Effects of Mutual Transits by Extrasolar Planet
... emissions come from the faint objects. In a single transit, on the other hand, thermal emissions from a transiting object at lower temperature make a difference in light curves during the secondary eclipse, when the object moves behind a parent star as observed for instance for HD209458b (Deming et ...
... emissions come from the faint objects. In a single transit, on the other hand, thermal emissions from a transiting object at lower temperature make a difference in light curves during the secondary eclipse, when the object moves behind a parent star as observed for instance for HD209458b (Deming et ...
PHYS3380_111615_bw - The University of Texas at Dallas
... 1967: Hewish and Bell discovered regularly spaced radio pulses P=1.337s, repeating from same point in sky - normal star too big to pulse that fast - star with hot spot couldn’t spin that fast - would fly apart ...
... 1967: Hewish and Bell discovered regularly spaced radio pulses P=1.337s, repeating from same point in sky - normal star too big to pulse that fast - star with hot spot couldn’t spin that fast - would fly apart ...
A New Variable Star in Perseus
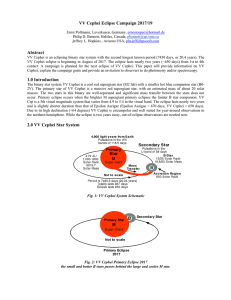
... The secondary minima are shown in Figure 6 and Figure 7. Using this two minima, the duration of the flat part of the secondary minimum is determined as 583 minutes. ...
... The secondary minima are shown in Figure 6 and Figure 7. Using this two minima, the duration of the flat part of the secondary minimum is determined as 583 minutes. ...
REACH FOR THE STARS MLK 2009
... Answer the following questions. If the Absolute magnitude and Apparent magnitude are equal, what do you know about the distance of the star? _____________________________________________ How many AU does light travel in one year? _____________ What are Hayashi tracks? _______________________________ ...
... Answer the following questions. If the Absolute magnitude and Apparent magnitude are equal, what do you know about the distance of the star? _____________________________________________ How many AU does light travel in one year? _____________ What are Hayashi tracks? _______________________________ ...
The Southern Winter PDF
... cavity presumably cleared by the radiation of its powerful central star. The central star is 40 times more massive than the Sun and is about three to four million years old — past the middle of its life span. Stars this massive may only live a few million years, so it is quickly depleting its fuel a ...
... cavity presumably cleared by the radiation of its powerful central star. The central star is 40 times more massive than the Sun and is about three to four million years old — past the middle of its life span. Stars this massive may only live a few million years, so it is quickly depleting its fuel a ...
DTU 8e Chap 11 Characterizing Stars
... How luminous is the Sun compared with other stars? What colors are stars, and why do they have these colors? Are brighter stars hotter than dimmer stars? Compared to the Sun, what sizes are other stars? Are most stars isolated from other stars, as the Sun is? ...
... How luminous is the Sun compared with other stars? What colors are stars, and why do they have these colors? Are brighter stars hotter than dimmer stars? Compared to the Sun, what sizes are other stars? Are most stars isolated from other stars, as the Sun is? ...
Stellar Physics
... when viewed from Earth. For example, imagine you are a rabbit crossing a country road in the pitch black of night. You see a single light which may be a motorcycle. How do you know how far way it is? (Is it a motorcycle or something else?) Practical demonstration: various small light sources of vary ...
... when viewed from Earth. For example, imagine you are a rabbit crossing a country road in the pitch black of night. You see a single light which may be a motorcycle. How do you know how far way it is? (Is it a motorcycle or something else?) Practical demonstration: various small light sources of vary ...
Chapter 14 – Chemical Analysis
... COG is independent of gravity • For ionized lines of ionized species (e.g Fe II in the Sun), the curves shift to the right with increasing gravity, roughly as g1/3 ...
... COG is independent of gravity • For ionized lines of ionized species (e.g Fe II in the Sun), the curves shift to the right with increasing gravity, roughly as g1/3 ...
Ch 20 Stellar Evolution
... • Stars spend most of their life on the Main Sequence • When fusion ceases in the core, it begins to collapse and heat. Hydrogen fusion starts in the shell surrounding the core. • The helium core begins to heat up; as long as the star is at least 0.25 solar masses, the helium will get hot enough ...
... • Stars spend most of their life on the Main Sequence • When fusion ceases in the core, it begins to collapse and heat. Hydrogen fusion starts in the shell surrounding the core. • The helium core begins to heat up; as long as the star is at least 0.25 solar masses, the helium will get hot enough ...