* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Star Life Cycles WS
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
Type II supernova wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
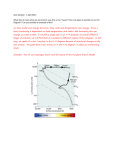
ESS Star Life Cycle Chart Name ___________________________ Period ______ Date _________ Learn the full life cycle of a star in this internet tutorial. Go to the following website. READ the text, view all the animations take the quizzes and answer all the questions on the tutorial: http://outreach.physics.utah.edu/Labs/StarLife/starlife_main.html (page 626) and/or this video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PM9CQDlQI0A or this game http://vital.cs.ohiou.edu/steamwebsite/downloads/StarLife.swf or this advanced interactive: http://starinabox.lcogt.net/# or this http://www.classzone.com/books/earth_science/terc/content/visualizations/es2807/es2807page01.cfm?chapter_no=28 Directions: 1. Inside each box label the name of each step in the star’s life cycle. 2. Label in the dashed line boxes to indicate the time span and fuel for each stage. Birth stellar life death Very Low Mass Years: Our Sun Years: Fuel: Years: Fuel: Fuel: Fuel: Fuel: Fuel(s): ESS Star Life Cycle Chart Concept Check Questions: Name ___________________________ Period ______ Date _________ Answer the following questions AS YOU WORK THROUGH THE TUTORIAL 1) The bigger a star is, the longer it will live. T *(hint – they follow in order with the tutorial) F 2) In a stable star, the ____________ pushing out from the center is equal with the ___________pulling atoms inward to the center – when these forces are equal, the star is at equilibrium. 3. There are three main fuels that a star uses for fusion: ___________, then ___________, and finally __________. 4. When a star is out of hydrogen fuel, what will happen to the temperature of the core? Increase decrease stay the same 5. A red giant is (hotter, cooler) due the (contraction, expansion) of gases in the outer layer. 6. At the end of its life, a low mass star (1.4 SM) shrinks to become a ______________. 7. At the end, a very MASSIVE star will follow sequence: a. white dwarf, planetary nebula, neutron star b. red giant, supernova, black hole c. red giant, white dwarf 8. According to the H-R diagram, a white dwarf such ad Sirius is characterized by a. very cool, very dim b. really hot and really bright c. really hot, very dim 9. In the H-R diagram, the most massive stars are located in the (upper, lower), and on the (left, right) side of the table. 10. In the H-R diagram, the oldest stars are located in the (upper, lower), and on the (left, right) side of the table. 11. The stars with the highest luminosity are found in the (upper, lower), and on the (left, right) side of the table. 12. An average mass main sequence star will become a red giant when it runs out of ______________ fuel.