Lecture 24 - Empyrean Quest Publishers
... from apparent brightness and distance (d). Apparent magnitude (old way). We can see about 1,000 stars in Northern Hemisphere with naked eye. Hipparchus rated them from 1 to 6. A '1' is 2.52 x brighter than a '2', etc. Range in brightness from the sun at '-26' magnitude to the faintest objects seen a ...
... from apparent brightness and distance (d). Apparent magnitude (old way). We can see about 1,000 stars in Northern Hemisphere with naked eye. Hipparchus rated them from 1 to 6. A '1' is 2.52 x brighter than a '2', etc. Range in brightness from the sun at '-26' magnitude to the faintest objects seen a ...
The star and the trees prostrate
... During most of a star's lifetime, nuclear fusion in the core generates electromagnetic radiation, including photons, the particles of light. This radiation exerts an outward pressure that exactly balances the inward pull of gravity caused by the star's mass. As the nuclear fuel is exhausted, the out ...
... During most of a star's lifetime, nuclear fusion in the core generates electromagnetic radiation, including photons, the particles of light. This radiation exerts an outward pressure that exactly balances the inward pull of gravity caused by the star's mass. As the nuclear fuel is exhausted, the out ...
Lecture 13. Black Holes - Politechnika Wrocławska
... • After a massive star supernova, if the core has a mass > 3 M, the force of gravity will be too strong for even neutron degeneracy to stop. • The star will collapse into oblivion. – GRAVITY FINALLY WINS!! ...
... • After a massive star supernova, if the core has a mass > 3 M, the force of gravity will be too strong for even neutron degeneracy to stop. • The star will collapse into oblivion. – GRAVITY FINALLY WINS!! ...
Slide 1
... How stars form: the basic process 1. A cold cloud of gas and dust starts to contract, pulled together by gravity. It breaks up into several smaller clouds and each continues to contract. 2. Within a contracting cloud, each particle attracts every other particle, so that the cloud collapses towards ...
... How stars form: the basic process 1. A cold cloud of gas and dust starts to contract, pulled together by gravity. It breaks up into several smaller clouds and each continues to contract. 2. Within a contracting cloud, each particle attracts every other particle, so that the cloud collapses towards ...
luminosity1
... Detector in front of cube collecting all the light that is coming from one side of the cube ...
... Detector in front of cube collecting all the light that is coming from one side of the cube ...
A Red Giant - Cloudfront.net
... A Pulsating Yellow Giant Which it will be for about 100 million years ...
... A Pulsating Yellow Giant Which it will be for about 100 million years ...
Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) Diagram Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram March 16 −
... • More like test questions • Do you understand…? • Fewer leading questions ...
... • More like test questions • Do you understand…? • Fewer leading questions ...
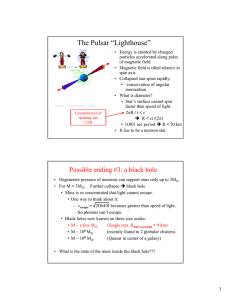
The Pulsar “Lighthouse”
... spin axis. • Collapsed star spins rapidly. • conservation of angular momentum. • What is diameter? • Star’s surface cannot spin faster than speed of light. 2πR / t < c Î R < ct /(2π) • 0.001 sec period Î R < 50 km • It has to be a neutron star. ...
... spin axis. • Collapsed star spins rapidly. • conservation of angular momentum. • What is diameter? • Star’s surface cannot spin faster than speed of light. 2πR / t < c Î R < ct /(2π) • 0.001 sec period Î R < 50 km • It has to be a neutron star. ...
The Sun - Center for Astrophysics and Space Astronomy CASA
... So what if we view this as a personal violation? Let’s go to the Department of Homeland Security and ask them to put up a shield that will protect us from these nasty neutrinos. We’ll make it out of one of the best materials for stopping them – lead. How thick will the shield have to be? ...
... So what if we view this as a personal violation? Let’s go to the Department of Homeland Security and ask them to put up a shield that will protect us from these nasty neutrinos. We’ll make it out of one of the best materials for stopping them – lead. How thick will the shield have to be? ...
Cosmology 2 - schoolphysics
... 1. Describe the model of the Universe proposed by Copernicus 2. If the time for Jupiter to make one orbit of the Sun is 11.86 years calculate the radius of its orbit. (Mass of the Sun = 2x1030 kg and G = 6.67x10-11 Nm2kg-2) 3. Write down Kepler’s three laws of planetary motion. 4. What piece of expe ...
... 1. Describe the model of the Universe proposed by Copernicus 2. If the time for Jupiter to make one orbit of the Sun is 11.86 years calculate the radius of its orbit. (Mass of the Sun = 2x1030 kg and G = 6.67x10-11 Nm2kg-2) 3. Write down Kepler’s three laws of planetary motion. 4. What piece of expe ...
Class 2 Solar System Characteristics Formation Exosolar Planets
... This indicates that one or more supernovae occurred near the Sun while it was forming. Spitzer reveals infrared radiation coming from dust particles heated by the supernova's shock wave. ...
... This indicates that one or more supernovae occurred near the Sun while it was forming. Spitzer reveals infrared radiation coming from dust particles heated by the supernova's shock wave. ...
Review Questions for Exam #2
... • Given the arrow that you have drawn, how are luminosity and mass related on the MS and why? • Put a big “R” in the place where on the diagram where the radii are the biggest. Put a “r” where the radii are the smallest. • Given the relation L = σT4(4πR2) explain why the “R” and “r” are at the locat ...
... • Given the arrow that you have drawn, how are luminosity and mass related on the MS and why? • Put a big “R” in the place where on the diagram where the radii are the biggest. Put a “r” where the radii are the smallest. • Given the relation L = σT4(4πR2) explain why the “R” and “r” are at the locat ...
The Life Cycle of a Star
... protons and electrons. • The gravity is so intense that if an object were to reach the surface it would disperse all of its subatomic particles and merge with the star! • The matter is so dense that a teaspoon would weigh billions of tonnes! • Some people view neutron stars as giant atoms. ...
... protons and electrons. • The gravity is so intense that if an object were to reach the surface it would disperse all of its subatomic particles and merge with the star! • The matter is so dense that a teaspoon would weigh billions of tonnes! • Some people view neutron stars as giant atoms. ...
Star Of Wonder
... supernova, the dramatic brightening of a star caused by an explosion of the entire star. Supernovas occur when a giant star, much more massive than our sun, runs out of nuclear fuel and, in just one second, "collapses" inward to become a far smaller object, ripping the entire star apart and throwing ...
... supernova, the dramatic brightening of a star caused by an explosion of the entire star. Supernovas occur when a giant star, much more massive than our sun, runs out of nuclear fuel and, in just one second, "collapses" inward to become a far smaller object, ripping the entire star apart and throwing ...
Stars - staff.harrisonburg.k12.va
... of a star in the sky when viewed from two different positions in earth’s revolution. – The closer a star is, the larger its parallax, or apparent movement. The farther away a star is, the smaller its parallax. ...
... of a star in the sky when viewed from two different positions in earth’s revolution. – The closer a star is, the larger its parallax, or apparent movement. The farther away a star is, the smaller its parallax. ...