BRC_prop1 - CoolWiki
... and dust found in abundance within disk components of spiral galaxies. Star formation may be triggered in a molecular cloud that is already contracting by shock waves from a variety of sources, including explosion of supernovae, ignition of a very hot star nearby, collision with another molecular cl ...
... and dust found in abundance within disk components of spiral galaxies. Star formation may be triggered in a molecular cloud that is already contracting by shock waves from a variety of sources, including explosion of supernovae, ignition of a very hot star nearby, collision with another molecular cl ...
Observational properties of stars
... Therefore “hot” objects are blue while “cool” objects are red. It is also worth noting that even though you can’t see it, black body energy is given off at all wavelengths, from those close to =0 to the longest wavelength. It is just that often the energy output at those wavelengths are too low to b ...
... Therefore “hot” objects are blue while “cool” objects are red. It is also worth noting that even though you can’t see it, black body energy is given off at all wavelengths, from those close to =0 to the longest wavelength. It is just that often the energy output at those wavelengths are too low to b ...
A-level Physics (Specification A) Teacher guide Teacher guide
... the light year and parsec. How the temperature of a star is measured is then described, before combining luminosity and temperature in the Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram. The different types of stars – and other astronomical objects – is then put in a context of observable properties rather than ...
... the light year and parsec. How the temperature of a star is measured is then described, before combining luminosity and temperature in the Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram. The different types of stars – and other astronomical objects – is then put in a context of observable properties rather than ...
Is the central binary system of the planetary nebula Henize 2
... in Abell 48 whose central star is a WN star (Todt et al., 2013). Most interestingly, in the study by Weidmann and Gamen (2011) there are several PNe that show a wide He II 5412 Å absorption line with a weak emission feature in the center of the wide absorption line. This forms a spectral structure ...
... in Abell 48 whose central star is a WN star (Todt et al., 2013). Most interestingly, in the study by Weidmann and Gamen (2011) there are several PNe that show a wide He II 5412 Å absorption line with a weak emission feature in the center of the wide absorption line. This forms a spectral structure ...
Leverhulme lectures on stellar magnetism. 1. Overview
... For detailed study of stars, spectra are particularly powerful data because of rich information content of lines Spectral lines arise from atomic transitions between two energy states or levels Detection of magnetic field is possible because energy levels of atoms and ions are perturbed by a field, ...
... For detailed study of stars, spectra are particularly powerful data because of rich information content of lines Spectral lines arise from atomic transitions between two energy states or levels Detection of magnetic field is possible because energy levels of atoms and ions are perturbed by a field, ...
Is Draco II one of the faintest dwarf galaxies? First study from Keck
... equivalent width measurements). Therefore, we are left to conclude that Dra II is not only a metal-poor system, but also has a metallicity dispersion. Going further and estimating tentative metallicity values for stars 2 and 10 via equation (A.1) of Starkenburg et al. (2010) for I-band magnitudes 2 ...
... equivalent width measurements). Therefore, we are left to conclude that Dra II is not only a metal-poor system, but also has a metallicity dispersion. Going further and estimating tentative metallicity values for stars 2 and 10 via equation (A.1) of Starkenburg et al. (2010) for I-band magnitudes 2 ...
An Eclectic View of our Milky Way Galaxy
... latter may be associated with the Hubble flow, while the former are clearly influenced by the gravitational influence of M31. An independent solution for the local circular velocity was derived by Reid et al. [42] using the positions, parallaxes, and proper motions of Galactic radio masers in conjun ...
... latter may be associated with the Hubble flow, while the former are clearly influenced by the gravitational influence of M31. An independent solution for the local circular velocity was derived by Reid et al. [42] using the positions, parallaxes, and proper motions of Galactic radio masers in conjun ...
Physics of Star Formation: Milky Way and Beyond
... binaries best explains our observations. Based on this simple model, we predict that the timescale for wide binaries to shrink into tight orbits is similar to the Class 0 lifetime and the timescale for the wide binaries to breakup into individual stars is half the Class 0 lifetime. We also obtain a ...
... binaries best explains our observations. Based on this simple model, we predict that the timescale for wide binaries to shrink into tight orbits is similar to the Class 0 lifetime and the timescale for the wide binaries to breakup into individual stars is half the Class 0 lifetime. We also obtain a ...
2_ISM - UCT Astronomy Department
... - derived from looking at pairs of stellar spectra with similar temperatures but different foreground extinctions. - The general extinction curve within each of the Milky Way, LMC, and SMC is fairly well defined - The overall increase to shorter wavelengths (approximately with absorption in magnitud ...
... - derived from looking at pairs of stellar spectra with similar temperatures but different foreground extinctions. - The general extinction curve within each of the Milky Way, LMC, and SMC is fairly well defined - The overall increase to shorter wavelengths (approximately with absorption in magnitud ...
printer-friendly version of benchmark
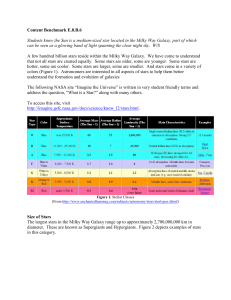
... Data about the luminosity and temperature of stars is typically plotted as a Hertzsprung-Russell (HR) diagram. As evidenced in Figure 5, most stars fall within the Main Sequence of this diagram. It is where the stars spend the majority of their evolutionary history. This particular diagram also show ...
... Data about the luminosity and temperature of stars is typically plotted as a Hertzsprung-Russell (HR) diagram. As evidenced in Figure 5, most stars fall within the Main Sequence of this diagram. It is where the stars spend the majority of their evolutionary history. This particular diagram also show ...
Discovery of White Dwarfs—8 Oct
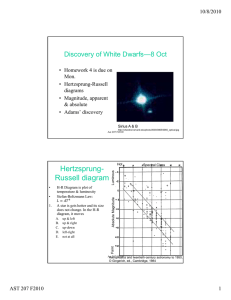
... Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram of nearby stars 1. Stars in region X are A. Dwarfs B. Giants C. White dwarfs ...
... Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram of nearby stars 1. Stars in region X are A. Dwarfs B. Giants C. White dwarfs ...
Extragalactic Distances from Planetary Nebulae
... The real problem comes from the absolute luminosity of the PNLF cutoff … M* = 4.47 corresponds to a luminosity of 600 L To produce 600 L of [O III] emission, a central star must have a luminosity of L > 6,000 L. A central star with L > 6,000 L must be more massive than M > 0.6 M. Such st ...
... The real problem comes from the absolute luminosity of the PNLF cutoff … M* = 4.47 corresponds to a luminosity of 600 L To produce 600 L of [O III] emission, a central star must have a luminosity of L > 6,000 L. A central star with L > 6,000 L must be more massive than M > 0.6 M. Such st ...
PDF format
... a) radiation from the supermassive black hole at the galactic center b) radiation from dense globular clusters in the galactic halo c) radiation from supernova explosions d) radiation from black hole accretion disks e) all of the above © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... a) radiation from the supermassive black hole at the galactic center b) radiation from dense globular clusters in the galactic halo c) radiation from supernova explosions d) radiation from black hole accretion disks e) all of the above © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
18th Cambridge Workshop on Cool Stars, Stellar Systems, and the... Proceedings of Lowell Observatory (9-13 June 2014)
... Julien Morin (University of Montpellier, France) In the next talk, Julien Morin presented a brief review of cool stars’ magnetic fields, the underlying engine of space weather phenomena. Cool stars generate their magnetic fields through dynamo action, hence their properties appear to correlate – at ...
... Julien Morin (University of Montpellier, France) In the next talk, Julien Morin presented a brief review of cool stars’ magnetic fields, the underlying engine of space weather phenomena. Cool stars generate their magnetic fields through dynamo action, hence their properties appear to correlate – at ...
3. Cosmology and the Origin and Evolution of Galaxies
... confusion-limited surveys and larger-area, shallower surveys of the high-redshift universe at mm wavelengths. Together with complementary multi-wavelength observations, these data will (i) identify the individual galaxies that supply that part of the FIR-mm background (~ 50% of the integrated energy ...
... confusion-limited surveys and larger-area, shallower surveys of the high-redshift universe at mm wavelengths. Together with complementary multi-wavelength observations, these data will (i) identify the individual galaxies that supply that part of the FIR-mm background (~ 50% of the integrated energy ...
The Galactic evolution of phosphorus
... Fig. 2. [P/Fe] as a function of the metallicity, [Fe/H]. The dimension of the symbols reflects the average line-to-line scatter of 0.045 dex. The error bars are the sum under quadrature of the uncertainties of P (the linear sum of line-to-line scatter and the systematic uncertainty) and of Fe, the l ...
... Fig. 2. [P/Fe] as a function of the metallicity, [Fe/H]. The dimension of the symbols reflects the average line-to-line scatter of 0.045 dex. The error bars are the sum under quadrature of the uncertainties of P (the linear sum of line-to-line scatter and the systematic uncertainty) and of Fe, the l ...
Origins: List of Evidences
... nothing before the universe. The universe came into being out of nothing, not even space or time. "17.6 The Origin of the Universe - If the universe is expanding, then it must have once been much smaller. If you could run the life of the universe in reverse, like a film, you would see the universe c ...
... nothing before the universe. The universe came into being out of nothing, not even space or time. "17.6 The Origin of the Universe - If the universe is expanding, then it must have once been much smaller. If you could run the life of the universe in reverse, like a film, you would see the universe c ...
The APEX Telescope Large Area Survey of the Galaxy (ATLASGAL)
... their ionisation fronts. Another five show 6.7 GHz methanol masers, tracers of very young embedded high-mass proto stars, in similar condensations. The conclusion from this study is that more than a quarter of the bubbles could have triggered the formation of massive objects. Star formation trigger ...
... their ionisation fronts. Another five show 6.7 GHz methanol masers, tracers of very young embedded high-mass proto stars, in similar condensations. The conclusion from this study is that more than a quarter of the bubbles could have triggered the formation of massive objects. Star formation trigger ...
Energy Production in Stars
... as are found in the interior of ordinary stars. The lighter elements (Li, Be, B) would "burn" in a very short time and are not replaced as is carbon in the cycle (2), whereas the heavier elements (0, F, etc.) react too slowly. Helium, which is abundant, does not react with protons because the produc ...
... as are found in the interior of ordinary stars. The lighter elements (Li, Be, B) would "burn" in a very short time and are not replaced as is carbon in the cycle (2), whereas the heavier elements (0, F, etc.) react too slowly. Helium, which is abundant, does not react with protons because the produc ...
Ch 20 Stellar Evolution
... flash before the star is once again in equilibrium. • The star develops a nonburning carbon core, surrounded by shells burning helium and hydrogen. • The shell expands into a planetary nebula, and the core is visible as a white dwarf. • The nebula dissipates, and the white dwarf gradually cools o ...
... flash before the star is once again in equilibrium. • The star develops a nonburning carbon core, surrounded by shells burning helium and hydrogen. • The shell expands into a planetary nebula, and the core is visible as a white dwarf. • The nebula dissipates, and the white dwarf gradually cools o ...