Enhanced lithium depletion in Sun-like stars with orbiting planets.
... 451 stars in the HARPS high precision (better than 1 m/s) radial velocity exoplanet survey11 spanning the effective temperature range between 4900 and 6500 K. These are unevolved, slowly rotating non-active stars from a CORALIE catalogue11. These stars have been monitored with high precision spectro ...
... 451 stars in the HARPS high precision (better than 1 m/s) radial velocity exoplanet survey11 spanning the effective temperature range between 4900 and 6500 K. These are unevolved, slowly rotating non-active stars from a CORALIE catalogue11. These stars have been monitored with high precision spectro ...
Galaxies and their properties
... Increasing λ from ∼ 0.05 to λ ∼ 0.5 thus requires a contraction by a factor of Ri /R ∼ 100. Consider a galaxy like the Milky way, with mass M ∼ 5 × 1010 M⊙ , and R ∼ 10 kpc. Since for the Milky Way λ ≈ 0.425, the radius of the initial cloud must have been 70 times larger than its current radius, or ...
... Increasing λ from ∼ 0.05 to λ ∼ 0.5 thus requires a contraction by a factor of Ri /R ∼ 100. Consider a galaxy like the Milky way, with mass M ∼ 5 × 1010 M⊙ , and R ∼ 10 kpc. Since for the Milky Way λ ≈ 0.425, the radius of the initial cloud must have been 70 times larger than its current radius, or ...
Examining the M67 Classification as an Open Cluster
... in the galactic field the total internal energy of a cluster should rise, ultimately leading to a complete breakup of the cluster. It turned out that the characteristic time for this process of destruction of dense stellar clusters is at most 1010 yr. Spitzer [16,17] has calculated the increase of e ...
... in the galactic field the total internal energy of a cluster should rise, ultimately leading to a complete breakup of the cluster. It turned out that the characteristic time for this process of destruction of dense stellar clusters is at most 1010 yr. Spitzer [16,17] has calculated the increase of e ...
Chapter 4 Hydrostatic Equilibrium
... • If hydrostatic equilibrium were not satisfied we would expect to see changes in a matter of hours, but the fossil record indicates that the Sun has been extremely stable for billions of years. • We conclude that the Sun is in very good hydrostatic equilibrium. In Table 4.2 we illustrate the hydrod ...
... • If hydrostatic equilibrium were not satisfied we would expect to see changes in a matter of hours, but the fossil record indicates that the Sun has been extremely stable for billions of years. • We conclude that the Sun is in very good hydrostatic equilibrium. In Table 4.2 we illustrate the hydrod ...
Stellar Explosions
... Nickel-56 is unstable and quickly decays to cobalt-56 which subsequently decays into iron-56 Iron-56 is the most stable nucleus, so it neither fuses nor decays Within the cores of the most massive stars, neutron capture can create heavier elements, all the way up to bismuth-209 The heaviest elements ...
... Nickel-56 is unstable and quickly decays to cobalt-56 which subsequently decays into iron-56 Iron-56 is the most stable nucleus, so it neither fuses nor decays Within the cores of the most massive stars, neutron capture can create heavier elements, all the way up to bismuth-209 The heaviest elements ...
Astronomy and Astrophysics (ASTRO)
... For the nonscientist. A survey of our view of the universe, and the exploration of the solar system and beyond. The sky: constellations; motions of the Sun, Moon, and planets; seasons and the calendar; eclipses. The solar system: origin and evolution; characteristics of the Sun, planets, satellites, ...
... For the nonscientist. A survey of our view of the universe, and the exploration of the solar system and beyond. The sky: constellations; motions of the Sun, Moon, and planets; seasons and the calendar; eclipses. The solar system: origin and evolution; characteristics of the Sun, planets, satellites, ...
Stars as thermonuclear reactors: their fuels and ashes
... the Big Bang, contains many more photons per particle of matter with mass, e.g. electrons, protons and neutrons. Because of the high entropy and the consequent low density of matter (on terrestrial or stellar scales) at any given temperature as the universe expanded, there was time to manufacture el ...
... the Big Bang, contains many more photons per particle of matter with mass, e.g. electrons, protons and neutrons. Because of the high entropy and the consequent low density of matter (on terrestrial or stellar scales) at any given temperature as the universe expanded, there was time to manufacture el ...
Document
... observed in the interstellar medium • Many complex molecules have been observed, including progenitors of the basic amino acids required to build life • These complex molecules can only survive in space when they are shielded by dense, dark, giant clouds containing dust • These giant clouds are inte ...
... observed in the interstellar medium • Many complex molecules have been observed, including progenitors of the basic amino acids required to build life • These complex molecules can only survive in space when they are shielded by dense, dark, giant clouds containing dust • These giant clouds are inte ...
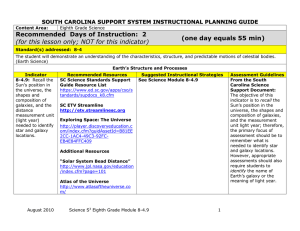
8-4.9 - S2TEM Centers SC
... and others are not. All galaxies, however, are composed of stars, dust, and gas. Tell students that they are going to sort or order the cards based on some trait or characteristic the cards have in common. They can sort their cards into groups based on similarities in the shapes or color of the gala ...
... and others are not. All galaxies, however, are composed of stars, dust, and gas. Tell students that they are going to sort or order the cards based on some trait or characteristic the cards have in common. They can sort their cards into groups based on similarities in the shapes or color of the gala ...
The accretion disk paradigm for young stars
... of a number of these objects, now known as YY Ori stars after their prototype, and had noticed the presence of red-displaced, highly variable absorption components in the Balmer lines of these objects, indicating infall velocity of up to 400 km/s. In these spectra the Balmer jump is clearly in emiss ...
... of a number of these objects, now known as YY Ori stars after their prototype, and had noticed the presence of red-displaced, highly variable absorption components in the Balmer lines of these objects, indicating infall velocity of up to 400 km/s. In these spectra the Balmer jump is clearly in emiss ...
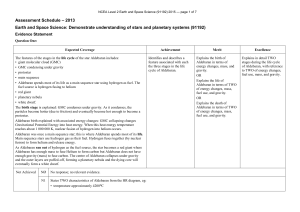
NCEA Level 2 Earth and Space Science (91192)
... fuel source is hydrogen fusing to helium • red giant • planetary nebula • white dwarf. The birth stage is explained: GMC condenses under gravity. As it condenses, the particles become hotter (due to friction) and eventually become hot enough to become a protostar. Aldebaran birth explained with asso ...
... fuel source is hydrogen fusing to helium • red giant • planetary nebula • white dwarf. The birth stage is explained: GMC condenses under gravity. As it condenses, the particles become hotter (due to friction) and eventually become hot enough to become a protostar. Aldebaran birth explained with asso ...
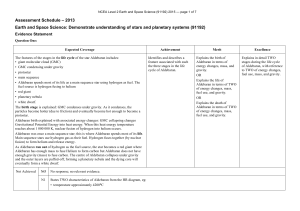
NCEA Level 2 Earth and Space Science (91192) 2013
... fuel source is hydrogen fusing to helium • red giant • planetary nebula • white dwarf. The birth stage is explained: GMC condenses under gravity. As it condenses, the particles become hotter (due to friction) and eventually become hot enough to become a protostar. Aldebaran birth explained with asso ...
... fuel source is hydrogen fusing to helium • red giant • planetary nebula • white dwarf. The birth stage is explained: GMC condenses under gravity. As it condenses, the particles become hotter (due to friction) and eventually become hot enough to become a protostar. Aldebaran birth explained with asso ...
PH607lec08
... The surface brightness within the bar is often fairly constant. Some bars appear to be ‘squared off’ at the ends. The true 3-D shapes of bars are difficult to determine, but many appear to be no thicker than the disks ...
... The surface brightness within the bar is often fairly constant. Some bars appear to be ‘squared off’ at the ends. The true 3-D shapes of bars are difficult to determine, but many appear to be no thicker than the disks ...
PDF
... Ground-based astrometry still has many science goals to pursue on its own. All current and future planned large-scale deep faster surveys of the sky, e.g. VISTA, LSST, PanSTARR, etc., can extend Gaia’s faint limit and obtain proper motion errors from 0.1 to 1 mas/year and parallax errors from 0.5 to ...
... Ground-based astrometry still has many science goals to pursue on its own. All current and future planned large-scale deep faster surveys of the sky, e.g. VISTA, LSST, PanSTARR, etc., can extend Gaia’s faint limit and obtain proper motion errors from 0.1 to 1 mas/year and parallax errors from 0.5 to ...
Edexcel GCE - The Student Room
... All quasars show large red shifts in the light received from them. This shows that they A ...
... All quasars show large red shifts in the light received from them. This shows that they A ...
Evolution of galaxy morphology - Lecture 1 - NCRA-TIFR
... Cosmology and Extragalactic astrophysics - 5510 papers in 2013 ...
... Cosmology and Extragalactic astrophysics - 5510 papers in 2013 ...
Hidden57_rf
... orbiting observatories have produced a wondrous and often breathtakingly beautiful view of a Universe whose richness could not have been imagined. A string of new discoveries has come from this fleet of new space-based instruments and observatories, and each new insight has been firmly placed into t ...
... orbiting observatories have produced a wondrous and often breathtakingly beautiful view of a Universe whose richness could not have been imagined. A string of new discoveries has come from this fleet of new space-based instruments and observatories, and each new insight has been firmly placed into t ...
Neutron Stars
... Note that M is independent of ρc and R in the ultra-relativistic limit. Thus as ρc → ∞, the electrons become more and more relativistic throughout the star, then R → 0 and the mass asymptotically will be given by equation (47). The mass limit (47) is called Chandrasekhar limit (MCh = 1.457M ) and i ...
... Note that M is independent of ρc and R in the ultra-relativistic limit. Thus as ρc → ∞, the electrons become more and more relativistic throughout the star, then R → 0 and the mass asymptotically will be given by equation (47). The mass limit (47) is called Chandrasekhar limit (MCh = 1.457M ) and i ...
Lec10_ch12_deathofstars
... Remains of the Low-Mass Star • After outer layers ejected in planetary nebula and solar wind, all that remains is the hot, dense carbon-oxygen core--a white dwarf! • Fusion has ceased, and core cools down over billions of years • White dwarf mass < 1.4 Msun due to Chandrasekhar limit – Degenerate e ...
... Remains of the Low-Mass Star • After outer layers ejected in planetary nebula and solar wind, all that remains is the hot, dense carbon-oxygen core--a white dwarf! • Fusion has ceased, and core cools down over billions of years • White dwarf mass < 1.4 Msun due to Chandrasekhar limit – Degenerate e ...
Life Stages of High
... • This double-shell burning stage never reaches equilibrium—fusion rate periodically spikes upward in a series of thermal pulses ...
... • This double-shell burning stage never reaches equilibrium—fusion rate periodically spikes upward in a series of thermal pulses ...
SRMP Stars Curriculum - American Museum of Natural History
... ACTIVITY: Stellar Temperature and Distance In this activity, students will be given two tables of data – one of nearby stars, and one of bright stars in our sky. There is some overlap in stars, but most of them are separate. The table includes each star’s name, spectral type, apparent and absolute m ...
... ACTIVITY: Stellar Temperature and Distance In this activity, students will be given two tables of data – one of nearby stars, and one of bright stars in our sky. There is some overlap in stars, but most of them are separate. The table includes each star’s name, spectral type, apparent and absolute m ...
Indications for an influence of Hot Jupiters
... through broadband light curve modulations. The projected stellar rotation velocity v sin i is easy to observe, but is an ambiguous measurement of stellar rotation if the stellar inclination is unknown. The planet-hosting stars in our sample, which are the primaries in their respective system, are we ...
... through broadband light curve modulations. The projected stellar rotation velocity v sin i is easy to observe, but is an ambiguous measurement of stellar rotation if the stellar inclination is unknown. The planet-hosting stars in our sample, which are the primaries in their respective system, are we ...