, Dalton did not conceive that with some elements atoms exist in molecules – e.g. pure oxygen exists as O2. He also mistakenly believed that the simplest compound betwe ...
Skill Sheet 19-B Chemical Formulas
... Have you ever heard of sodium nitrate? It’s a preservative used in foods like hot dogs. The chemical formula for sodium nitrate is NaNO3. How many types of atoms does this compound contain? You are right if you said three: sodium, nitrogen, and oxygen. The nitrogen and oxygen atoms have a shared-ele ...
... Have you ever heard of sodium nitrate? It’s a preservative used in foods like hot dogs. The chemical formula for sodium nitrate is NaNO3. How many types of atoms does this compound contain? You are right if you said three: sodium, nitrogen, and oxygen. The nitrogen and oxygen atoms have a shared-ele ...
Chemical element
A chemical element (or element) is a chemical substance consisting of atoms having the same number of protons in their atomic nuclei (i.e. the same atomic number, Z). There are 118 elements that have been identified, of which the first 94 occur naturally on Earth with the remaining 24 being synthetic elements. There are 80 elements that have at least one stable isotope and 38 that have exclusively radioactive isotopes, which decay over time into other elements. Iron is the most abundant element (by mass) making up the Earth, while oxygen is the most common element in the crust of the earth.Chemical elements constitute approximately 15% of the matter in the universe: the remainder is dark matter, the composition of it is unknown, but it is not composed of chemical elements.The two lightest elements, hydrogen and helium were mostly formed in the Big Bang and are the most common elements in the universe. The next three elements (lithium, beryllium and boron) were formed mostly by cosmic ray spallation, and are thus more rare than those that follow. Formation of elements with from six to twenty six protons occurred and continues to occur in main sequence stars via stellar nucleosynthesis. The high abundance of oxygen, silicon, and iron on Earth reflects their common production in such stars. Elements with greater than twenty six protons are formed by supernova nucleosynthesis in supernovae, which, when they explode, blast these elements far into space as planetary nebulae, where they may become incorporated into planets when they are formed.When different elements are chemically combined, with the atoms held together by chemical bonds, they form chemical compounds. Only a minority of elements are found uncombined as relatively pure minerals. Among the more common of such ""native elements"" are copper, silver, gold, carbon (as coal, graphite, or diamonds), and sulfur. All but a few of the most inert elements, such as noble gases and noble metals, are usually found on Earth in chemically combined form, as chemical compounds. While about 32 of the chemical elements occur on Earth in native uncombined forms, most of these occur as mixtures. For example, atmospheric air is primarily a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, and argon, and native solid elements occur in alloys, such as that of iron and nickel.The history of the discovery and use of the elements began with primitive human societies that found native elements like carbon, sulfur, copper and gold. Later civilizations extracted elemental copper, tin, lead and iron from their ores by smelting, using charcoal. Alchemists and chemists subsequently identified many more, with almost all of the naturally-occurring elements becoming known by 1900. The properties of the chemical elements are summarized on the periodic table, which organizes the elements by increasing atomic number into rows (""periods"") in which the columns (""groups"") share recurring (""periodic"") physical and chemical properties. Save for unstable radioactive elements with short half-lives, all of the elements are available industrially, most of them in high degrees of purity.