3.2 Black body Radiation
... space astronomy - is an extremely important part of modern astronomy which has fantastically enriched our view of the universe over the past few decades. However, space astronomy is very expensive and difficult to carry out. ...
... space astronomy - is an extremely important part of modern astronomy which has fantastically enriched our view of the universe over the past few decades. However, space astronomy is very expensive and difficult to carry out. ...
here - NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database
... (atomic weight less than 30), such as carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen (Maeder 1981, Sparke & Gallagher 2000). During their red supergiant phase, massive stars also make a significant contribution to the dust content, particularly for star-burst systems and galaxies at large look-back times where AGBs h ...
... (atomic weight less than 30), such as carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen (Maeder 1981, Sparke & Gallagher 2000). During their red supergiant phase, massive stars also make a significant contribution to the dust content, particularly for star-burst systems and galaxies at large look-back times where AGBs h ...
Time, quantum and information
... into one helium-4 nucleus is accompanied by a mass loss of 0.71 per cent of the initial masses, or 0.029 u. It is converted into an energy of about 26.2 MeV, including the annihilation energy of the two positrons that are produced, and the energy that is carried away by two electron neutrinos. From ...
... into one helium-4 nucleus is accompanied by a mass loss of 0.71 per cent of the initial masses, or 0.029 u. It is converted into an energy of about 26.2 MeV, including the annihilation energy of the two positrons that are produced, and the energy that is carried away by two electron neutrinos. From ...
PowerPoint
... Tunnel to another universe, or another part of our own? No: Wormhole throat is unstable, and pinches off Once you fall through one horizon, you can’t come out through another Also: Stellar collapse to a black hole does not produce a wormhole So: mathematically allowed, but unphysical in general rela ...
... Tunnel to another universe, or another part of our own? No: Wormhole throat is unstable, and pinches off Once you fall through one horizon, you can’t come out through another Also: Stellar collapse to a black hole does not produce a wormhole So: mathematically allowed, but unphysical in general rela ...
arXiv:astro-ph/0508448v1 22 Aug 2005
... stars. One system is known in which there is strong evidence for an origin through the dynamical ejection scenario. AE Aur and µ Col are both O9.5V stars with similar ages which are running away in opposite directions with velocities relative to the local standard of rest of 113.3 and 107.8 kms−1 re ...
... stars. One system is known in which there is strong evidence for an origin through the dynamical ejection scenario. AE Aur and µ Col are both O9.5V stars with similar ages which are running away in opposite directions with velocities relative to the local standard of rest of 113.3 and 107.8 kms−1 re ...
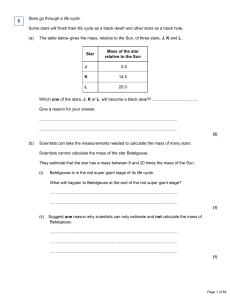
Stars go through a life cycle. Some stars will finish their life cycle as
... In this question you will be assessed on using good English, organising information clearly and using specialist terms where appropriate. Describe what happens to a star much bigger than the Sun, once the star reaches the end of the ‘main sequence’ period of its life cycle. Your answer should includ ...
... In this question you will be assessed on using good English, organising information clearly and using specialist terms where appropriate. Describe what happens to a star much bigger than the Sun, once the star reaches the end of the ‘main sequence’ period of its life cycle. Your answer should includ ...
A re-appraisal of the habitability of planets around M dwarf
... provide, within a few years thereafter, the demographics of terrestrial-size planets within the HZs of stars as a function of spectral type, from F to at least M5 dwarfs. The Allen Telescope Array is currently under construction in Northern California (http://astron. berkeley.edu/ral/ata/), and effi ...
... provide, within a few years thereafter, the demographics of terrestrial-size planets within the HZs of stars as a function of spectral type, from F to at least M5 dwarfs. The Allen Telescope Array is currently under construction in Northern California (http://astron. berkeley.edu/ral/ata/), and effi ...
A Reappraisal of The Habitability of Planets around M Dwarf Stars
... provide, within a few years thereafter, the demographics of terrestrial-size planets within the HZs of stars as a function of spectral type, from F to at least M5 dwarfs. The Allen Telescope Array is currently under construction in Northern California (http://astron. berkeley.edu/ral/ata/), and effi ...
... provide, within a few years thereafter, the demographics of terrestrial-size planets within the HZs of stars as a function of spectral type, from F to at least M5 dwarfs. The Allen Telescope Array is currently under construction in Northern California (http://astron. berkeley.edu/ral/ata/), and effi ...
Sample pages 1 PDF
... there is an exchange of material between the core and the photospheres in such stars due to the nature of their convective cores. Some AGB stars have photospheres that are heavily obscured by carbon dust, which indicates the nature of their cores. Others have high incidences of oxygen and the spectr ...
... there is an exchange of material between the core and the photospheres in such stars due to the nature of their convective cores. Some AGB stars have photospheres that are heavily obscured by carbon dust, which indicates the nature of their cores. Others have high incidences of oxygen and the spectr ...
The Hipparcos Star Globe Booklet - Cosmos
... cluster, the ‘jaw’ of the bull in the Taurus constellation. The data showed that some of the stars that were apparently part of this cluster were impostors: they are not in fact travelling with the cluster, and over time will part company with its true members. ...
... cluster, the ‘jaw’ of the bull in the Taurus constellation. The data showed that some of the stars that were apparently part of this cluster were impostors: they are not in fact travelling with the cluster, and over time will part company with its true members. ...
Chapter15- Our Galaxy-pptx - SFA Physics and Astronomy
... Lower-mass stars return gas to interstellar space through stellar winds and planetary nebulae. © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... Lower-mass stars return gas to interstellar space through stellar winds and planetary nebulae. © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
QUESTION
... • ANSWER: Sequence that an average size star goes through late in its life • QUESTION: What is red giant – white dwarf – black dwarf? ...
... • ANSWER: Sequence that an average size star goes through late in its life • QUESTION: What is red giant – white dwarf – black dwarf? ...
Asteroseismic constraints on Asymmetric Dark Matter: Light particles
... For comparison of ADM and WIMP accumulation, figures 1a and 1b show analytical approximations to the present solar fraction of the number of trapped DM particles in the ADM scenario relative to the WIMP picture. The number of ADM particles trapped inside the Sun is greater than that of WIMPs by a fa ...
... For comparison of ADM and WIMP accumulation, figures 1a and 1b show analytical approximations to the present solar fraction of the number of trapped DM particles in the ADM scenario relative to the WIMP picture. The number of ADM particles trapped inside the Sun is greater than that of WIMPs by a fa ...
Carbon Stars - The OzSky Star Safari
... off in different colors. Hot stars give off more blue light than red; cool stars give off more red light than blue. • Colored filters are used to measure different wavelengths of light from stars. The magnitude of the star is measured first through a standardized blue (B‐ band) filter and then t ...
... off in different colors. Hot stars give off more blue light than red; cool stars give off more red light than blue. • Colored filters are used to measure different wavelengths of light from stars. The magnitude of the star is measured first through a standardized blue (B‐ band) filter and then t ...
Metal-poor Stars
... processes. The main indicator used to determine stellar metallicity is the iron abundance, [Fe/H], which is defined as [A/B]= log10 (NA/NB )? −log10(NA /NB ) for the number N of atoms of elements A and B, and refers to the Sun. With few exceptions, [Fe/H] traces the overall metallicity of the obj ...
... processes. The main indicator used to determine stellar metallicity is the iron abundance, [Fe/H], which is defined as [A/B]= log10 (NA/NB )? −log10(NA /NB ) for the number N of atoms of elements A and B, and refers to the Sun. With few exceptions, [Fe/H] traces the overall metallicity of the obj ...
13 – Synthesis of heavier elements
... What happens to low mass stars? Low mass stars (< 2.3 M¤) can leave the main sequence (MS) after the hydrogen burning stops. - The hydrogen shell increases and the star leaves the MS in the HR diagram (going up). - Its core shrinks, and the outer layers expand and cool. Its luminosity increases. ...
... What happens to low mass stars? Low mass stars (< 2.3 M¤) can leave the main sequence (MS) after the hydrogen burning stops. - The hydrogen shell increases and the star leaves the MS in the HR diagram (going up). - Its core shrinks, and the outer layers expand and cool. Its luminosity increases. ...
Supernovae and Gamma-Ray Bursts (draft)
... Unfortunately, there are many further complications going beyond this simple scheme. The progenitor of supernova 1987A (SN 1987A, see § 4) had a large H-rich envelope, but did not have an extended plateau phase (see Fig. 3) and therefore SN 1987A defines a class of its own. Other supernovae appear t ...
... Unfortunately, there are many further complications going beyond this simple scheme. The progenitor of supernova 1987A (SN 1987A, see § 4) had a large H-rich envelope, but did not have an extended plateau phase (see Fig. 3) and therefore SN 1987A defines a class of its own. Other supernovae appear t ...
Lecture 9: The interstellar medium (ISM)
... • Cloud mass may be ~ 103 M⊙ • Cloud size ~ 10 pc • Dense molecular clouds are often very dusty ...
... • Cloud mass may be ~ 103 M⊙ • Cloud size ~ 10 pc • Dense molecular clouds are often very dusty ...
Gaps
... • Fast HB rotation, although maybe not present in all clusters, is a fairly common feature. ...
... • Fast HB rotation, although maybe not present in all clusters, is a fairly common feature. ...
Galaxy Sorting
... galaxies contain mostly old stars, with very little gas and dust found between stars. Since new stars form from clouds of interstellar gas and dust, elliptical galaxies lack the raw ingredients to make new stars. Spiral galaxies, on the other hand, have a mix of young and old stars. Interstellar ...
... galaxies contain mostly old stars, with very little gas and dust found between stars. Since new stars form from clouds of interstellar gas and dust, elliptical galaxies lack the raw ingredients to make new stars. Spiral galaxies, on the other hand, have a mix of young and old stars. Interstellar ...
CH15.AST1001.F16.EDS
... remnant cools and begins to emit visible light as it expands. New elements made by supernova mix into interstellar medium. © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... remnant cools and begins to emit visible light as it expands. New elements made by supernova mix into interstellar medium. © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Stellar populations in the nuclear regions of nearby radio galaxies
... q 2001 RAS, MNRAS 325, 636–648 ...
... q 2001 RAS, MNRAS 325, 636–648 ...
ph507weeks1
... parallax accuracy to 0.001” within a few years. Before 1990, fewer than 10,000 stellar parallaxes had been measured (and only 500 known well), but there are about 1012 stars in our Galaxy. Space observations made by the European Space Agency with the Hipparcos mission (1989-1993) accurately determin ...
... parallax accuracy to 0.001” within a few years. Before 1990, fewer than 10,000 stellar parallaxes had been measured (and only 500 known well), but there are about 1012 stars in our Galaxy. Space observations made by the European Space Agency with the Hipparcos mission (1989-1993) accurately determin ...
1 Introduction - High Point University
... (Dwarfs (V)) is known as the main sequence and contains all stars that are fusing hydrogen into helium as their primary energy source. Over 90% of all stars fall in this region on the H-R diagram. Move the active cursor up and down the main sequence and explore the different values of stellar radius ...
... (Dwarfs (V)) is known as the main sequence and contains all stars that are fusing hydrogen into helium as their primary energy source. Over 90% of all stars fall in this region on the H-R diagram. Move the active cursor up and down the main sequence and explore the different values of stellar radius ...