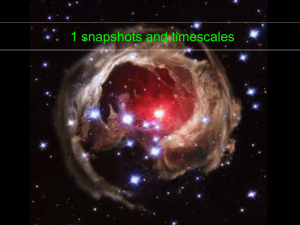
Stars
... Life Track After Main Sequence • Observations of star clusters show that a star becomes larger, redder, and more luminous after its time on the main sequence is over. • At the end of their main sequence life time - when hydrogen in the core is exhausted - stars ascend the red giant branch. © 2007 P ...
... Life Track After Main Sequence • Observations of star clusters show that a star becomes larger, redder, and more luminous after its time on the main sequence is over. • At the end of their main sequence life time - when hydrogen in the core is exhausted - stars ascend the red giant branch. © 2007 P ...
Testing the strong-field dynamics of general relativity with gravitional
... Analysis problem much harder From simulations that assume zero spins: 0.5% deviation at (v/c)6 beyond leading order can be seen (!) Work in progress ...
... Analysis problem much harder From simulations that assume zero spins: 0.5% deviation at (v/c)6 beyond leading order can be seen (!) Work in progress ...
Unit 1: The Foundations of Astronomy
... 1. Science builds upon itself over time. As new evidence arises and we acquire new understandings, old theories are revised or replaced by new ones. 2. Early astronomers tracked the motion of objects in the sky and used that information to describe the universe. 3. Mathematical tools and the use of ...
... 1. Science builds upon itself over time. As new evidence arises and we acquire new understandings, old theories are revised or replaced by new ones. 2. Early astronomers tracked the motion of objects in the sky and used that information to describe the universe. 3. Mathematical tools and the use of ...
Research Papers-Cosmology/Download/6307
... century the Earth hurried more than 1s in the year. After 1900 year, it was lagged less than 1s in the year. Since 1920 year she began again to hurry. ...
... century the Earth hurried more than 1s in the year. After 1900 year, it was lagged less than 1s in the year. Since 1920 year she began again to hurry. ...
The major properties of the Interstellar Medium (ISM) are described
... The interstellar medium is defined as the space between the stars. The average number of particles atoms, molecules and larger particles, in a cubic metre of interstellar space is only about one million. By comparison a cubic metre of gas in the lecture theatre contains about 1025 particles. Under t ...
... The interstellar medium is defined as the space between the stars. The average number of particles atoms, molecules and larger particles, in a cubic metre of interstellar space is only about one million. By comparison a cubic metre of gas in the lecture theatre contains about 1025 particles. Under t ...
Chapter 1 Introduction
... emission originates from the high excitation temperature region. This is true for both the red-shifted and blue-shifted side. In the infall case (panel a), however, only the red-shifted emission passes through the locus intersection in the low excitation temperature region, where part of the emissio ...
... emission originates from the high excitation temperature region. This is true for both the red-shifted and blue-shifted side. In the infall case (panel a), however, only the red-shifted emission passes through the locus intersection in the low excitation temperature region, where part of the emissio ...
Chapter 12: The Life Cycle of Stars (contʼd)
... • the period of a massive star's life when carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen are fusing in different shells outside the core • a type of hydrogen fusion that uses carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen atoms as catalysts • the process by which helium is fused into carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen • the perio ...
... • the period of a massive star's life when carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen are fusing in different shells outside the core • a type of hydrogen fusion that uses carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen atoms as catalysts • the process by which helium is fused into carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen • the perio ...
1 - Piscataway High School
... of the gas would weigh more than an automobile. In this degenerate matter, the pressure does not depend on temperature, and that means the pressure–temperature thermostat does not regulate energy production. When the temperature becomes hot enough, helium fusion begins to make energy, and the temper ...
... of the gas would weigh more than an automobile. In this degenerate matter, the pressure does not depend on temperature, and that means the pressure–temperature thermostat does not regulate energy production. When the temperature becomes hot enough, helium fusion begins to make energy, and the temper ...
Astro 102 Practice Test 3
... d. a measure of the ease with which photons can pass through a gas. e. the temperature and density at which a gas will undergo thermonuclear fusion. 8. As a star begin to form the initial energy source is from a. nuclear fusion. b. nuclear fission. c. gravitational potential energy. d. magnetic fiel ...
... d. a measure of the ease with which photons can pass through a gas. e. the temperature and density at which a gas will undergo thermonuclear fusion. 8. As a star begin to form the initial energy source is from a. nuclear fusion. b. nuclear fission. c. gravitational potential energy. d. magnetic fiel ...
chapter17StarStuff
... What happens in a low-mass star when core temperature rises enough for helium fusion to begin? A. Helium fusion slowly starts up B. Hydrogen fusion stops C. Helium fusion rises very sharply Hint: Degeneracy pressure is the main form of pressure in the inert helium core ...
... What happens in a low-mass star when core temperature rises enough for helium fusion to begin? A. Helium fusion slowly starts up B. Hydrogen fusion stops C. Helium fusion rises very sharply Hint: Degeneracy pressure is the main form of pressure in the inert helium core ...
High-Mass Star Formation
... L/M is 100x higher than estimates from CO and has a smaller dispersion L/M 2x higher for cores with UCHII and/or HII regions Lbol strongly correlates with Mvir. Combined with low dispersion of L/M perhaps indicates that mass of most massive star is related to the mass of the core ...
... L/M is 100x higher than estimates from CO and has a smaller dispersion L/M 2x higher for cores with UCHII and/or HII regions Lbol strongly correlates with Mvir. Combined with low dispersion of L/M perhaps indicates that mass of most massive star is related to the mass of the core ...
Stars - Emera Astronomy Center
... blue is hotter than yellow, and yellow is hotter than red. The Sun is much hotter than a candle flame. Unlike a candle, the Sun uses nuclear fusion as its energy source, not a chemical reaction like burning oil or wood. Stars are different colors because they are different temperatures. They are all ...
... blue is hotter than yellow, and yellow is hotter than red. The Sun is much hotter than a candle flame. Unlike a candle, the Sun uses nuclear fusion as its energy source, not a chemical reaction like burning oil or wood. Stars are different colors because they are different temperatures. They are all ...
A Hero`s Little Horse: Discovery of a Dissolving Star Cluster in
... Survey (York et al. 2000; Ahn et al. 2014) have significantly contributed to the discoveries of new stellar objects in the Milky Way halo including satellite galaxies (e.g Willman et al. 2005; Belokurov et al. 2006; Irwin et al. 2007; Walsh et al. 2007) and star clusters (Koposov et al. 2007; Beloku ...
... Survey (York et al. 2000; Ahn et al. 2014) have significantly contributed to the discoveries of new stellar objects in the Milky Way halo including satellite galaxies (e.g Willman et al. 2005; Belokurov et al. 2006; Irwin et al. 2007; Walsh et al. 2007) and star clusters (Koposov et al. 2007; Beloku ...
The coronal temperatures of low-mass main
... The mass dependence of coronal temperature in the saturated regime is an interesting consequence of the fact that coronal temperature depends on FX and not RX and can have consequences for the influence of stellar high-energy radiation on the upper atmospheres of planets. Given that the location of ...
... The mass dependence of coronal temperature in the saturated regime is an interesting consequence of the fact that coronal temperature depends on FX and not RX and can have consequences for the influence of stellar high-energy radiation on the upper atmospheres of planets. Given that the location of ...
Goal: To understand clusters of stars
... • Open clusters are YOUNG clusters that drift apart in about a billion years. • As viewed from Earth you tend to see the blue high mass stars. • Those are always young stars as they don’t last long. • These are clusters with stars of equal age, distance, and composition, but range in mass. ...
... • Open clusters are YOUNG clusters that drift apart in about a billion years. • As viewed from Earth you tend to see the blue high mass stars. • Those are always young stars as they don’t last long. • These are clusters with stars of equal age, distance, and composition, but range in mass. ...
Variable Stars – II. Pulsating stars
... In this case the star is unstable to pulsation and any small variation, will be reinforced – the pulsation will grow until the energy input by the κ-mechanism reaches a limit. The star will then be pulsating with a stable period and amplitude. Note that the partial ionization zones can be near the s ...
... In this case the star is unstable to pulsation and any small variation, will be reinforced – the pulsation will grow until the energy input by the κ-mechanism reaches a limit. The star will then be pulsating with a stable period and amplitude. Note that the partial ionization zones can be near the s ...
Wandering in the Redshift Desert
... helps to go into the near-infrared. Figures 8 and 9 are analogous to the previNTR SVN jFTQDR ATS 2%1 @MC M* are now plotted v. the J-band magnitude instead of the B-band. Clearly, whereas a B < 25 mag selection misses most of the SFR and most of the stellar mass at zp] @ J < 24 mag selection would p ...
... helps to go into the near-infrared. Figures 8 and 9 are analogous to the previNTR SVN jFTQDR ATS 2%1 @MC M* are now plotted v. the J-band magnitude instead of the B-band. Clearly, whereas a B < 25 mag selection misses most of the SFR and most of the stellar mass at zp] @ J < 24 mag selection would p ...