Test#4
... 18. The reason the Solar system does not have a lot of dust and gas between the planets is a) the solar wind blew the dust and gas out of the Solar system b) the planets accreted all the gas and dust c) the early Solar system was made up only of Hydrogen and Helium d) the Sun burns them up 19. All ...
... 18. The reason the Solar system does not have a lot of dust and gas between the planets is a) the solar wind blew the dust and gas out of the Solar system b) the planets accreted all the gas and dust c) the early Solar system was made up only of Hydrogen and Helium d) the Sun burns them up 19. All ...
Almach or Alberio
... Imagine seeing the stars of Alberio, but much closer together, both in separation on the sky and in true distance from each other. The pair's primary is a giant golden star which has a diameter 80 times that of our Sun (large enough to swallow the orbit of Venus) and a luminosity 2,000 times that of ...
... Imagine seeing the stars of Alberio, but much closer together, both in separation on the sky and in true distance from each other. The pair's primary is a giant golden star which has a diameter 80 times that of our Sun (large enough to swallow the orbit of Venus) and a luminosity 2,000 times that of ...
The IC 348 surface density in the Perseus molecular cloud L. Cambrésy Observatoire de Strasbourg, France
... the cluster morphology cluster morphology ...
... the cluster morphology cluster morphology ...
Your Star: _____________________ d = 1 / p
... Write down your star's apparent brightness. Round it to one significant digit. ...
... Write down your star's apparent brightness. Round it to one significant digit. ...
parallax in arc seconds
... The closest star to Earth is Proxima Centauri. It is a member of a triple star system called the Alpha Centauri System. Proxima Centauri has the largest known stellar parallax at 0.76”. ...
... The closest star to Earth is Proxima Centauri. It is a member of a triple star system called the Alpha Centauri System. Proxima Centauri has the largest known stellar parallax at 0.76”. ...
labex7
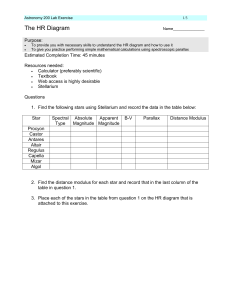
... online notes Chp 8.5) Record this in the table shown above. Also estimate the radius for each star from the HR diagram and where you placed these stars. 6. Use the distance modulus found earlier to compute the distance to these stars. (See Chp 8.1) Star ...
... online notes Chp 8.5) Record this in the table shown above. Also estimate the radius for each star from the HR diagram and where you placed these stars. 6. Use the distance modulus found earlier to compute the distance to these stars. (See Chp 8.1) Star ...
Endpoints of Stellar Evolution
... star collapses into a neutron star or a black hole • Increasing the mass decreases the radius: R ~ M–1/3 • Typical composition: C and/or O • Neutron stars are the equivalent of white dwarfs, but the degeneracy pressure is provided by neutrons, not electrons • The star cools passively as it radia ...
... star collapses into a neutron star or a black hole • Increasing the mass decreases the radius: R ~ M–1/3 • Typical composition: C and/or O • Neutron stars are the equivalent of white dwarfs, but the degeneracy pressure is provided by neutrons, not electrons • The star cools passively as it radia ...
Practice questions for Stars File
... Life cycle of large and massive stars 1. Describe the difference in the stages of the life cycle for a large and massive star compared to an average star 2. Describe the fuel use changes from birth to death for a black hole 3. Describe the fuel use changes from birth to death for a neutron star 4. E ...
... Life cycle of large and massive stars 1. Describe the difference in the stages of the life cycle for a large and massive star compared to an average star 2. Describe the fuel use changes from birth to death for a black hole 3. Describe the fuel use changes from birth to death for a neutron star 4. E ...
Earth Science: Chapter 7: Stellar Evolution: Spring 2017: Student
... SUPERNOVA (see below)and form a NEUTRON STAR (see below) Greater than 20 Less than 10 million years Same as above except the mass is great enough to solar masses form a BLACK HOLE (see below) Planetary nebula: after a red giant forms material from the star is ejected and forms what looks like a nebu ...
... SUPERNOVA (see below)and form a NEUTRON STAR (see below) Greater than 20 Less than 10 million years Same as above except the mass is great enough to solar masses form a BLACK HOLE (see below) Planetary nebula: after a red giant forms material from the star is ejected and forms what looks like a nebu ...
Lifecycle of Stars - Mrs. Plante Science
... forming larger and larger balls of gas and dust molecules. • When the mass becomes large enough, gravitational contraction results in high pressure and temperature, and a protostar is formed. ...
... forming larger and larger balls of gas and dust molecules. • When the mass becomes large enough, gravitational contraction results in high pressure and temperature, and a protostar is formed. ...
1 Kepler`s Third Law
... most energy. Low frequency (long wavelength) photons are the least energetic. The constant, h, is called Plank’s constant and once again its purpose is to scale the equation so that it agrees with our system of measurement. Example: Q: Which type of photon carries the most energy, ultraviolet photon ...
... most energy. Low frequency (long wavelength) photons are the least energetic. The constant, h, is called Plank’s constant and once again its purpose is to scale the equation so that it agrees with our system of measurement. Example: Q: Which type of photon carries the most energy, ultraviolet photon ...
neutron star - Adams State University
... It requires higher temperatures, so it only occurs in stars that are over 2 times larger than the Sun. ...
... It requires higher temperatures, so it only occurs in stars that are over 2 times larger than the Sun. ...