Brightness and Distance
... the term luminosity to describe the amount of energy the star radiates in all directions per unit time. Visual luminosity means the luminosity at visual wavelengths, that is wavelengths that humans can see. Bolometric luminosity is the luminosity at all wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum. T ...
... the term luminosity to describe the amount of energy the star radiates in all directions per unit time. Visual luminosity means the luminosity at visual wavelengths, that is wavelengths that humans can see. Bolometric luminosity is the luminosity at all wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum. T ...
В современной астрофизике одной из наиболее
... nonuniformities makes up 6270K 11. Thus, the difference between the experimental and theoretical values equals 0.31 %. This divergence seems to be connected with the final heat conduction of the sun’s shell as the calculated temperature correspond to the inner side of the sun’s shell. It follows fro ...
... nonuniformities makes up 6270K 11. Thus, the difference between the experimental and theoretical values equals 0.31 %. This divergence seems to be connected with the final heat conduction of the sun’s shell as the calculated temperature correspond to the inner side of the sun’s shell. It follows fro ...
CHP 11
... Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ ...
... Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ ...
FROM MOLECULAR CLOUDS TO STARS 1 Star formation and the
... The different phases of the evolution of a GMC are schematically represented in fig.4 from Lada (1999). The upper panel represents the first stages: the cloud is very cold and only low mass stars are formed. They have not enough UV photons to create large ionised regions (HII regions). In the warmes ...
... The different phases of the evolution of a GMC are schematically represented in fig.4 from Lada (1999). The upper panel represents the first stages: the cloud is very cold and only low mass stars are formed. They have not enough UV photons to create large ionised regions (HII regions). In the warmes ...
Motions of the Celestial Sphere
... star is along the celestial equator. The zero point for right ascension is the vernal equinox. To find the right ascension of a star follow an hour circle "straight down" from the star to the celestial equator. The angle from the vernal equinox eastward to the foot of that hour circle is the star's ...
... star is along the celestial equator. The zero point for right ascension is the vernal equinox. To find the right ascension of a star follow an hour circle "straight down" from the star to the celestial equator. The angle from the vernal equinox eastward to the foot of that hour circle is the star's ...
constellations are not real!
... The celestial sphere is assumed to be fixed, so as the Earth rotates the celestial sphere appears to rotate in the opposite direction once per day. This apparent rotation of the celestial sphere presents us with an obvious means of defining a coordinate system for the surface of the celestial spher ...
... The celestial sphere is assumed to be fixed, so as the Earth rotates the celestial sphere appears to rotate in the opposite direction once per day. This apparent rotation of the celestial sphere presents us with an obvious means of defining a coordinate system for the surface of the celestial spher ...
The Distribution of Stars Most Likely to Harbor Intelligent Life
... lifetime changes by less than 50%. ...
... lifetime changes by less than 50%. ...
G W ORIONIS, A 20000 YEARS OLD T TAURI STAR? 1\/"", _ 0.14
... we may be observing stars with ages 01' the onler 01' 10 000 years came indirectly from the analysis 01' the density distribution in the Orion nebula (Kahn am! Menon ]9(1) which showed that the latter could not have existed as an H ]] region 1'01' a period much longer than 10 000 years, thus setting ...
... we may be observing stars with ages 01' the onler 01' 10 000 years came indirectly from the analysis 01' the density distribution in the Orion nebula (Kahn am! Menon ]9(1) which showed that the latter could not have existed as an H ]] region 1'01' a period much longer than 10 000 years, thus setting ...
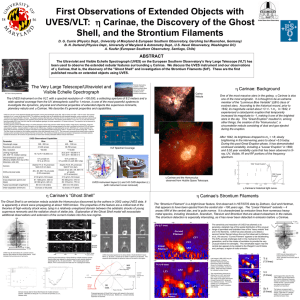
spie_poster1 - UMD Physics
... UVES is a two-arm cross-dispersed Echelle spectrograph covering the wavelength range 300 - 500 nm (blue) and 420 - 1100 nm (red). The spectral resolution for a 1 arcsec slit is about 40,000. The maximum resolution that can be attained with still adequate sampling, using a narrow slit, is about 110,0 ...
... UVES is a two-arm cross-dispersed Echelle spectrograph covering the wavelength range 300 - 500 nm (blue) and 420 - 1100 nm (red). The spectral resolution for a 1 arcsec slit is about 40,000. The maximum resolution that can be attained with still adequate sampling, using a narrow slit, is about 110,0 ...
P10263v1.2 Lab 5 Text
... So, if you can determine m, M and x, you can just plug them into this equation and solve for the distance to the star. As an example, suppose m = 6, M = 1 and x = 0. r(pc) is then equal to 10 to the [(6 - 1 + 5 - 0)/5] power, or 10 to the 2nd power, which is 100. So r would be 100 parsecs. Most sta ...
... So, if you can determine m, M and x, you can just plug them into this equation and solve for the distance to the star. As an example, suppose m = 6, M = 1 and x = 0. r(pc) is then equal to 10 to the [(6 - 1 + 5 - 0)/5] power, or 10 to the 2nd power, which is 100. So r would be 100 parsecs. Most sta ...
The birth and life of stars
... 1. How do stars form? 2. Are stars still forming today? If so, where? 3. Do more massive stars shine longer than less massive ones? What is the reason? ...
... 1. How do stars form? 2. Are stars still forming today? If so, where? 3. Do more massive stars shine longer than less massive ones? What is the reason? ...
Put your title in here…
... Outline Overview of Black Holes The Stellar Disruption Event The Flare The Stellar Wind Core Remnants ...
... Outline Overview of Black Holes The Stellar Disruption Event The Flare The Stellar Wind Core Remnants ...
Slides from the fourth lecture
... South Africa owns this time zone for the southern sky. Need to coordinate smaller telescopes with the SALT. SALT at a disadvantage because it must wait for GRB to transit into observable ring, but there will still be opportunities. ...
... South Africa owns this time zone for the southern sky. Need to coordinate smaller telescopes with the SALT. SALT at a disadvantage because it must wait for GRB to transit into observable ring, but there will still be opportunities. ...
Basic principles of celestial navigation
... whose radius is very much greater than that of the Earth, with its center at O and its polar axis coincident with the Earth’s rotational axis. The position of each celestial object is represented by the point on the celestial sphere at which a line to it from O intersects this sphere. Inasmuch as th ...
... whose radius is very much greater than that of the Earth, with its center at O and its polar axis coincident with the Earth’s rotational axis. The position of each celestial object is represented by the point on the celestial sphere at which a line to it from O intersects this sphere. Inasmuch as th ...