Procedurally Generating an Artificial Galaxy
... Instead of having artists design everything in the virtual world of a videogame or a CGI sequence in a movie, certain aspects can be handed over to algorithms for procedural generation. This can either be done beforehand or as the scene plays out. It can be as simple as generating numbers that deter ...
... Instead of having artists design everything in the virtual world of a videogame or a CGI sequence in a movie, certain aspects can be handed over to algorithms for procedural generation. This can either be done beforehand or as the scene plays out. It can be as simple as generating numbers that deter ...
AGN surveys to study galaxy evolution along cosmic times
... ∼93%, which were used for calculating the AGN luminosity function and X-ray absorption distribution. Malizia et al. (2012) have studied the fraction of Compton-thick sources in an INTEGRAL complete AGN sample. Assuming as a dividing line between absorbed and unabsorbed AGN a column density of NH =10 ...
... ∼93%, which were used for calculating the AGN luminosity function and X-ray absorption distribution. Malizia et al. (2012) have studied the fraction of Compton-thick sources in an INTEGRAL complete AGN sample. Assuming as a dividing line between absorbed and unabsorbed AGN a column density of NH =10 ...
3P15.pdf
... all the stars of the sample, the mean value of the excess emission of the Hα line vs. the mean value of the excess emission of other chromospheric lines (Ca II λ8542Å, Ca II K, Hβ and Hγ). Fig. 4b to 7b show the same but only for the flare stars of this work and Fig. 8 and 9 include the He I D3 and ...
... all the stars of the sample, the mean value of the excess emission of the Hα line vs. the mean value of the excess emission of other chromospheric lines (Ca II λ8542Å, Ca II K, Hβ and Hγ). Fig. 4b to 7b show the same but only for the flare stars of this work and Fig. 8 and 9 include the He I D3 and ...
Stellar Structure and Evolution II
... Life Stages of High-Mass Stars • Late life stages of high-mass stars are similar to those of low-mass stars: – Hydrogen core fusion (main sequence) – Hydrogen shell burning (supergiant) – Helium core fusion (supergiant) ...
... Life Stages of High-Mass Stars • Late life stages of high-mass stars are similar to those of low-mass stars: – Hydrogen core fusion (main sequence) – Hydrogen shell burning (supergiant) – Helium core fusion (supergiant) ...
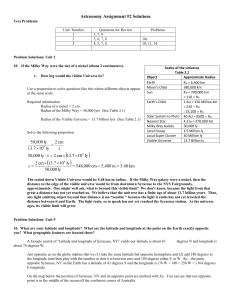
Astronomy Assignment #1
... declinations of +87, -40, and -67. Which of these objects can you observe? This question requires a fairly complete understanding of the celestial coordinate system and the celestial sphere model. According to the last sentence on page 43 “if a star’s declination matches your latitude it will pas ...
... declinations of +87, -40, and -67. Which of these objects can you observe? This question requires a fairly complete understanding of the celestial coordinate system and the celestial sphere model. According to the last sentence on page 43 “if a star’s declination matches your latitude it will pas ...
Summer 2004 ISP 205: Visions of the Universe Professor: ER Capriotti Sample Questions
... C. believed the Earth went around the Sun. D. made very accurate predictions of planetary motion. E. believed the Sun went around the Earth. 22. The Copernican universe has in order of increasing distance from the sun A. Mercury, Venus, Mars, Earth, Jupiter, Saturn. B. Earth, Venus, Mars, Mercury, S ...
... C. believed the Earth went around the Sun. D. made very accurate predictions of planetary motion. E. believed the Sun went around the Earth. 22. The Copernican universe has in order of increasing distance from the sun A. Mercury, Venus, Mars, Earth, Jupiter, Saturn. B. Earth, Venus, Mars, Mercury, S ...
Properties of Stars - Montana State University Extended University
... A poorly selected sample that is unrepresentative of the larger set can lead to biased results. Such biases can be found in any sample of objects or people. Public officials and politicians who base their decisions on what the polls say people believe or think about different issues, are usually wor ...
... A poorly selected sample that is unrepresentative of the larger set can lead to biased results. Such biases can be found in any sample of objects or people. Public officials and politicians who base their decisions on what the polls say people believe or think about different issues, are usually wor ...
Next Generation VLA Science White Paper
... document we discuss the motivation to build such a facility from the perspective of this broad “galaxy ecosystems” area. We describe how the ngVLA will emphasize the qualitative improvement in the diagnostic power of such a telescope. It would represent an enormous improvement even beyond ALMA as bo ...
... document we discuss the motivation to build such a facility from the perspective of this broad “galaxy ecosystems” area. We describe how the ngVLA will emphasize the qualitative improvement in the diagnostic power of such a telescope. It would represent an enormous improvement even beyond ALMA as bo ...
Comparison of low- and high-mass star formation
... McKee–Tan core (McKee & Tan 2003). However, the “cores” so identified are transient objects that are not in equilibrium. They are evolving constantly, with mass growing (from converging or collapsing flow) and depleting (into one or more collapsed objects) at the same time. The replenishment of dens ...
... McKee–Tan core (McKee & Tan 2003). However, the “cores” so identified are transient objects that are not in equilibrium. They are evolving constantly, with mass growing (from converging or collapsing flow) and depleting (into one or more collapsed objects) at the same time. The replenishment of dens ...
Stellar Evolution
... Evolution of Stars More Massive than the Sun A star of more than 8 solar masses can fuse elements far beyond carbon in its core, leading to a very different fate Its path across the H-R diagram is essentially a straight line It stays at just about the same luminosity as it cools off Eventually the ...
... Evolution of Stars More Massive than the Sun A star of more than 8 solar masses can fuse elements far beyond carbon in its core, leading to a very different fate Its path across the H-R diagram is essentially a straight line It stays at just about the same luminosity as it cools off Eventually the ...
PDF format
... have very short lifetimes. c) False, stars have similar lifetimes despite their different masses. d) False, more massive stars are much more luminous than low mass stars and use up their hydrogen faster, even though they have more of it. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... have very short lifetimes. c) False, stars have similar lifetimes despite their different masses. d) False, more massive stars are much more luminous than low mass stars and use up their hydrogen faster, even though they have more of it. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Here
... this rate is appreciable, we find it is overwhelmed by the second new source of energy, the radiation from the protostar and its surrounding disk. This luminosity stems from the kinetic energy of infall and is generated at the stellar and disk surfaces (Chapter 11). It is the dust grains within the ...
... this rate is appreciable, we find it is overwhelmed by the second new source of energy, the radiation from the protostar and its surrounding disk. This luminosity stems from the kinetic energy of infall and is generated at the stellar and disk surfaces (Chapter 11). It is the dust grains within the ...
Anatomy of a Supernova - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... models was that the supersonic waves moved so rapidly that the stellar material couldn't expand before it burned. Since combustion at very bigh densities and temperatures is extremely thorough, everything that can burn, does. All that's left are iron, cobalt, and nickel — the socalled iron-peak elem ...
... models was that the supersonic waves moved so rapidly that the stellar material couldn't expand before it burned. Since combustion at very bigh densities and temperatures is extremely thorough, everything that can burn, does. All that's left are iron, cobalt, and nickel — the socalled iron-peak elem ...
Lecture 13 Main Sequence and Low Mass Evolution
... young as they only live for a few Million years. • You can’t tell how old an M dwarf is because their lives can be so long. • The Sun is ~ 5 Billion years old, so it will last only for ~ 5 Billion years longer. ...
... young as they only live for a few Million years. • You can’t tell how old an M dwarf is because their lives can be so long. • The Sun is ~ 5 Billion years old, so it will last only for ~ 5 Billion years longer. ...
Worked Problem In a spherical galaxy, the density of matter varies
... the planet, travelling around the Sun, goes over and over the same elliptical orbit as a result. The ratio of the two periods Tθ /Tr is in general not a rational number, and so the typical orbit of a star in a spherically symmetric potential will be a rosette bound between two concentric circles of ...
... the planet, travelling around the Sun, goes over and over the same elliptical orbit as a result. The ratio of the two periods Tθ /Tr is in general not a rational number, and so the typical orbit of a star in a spherically symmetric potential will be a rosette bound between two concentric circles of ...
the text the talk here
... clockwork universe. In the fifth century BC, geometry as a deductive system developed rapidly in Athens. In terms of philosophy, geometry was seen as a procedure for establishing indisputable truths about the real world. Raphael’s Plato holds his right index finger aloft, gesturing towards the heave ...
... clockwork universe. In the fifth century BC, geometry as a deductive system developed rapidly in Athens. In terms of philosophy, geometry was seen as a procedure for establishing indisputable truths about the real world. Raphael’s Plato holds his right index finger aloft, gesturing towards the heave ...
LESSON 8: STARS
... The most apparent difference between high mass (10 to 30 solar masses) and low mass (0.5 to 10 solar masses) stars are the events leading up to the eventual death of the star. Low mass stars do not have the mass required to increase the core temperature enough to allow the carbon to fuse into heavie ...
... The most apparent difference between high mass (10 to 30 solar masses) and low mass (0.5 to 10 solar masses) stars are the events leading up to the eventual death of the star. Low mass stars do not have the mass required to increase the core temperature enough to allow the carbon to fuse into heavie ...
Continuous Spectrum—Kirchoff`s First Law
... This plot shows us that the main sequence is a mass sequence. The more massive a main sequence star is, the brighter and hotter it is. To understand this, we will consider the physics that goes on inside of stars. For the moment, we will just take it as a fact that we have determined observationally ...
... This plot shows us that the main sequence is a mass sequence. The more massive a main sequence star is, the brighter and hotter it is. To understand this, we will consider the physics that goes on inside of stars. For the moment, we will just take it as a fact that we have determined observationally ...
General Astrophysics And Comparative Planetology
... planetology we mean the study of all the components of planetary systems, including planets, small body belts, and dust; by comparative planetology, we mean considering a planetary system’s components collectively and making comparisons among different planetary systems, including the solar system. ...
... planetology we mean the study of all the components of planetary systems, including planets, small body belts, and dust; by comparative planetology, we mean considering a planetary system’s components collectively and making comparisons among different planetary systems, including the solar system. ...