Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... – in order of their apparent brightness – labeled alphabetically in Greek alphabet – Alpha Centauri is the brightest star in constellation ...
... – in order of their apparent brightness – labeled alphabetically in Greek alphabet – Alpha Centauri is the brightest star in constellation ...
Model of Stars—5 Oct Outline •
... The luminosity of a star (the energy produced every second) depends on temperature and size. What can I do to make the same hot‐plate at the same setting burn my hand and not burn my hand? (Without modifying the sun, what can I do to make the sun brighter or fainter?) A. B. ...
... The luminosity of a star (the energy produced every second) depends on temperature and size. What can I do to make the same hot‐plate at the same setting burn my hand and not burn my hand? (Without modifying the sun, what can I do to make the sun brighter or fainter?) A. B. ...
2009 Assessment Schedule (90764)
... Explains that spectra are directly related to atomic structures. Thus hydrogen and helium will show the spectral characteristics unique to hydrogen and helium. (m) ...
... Explains that spectra are directly related to atomic structures. Thus hydrogen and helium will show the spectral characteristics unique to hydrogen and helium. (m) ...
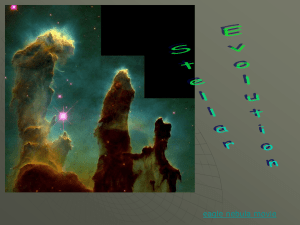
Stellar Evolution
... Without the outward pressure generated from these reactions to counteract the force of gravity, the outer layers of the star begin to collapse inward. Just as during formation, when the material contracts, the temperature and pressure increase. This newly generated heat temporarily counteracts the f ...
... Without the outward pressure generated from these reactions to counteract the force of gravity, the outer layers of the star begin to collapse inward. Just as during formation, when the material contracts, the temperature and pressure increase. This newly generated heat temporarily counteracts the f ...
CHAPTER 2 NOTES (STARS AND GALAXIES)
... spectroscope- breaks up the light from a distant star into its characteristic colors Stars rapidly approaching the Earth have light waves from the star that will be compressed (pushed together) and appear shorter- blue and violet light (blue shift) Stars moving away from the Earth have light waves f ...
... spectroscope- breaks up the light from a distant star into its characteristic colors Stars rapidly approaching the Earth have light waves from the star that will be compressed (pushed together) and appear shorter- blue and violet light (blue shift) Stars moving away from the Earth have light waves f ...
Can you write numbers in scientific notation
... What determines what object will be left behind after a star dies out? What are the properties of each of those objects? How does Einstein’s model of gravity differ from Newton’s description? Why Einstein’s description taken to be “more complete” than Newton’s? What are the effects an outside obser ...
... What determines what object will be left behind after a star dies out? What are the properties of each of those objects? How does Einstein’s model of gravity differ from Newton’s description? Why Einstein’s description taken to be “more complete” than Newton’s? What are the effects an outside obser ...
Due Date: Thursday, November 16, 2006
... The most significant difference between a high-mass star and the Sun will be their lifetime! Look at the HR diagram in Figure 11.1. The lifetime of Spica (10 Msun) is only about 10 million years. The lifetime of Achernar (6 Msun) is only 100 million years…so when we really should not expect the Sun ...
... The most significant difference between a high-mass star and the Sun will be their lifetime! Look at the HR diagram in Figure 11.1. The lifetime of Spica (10 Msun) is only about 10 million years. The lifetime of Achernar (6 Msun) is only 100 million years…so when we really should not expect the Sun ...
Stellar Evolution Slideshow
... After a star explodes, sometimes only neutrons are left (Guess where the name “Neutron Stars” came from?) Also called Pulsars because they emit radio waves with incredible regularity. Appear to be rapidly rotating neutron star ...
... After a star explodes, sometimes only neutrons are left (Guess where the name “Neutron Stars” came from?) Also called Pulsars because they emit radio waves with incredible regularity. Appear to be rapidly rotating neutron star ...
Star Life Cycles WS
... Answer the following questions AS YOU WORK THROUGH THE TUTORIAL 1) The bigger a star is, the longer it will live. ...
... Answer the following questions AS YOU WORK THROUGH THE TUTORIAL 1) The bigger a star is, the longer it will live. ...
Answers Universe Cornell Notes Chapter 8, Sec 2
... and size. Supergiant star, giant star, medium-sized star, white dwarf star, neutron star A star’s color reveals its temperature. Red, yellow - white, blue - white Brightness depends on the star’s size and temperature. It’s brightness as seen from Earth. Apparent brightness is how bright it appears t ...
... and size. Supergiant star, giant star, medium-sized star, white dwarf star, neutron star A star’s color reveals its temperature. Red, yellow - white, blue - white Brightness depends on the star’s size and temperature. It’s brightness as seen from Earth. Apparent brightness is how bright it appears t ...
Day-6
... The Milky Way probably formed by the merger of many smaller protogalaxies. Several of these are still orbiting the Milky Way as satellite galaxies. These can contain significant amounts of gas. The gas delivered by the protogalaxies was a significant source of star formation. Evidence for ...
... The Milky Way probably formed by the merger of many smaller protogalaxies. Several of these are still orbiting the Milky Way as satellite galaxies. These can contain significant amounts of gas. The gas delivered by the protogalaxies was a significant source of star formation. Evidence for ...
The astronauts in the upper left of this photo are working on the
... coefficient of static friction for a car not to skid when traveling at 95 km h? ...
... coefficient of static friction for a car not to skid when traveling at 95 km h? ...
Compare the following sets of stars using the words: BRIGHTER or
... 24. Put the following structures in order from smallest to largest: Universe, star, galaxy, asteroid, planet, solar system, International Space Station, Earth’s moon ...
... 24. Put the following structures in order from smallest to largest: Universe, star, galaxy, asteroid, planet, solar system, International Space Station, Earth’s moon ...