* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Life Cycle of a Star
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Nebular hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
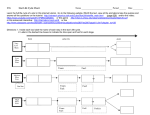
Life Cycle of a Star Notes using the foldable How long a star lives depends on the mass Life Cycle of a Star The smaller the stars, the longer the life because they use up their fuel more slowly Red Dwarf Red Giant White Dwarf Black Dwarf Nebula Protostar Yellow Star Blue Giant Red Super Giant Supernova Black Hole Neutron Star Nebula • All stars begin as parts of nebulas • A large cloud of gas and dust • large amount of gas in a small volume, very dense Protostar • The 1st stage of a star’s life • A contracting cloud of gas and dust • Pressure and heat start nuclear fusion Different Masses mean different types of stars Mass of star How long a star lives depends on how much mass it has A small mass star uses less fuel so it lasts longer so . . . The smaller the mass the longer it lasts Red Dwarf • A small mass star • Can last up to 200 billion years Yellow Star • A medium mass star • Our sun is a yellow star • Lives for 10 billion years Blue Giant • • • • A large mass star 10-15 times larger than the sun VERY hot Short lives because they have used up a lot of fuel Red Giant • • • • The star runs out of fuel outer parts expand, then the core shrinks It turns red as it is cooling This phase will last until the star exhausts its remaining fuel. • The pressure of the nuclear reaction is not strong enough to equalize the force of gravity so the star will collapse. Red Super Giant • The star runs out of fuel • The core shrinks and the outer parts expand • It turns red as it is cooling • This phase will last until the star exhausts its remaining fuel. • The pressure of the nuclear reaction is not strong enough to equalize the force of gravity so the star will collapse. White Dwarf • • • • • No more fuel left Faint glow from left over energy Outer parts drift out into space Small blue white hot core is left About the size of Earth Supernova • As the core shrinks, pressure increases • Results in an explosion Black Dwarf • When the white dwarf stops glowing it is dead\very dense Black Hole • Remains of explosion collapse into a black hole • Most large mass stars turn into black holes Neutron Star • After explosion some material left behind • Forms a neutron star • Dense and small