Structure of Neutron Stars
... Remember about the difference between baryonic and gravitational masses in the case of neutron stars! ...
... Remember about the difference between baryonic and gravitational masses in the case of neutron stars! ...
The ultra-luminous x-ray sources near center of M82
... Best Candidate of IMBH – M82 X-1 has luminosity ~ 1041 erg/sec not at the center of the galaxy => Not an AGN has a period of 62 days very close to a young star cluster MGG-11 ...
... Best Candidate of IMBH – M82 X-1 has luminosity ~ 1041 erg/sec not at the center of the galaxy => Not an AGN has a period of 62 days very close to a young star cluster MGG-11 ...
Part1
... dust and the dust-to-gas ratio is intimately related to heavy element enrichment (e.g., you need dust to see IR!). o Along similar lines, millimeter line tracers of the ISM are key to robustly measure the dust-to-gas ratio in large systems. o CO (and other molecules) are known to be suppressed relat ...
... dust and the dust-to-gas ratio is intimately related to heavy element enrichment (e.g., you need dust to see IR!). o Along similar lines, millimeter line tracers of the ISM are key to robustly measure the dust-to-gas ratio in large systems. o CO (and other molecules) are known to be suppressed relat ...
THE INNER CORE OF A NEUTRON STAR Part 1
... further collapse by super compression gravitational forces, such as quantum degeneracy pressure, due to the phenomenon described by the Pauli exclusion principle. This states that: ”No two neutrons (or any other fermionic particles) can occupy the same place and quantum state simultaneously”. Althou ...
... further collapse by super compression gravitational forces, such as quantum degeneracy pressure, due to the phenomenon described by the Pauli exclusion principle. This states that: ”No two neutrons (or any other fermionic particles) can occupy the same place and quantum state simultaneously”. Althou ...
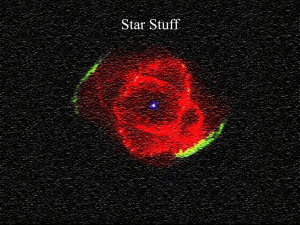
chapter17StarStuff
... carbon in a shell around the carbon core, and H fuses to He in a shell around the helium layer • This double-shell burning stage never reaches equilibrium—fusion rate periodically spikes upward in a series of thermal pulses • With each spike, convection dredges carbon up from core and transports it ...
... carbon in a shell around the carbon core, and H fuses to He in a shell around the helium layer • This double-shell burning stage never reaches equilibrium—fusion rate periodically spikes upward in a series of thermal pulses • With each spike, convection dredges carbon up from core and transports it ...
Calculate the Mass of the Milky Way Galaxy
... • During the uncertainties of the era, Hubble was able to observe galaxies at distances up to 7 million light years away. By doing so he was able to come up with Hubble's Law, which said that the further galaxies were away from earth the faster they moved away from our planet. Hubble's rule proved t ...
... • During the uncertainties of the era, Hubble was able to observe galaxies at distances up to 7 million light years away. By doing so he was able to come up with Hubble's Law, which said that the further galaxies were away from earth the faster they moved away from our planet. Hubble's rule proved t ...
Definitions of Magnitudes and Surface Brightness
... One often does not convert absolute magnitudes directly to W m – 2 . One usually goes by the round about process of referring to the absolute magnitude of the sun. In the B andV bands for example, this is: ...
... One often does not convert absolute magnitudes directly to W m – 2 . One usually goes by the round about process of referring to the absolute magnitude of the sun. In the B andV bands for example, this is: ...
Big Bang Theory
... B. Turn on Show trendline. What is the slope of this trendline? This value, known as the Hubble constant, describes how recessional velocity is related to distance. The modern value of this constant is about 70 km/s/Mpc. C. How does Hubble’s law provide evidence that the universe is expanding? (Hint ...
... B. Turn on Show trendline. What is the slope of this trendline? This value, known as the Hubble constant, describes how recessional velocity is related to distance. The modern value of this constant is about 70 km/s/Mpc. C. How does Hubble’s law provide evidence that the universe is expanding? (Hint ...
Impact on stellar properties of changing physics SAC Summer
... Stellar evolution describes the radical changes which stars undergo throughout their lifetime. The timescales of these processes differ substantially based on the physical process occurring in the stellar interior. Nuclear fusion is the primary energy production process for the majority of a star’s ...
... Stellar evolution describes the radical changes which stars undergo throughout their lifetime. The timescales of these processes differ substantially based on the physical process occurring in the stellar interior. Nuclear fusion is the primary energy production process for the majority of a star’s ...
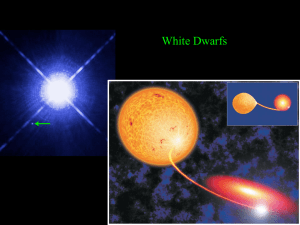
electron degeneracy pressure and white dwarfs
... Most stable stars are stable because their weight is held up by gas pressure. Do stars exist that are held up by electron degeneracy pressure, rather than gas pressure? • Yes: white dwarfs. How are such stars made? • From normal stars at the end of life, when they have run out of fuel, can’t gen ...
... Most stable stars are stable because their weight is held up by gas pressure. Do stars exist that are held up by electron degeneracy pressure, rather than gas pressure? • Yes: white dwarfs. How are such stars made? • From normal stars at the end of life, when they have run out of fuel, can’t gen ...
Learning Objectives
... An object of known luminosity is called a standard candle. Most stars are not standard candles – their luminosities are not known and consequently their distances cannot be easily calculated. However, some special types of variable and exploding stars do have known, standard luminosities. Consequen ...
... An object of known luminosity is called a standard candle. Most stars are not standard candles – their luminosities are not known and consequently their distances cannot be easily calculated. However, some special types of variable and exploding stars do have known, standard luminosities. Consequen ...
20_LectureOutline
... • In Sun-like stars, the helium burning starts with a helium flash before the star is once again in equilibrium. • The star develops a nonburning carbon core, surrounded by shells burning helium and hydrogen. • The shell expands into a planetary nebula, and the core is visible as a white dwarf. • Th ...
... • In Sun-like stars, the helium burning starts with a helium flash before the star is once again in equilibrium. • The star develops a nonburning carbon core, surrounded by shells burning helium and hydrogen. • The shell expands into a planetary nebula, and the core is visible as a white dwarf. • Th ...
Neither Star nor Trigram - 5 Yellow Focus of Attention
... lines’. That may be so, but we may also see depiction of any one phenomenon, then the phenomenon one time captured at its momentum of ‘switch on’, another time captured at its momentum of ‘switch off’. As here, all comes under instigation of 5 Yellow, then 5 Yellow present in everything, you would e ...
... lines’. That may be so, but we may also see depiction of any one phenomenon, then the phenomenon one time captured at its momentum of ‘switch on’, another time captured at its momentum of ‘switch off’. As here, all comes under instigation of 5 Yellow, then 5 Yellow present in everything, you would e ...
Doppler Effect Demo
... that are close to the Milky Way actually move toward us and are blue-shifted. However, all galaxies beyond a certain distance are red-shifted. Is it possible to see any planets orbiting other stars? As of the time of this writing (August 2002) no planets have been directly observed. Most extra-solar ...
... that are close to the Milky Way actually move toward us and are blue-shifted. However, all galaxies beyond a certain distance are red-shifted. Is it possible to see any planets orbiting other stars? As of the time of this writing (August 2002) no planets have been directly observed. Most extra-solar ...