A Theory of the Origin of the Solar System There have been
... inspection of the families of the planets reveals that they show the same salient features as exhibited by the family of the Sun — the coplaner orbits of small eccentricity. This indicates that all might have been formed through the same stages of evolution. The idea may also be extended to one gene ...
... inspection of the families of the planets reveals that they show the same salient features as exhibited by the family of the Sun — the coplaner orbits of small eccentricity. This indicates that all might have been formed through the same stages of evolution. The idea may also be extended to one gene ...
ASTRONOMY 301 PROBLEM SET NUMBER 3 DUE IN CLASS
... problem and any formulae you used and algebraic manipulation that you did. You are encouraged to work together to figure out the method of solution, but you must write out the solutions independently in your own words. Do all five problems; each problem counts 1 point. Turn in your answers in class ...
... problem and any formulae you used and algebraic manipulation that you did. You are encouraged to work together to figure out the method of solution, but you must write out the solutions independently in your own words. Do all five problems; each problem counts 1 point. Turn in your answers in class ...
Pattern recognition of star constellations for spacecraft
... with the raw SC. This would place a heavy burden on the onboard CPU. ...
... with the raw SC. This would place a heavy burden on the onboard CPU. ...
File
... I am a large star. One of the planets in my solar system has an amazing moon! It is the planet that is the furthest out and while it is a large planet it is still much smaller than me. I want that moon! I know that mass is a factor in gravitational force so why doesn't the moon orbit me? Is there an ...
... I am a large star. One of the planets in my solar system has an amazing moon! It is the planet that is the furthest out and while it is a large planet it is still much smaller than me. I want that moon! I know that mass is a factor in gravitational force so why doesn't the moon orbit me? Is there an ...
Chapter 12: The Life Cycle of Stars (contʼd)
... • the period of a massive star's life when carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen are fusing in different shells outside the core • a type of hydrogen fusion that uses carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen atoms as catalysts • the process by which helium is fused into carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen • the perio ...
... • the period of a massive star's life when carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen are fusing in different shells outside the core • a type of hydrogen fusion that uses carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen atoms as catalysts • the process by which helium is fused into carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen • the perio ...
X-ray Emission from Massive Stars
... The wind profile model provides statistically good fits to all the lines. The onset radii (left) are exactly what’s expected from the standard wind-shock picture. There is evidence for attenuation by the cold wind (right), but at levels nearly 10 times lower than expected. This is the same result th ...
... The wind profile model provides statistically good fits to all the lines. The onset radii (left) are exactly what’s expected from the standard wind-shock picture. There is evidence for attenuation by the cold wind (right), but at levels nearly 10 times lower than expected. This is the same result th ...
Project 8 : Stellar Spectra: Classification
... Objective: The main objective of this project is to learn how to estimate the spectral type of stars from their stellar spectra. At the completion of the project the students should i) understand the process of classifying different spectra by the relative strengths ...
... Objective: The main objective of this project is to learn how to estimate the spectral type of stars from their stellar spectra. At the completion of the project the students should i) understand the process of classifying different spectra by the relative strengths ...
6 March 2013 Exoplanets and Where to Find Them Professor
... The bright southern star Fomalhaut lies 25 light-years distant and is also surrounded by a debris disc - but one that is particularly immense, spanning an annulus from about 24 to 30 billion km around the star. This is a case, however, where we can observe not just the debris disc but also a newly-f ...
... The bright southern star Fomalhaut lies 25 light-years distant and is also surrounded by a debris disc - but one that is particularly immense, spanning an annulus from about 24 to 30 billion km around the star. This is a case, however, where we can observe not just the debris disc but also a newly-f ...
Chapter 12 Stellar Evolution
... • A supernova is incredibly luminous, as can be seen from these curves—more than a million times as bright as a nova. ...
... • A supernova is incredibly luminous, as can be seen from these curves—more than a million times as bright as a nova. ...
Big Bear Valley Astronomical Society
... connected to Sirius as the constellation itself did not take on its current form until Roman times. Sirius is a hot white star that will shine brightly for a long time to come. It is also a known binary system, with a tiny white dwarf star, coloquially known as 'the Pup', circling the brighter prima ...
... connected to Sirius as the constellation itself did not take on its current form until Roman times. Sirius is a hot white star that will shine brightly for a long time to come. It is also a known binary system, with a tiny white dwarf star, coloquially known as 'the Pup', circling the brighter prima ...
Word
... 22) A uniform, solid sphere of mass 350 grams and radius 25.0 cm has an axle attached to it tangent to its surface. The axle is oriented horizontally, causing the sphere to be suspended below it, its center of mass directly below the axle. (See diagram below left.) Someone lifts the sphere until its ...
... 22) A uniform, solid sphere of mass 350 grams and radius 25.0 cm has an axle attached to it tangent to its surface. The axle is oriented horizontally, causing the sphere to be suspended below it, its center of mass directly below the axle. (See diagram below left.) Someone lifts the sphere until its ...
Far Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Explorer
... Some massive star SNe appear to be related to Gamma Ray Bursts. Hubble Space Telescope has played a key role in understanding these objects. ...
... Some massive star SNe appear to be related to Gamma Ray Bursts. Hubble Space Telescope has played a key role in understanding these objects. ...
E3 – Stellar distances
... • At distances greater than Mpc, neither parallax nor spectroscopic parallax can be relied upon to measure the distance to a star. • When we observe another galaxy, all of the stars in that galaxy are approximately the same distance away from the earth. What we really need is a light source of known ...
... • At distances greater than Mpc, neither parallax nor spectroscopic parallax can be relied upon to measure the distance to a star. • When we observe another galaxy, all of the stars in that galaxy are approximately the same distance away from the earth. What we really need is a light source of known ...
“White Hot” Star Lab
... - Use the same setup as in the Trial Run. - Be sure to pull the tape at a slow consistent speed. - Make sure to record the time and to tally the number of wavelength lines seen. 15. Make sure everyone in the group has filled in the data on their own data sheets. 16. Determine the average number of w ...
... - Use the same setup as in the Trial Run. - Be sure to pull the tape at a slow consistent speed. - Make sure to record the time and to tally the number of wavelength lines seen. 15. Make sure everyone in the group has filled in the data on their own data sheets. 16. Determine the average number of w ...
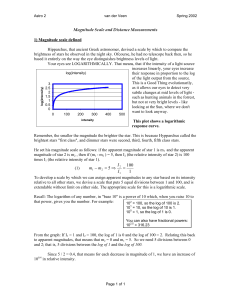
Stellar Magnitudes & Distances
... • Raise 2.512 to that power. • Example: How many times brighter is Polaris (a 2nd magnitude star) than a barely-visible 6th magnitude star? • 6 - 2 = 4. So 2.5124 = 39.8 times. Polaris is almost 40 times brighter than the faintest visible star! ...
... • Raise 2.512 to that power. • Example: How many times brighter is Polaris (a 2nd magnitude star) than a barely-visible 6th magnitude star? • 6 - 2 = 4. So 2.5124 = 39.8 times. Polaris is almost 40 times brighter than the faintest visible star! ...