Evidence for a signature of the galactic bar in the solar neighbourhood
... 3. Kinematical properties of the sample For the preparation of the HIPPARCOS mission and for the obtention of photometric and kinematic data complementary to astrometry, all programme stars south of δ = +10◦ were observed at the Swiss telescope at La Silla, from 1981 on. A total of 39435 measurement ...
... 3. Kinematical properties of the sample For the preparation of the HIPPARCOS mission and for the obtention of photometric and kinematic data complementary to astrometry, all programme stars south of δ = +10◦ were observed at the Swiss telescope at La Silla, from 1981 on. A total of 39435 measurement ...
Supernovae
... the final stages of evolution. The mass of the remaining white dwarf is always less than the Chandrasekhar limit, 1.4 M . A white dwarf, consisting mainly of C and O and detached degenerate electrons (the term degenerate means that electrons occupy all possible quantum states below a certain energy ...
... the final stages of evolution. The mass of the remaining white dwarf is always less than the Chandrasekhar limit, 1.4 M . A white dwarf, consisting mainly of C and O and detached degenerate electrons (the term degenerate means that electrons occupy all possible quantum states below a certain energy ...
Introduction
... information on the contribution of low and intermediate mass stars to the interstellar medium can be obtained. With the aid of evolutionary models the nucleosynthetic history of the star can be reconstructed to learn the detailed history and characteristics of the progenitor star from which it evolv ...
... information on the contribution of low and intermediate mass stars to the interstellar medium can be obtained. With the aid of evolutionary models the nucleosynthetic history of the star can be reconstructed to learn the detailed history and characteristics of the progenitor star from which it evolv ...
Low-Res Version - Chandra X
... sun. Its mass has been estimated at 120 times the mass of our sun, making it a candidate for the most massive known star in our galaxy. The Chandra observation shows three distinct structures: an outer, horseshoe-shaped ring associated with a shock wave from matter blown away from the star about 200 ...
... sun. Its mass has been estimated at 120 times the mass of our sun, making it a candidate for the most massive known star in our galaxy. The Chandra observation shows three distinct structures: an outer, horseshoe-shaped ring associated with a shock wave from matter blown away from the star about 200 ...
Neutron Stars, first class
... presence of iron nuclei that can survive at law densities, but will progressively disintegrate beyond the neutron drip density (4 1011 g/cm3) ...
... presence of iron nuclei that can survive at law densities, but will progressively disintegrate beyond the neutron drip density (4 1011 g/cm3) ...
Chapter 15 Surveying the Stars
... • All stars become larger and redder after exhausting their core hydrogen: giants and supergiants. • Most stars end up small and white after fusion has ceased: white dwarfs. © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... • All stars become larger and redder after exhausting their core hydrogen: giants and supergiants. • Most stars end up small and white after fusion has ceased: white dwarfs. © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Galaxies and Stars
... 19. The star Algol is estimated to have approximately the same luminosity as the star Aldebaran approximately the same temperature as the Rigel. Algol is best classified as a A) main sequence star C) white dwarf star ...
... 19. The star Algol is estimated to have approximately the same luminosity as the star Aldebaran approximately the same temperature as the Rigel. Algol is best classified as a A) main sequence star C) white dwarf star ...
Student Paper (Klongcheongsan)
... equations from the center outwards to the fitting point at the mass fraction equal to about 0.5 of the solar mass using boundary values of temperature and mass density at the center. It is normal to integrate the stellar structure equations from the surface inwards to the fitting point using outer b ...
... equations from the center outwards to the fitting point at the mass fraction equal to about 0.5 of the solar mass using boundary values of temperature and mass density at the center. It is normal to integrate the stellar structure equations from the surface inwards to the fitting point using outer b ...
Star formation PowerPoint
... The differences between the H-R diagrams of open and globular clusters are that the globular clusters are very old, whereas the open clusters are much younger. The absence of massive main sequence stars in the globular cluster is due to its extreme age—those stars have already used up their fuel and ...
... The differences between the H-R diagrams of open and globular clusters are that the globular clusters are very old, whereas the open clusters are much younger. The absence of massive main sequence stars in the globular cluster is due to its extreme age—those stars have already used up their fuel and ...
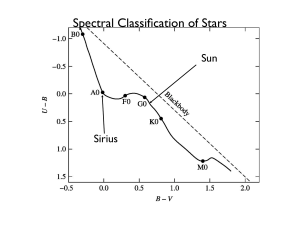
Compa ring between Spectroscopic and Photometric Method for
... This is the most popular and accessible method in astronomy. Photometry is the measurement of the intensity of electromagnetic radiation usually expressed in apparent magnitude. Apparent magnitude is a numerical scale to describe how bright each star appears in the sky. The lower the magnitude, the ...
... This is the most popular and accessible method in astronomy. Photometry is the measurement of the intensity of electromagnetic radiation usually expressed in apparent magnitude. Apparent magnitude is a numerical scale to describe how bright each star appears in the sky. The lower the magnitude, the ...
HR Diagram Explorer
... indicated by a red x. This active location can be dragged around the diagram. The options panel allows you control the variables plotted on the x-axis: (temperature, B-V, or spectral type) and those plotted on the y-axis (luminosity or absolute magnitude). One can also show the main sequence, lumino ...
... indicated by a red x. This active location can be dragged around the diagram. The options panel allows you control the variables plotted on the x-axis: (temperature, B-V, or spectral type) and those plotted on the y-axis (luminosity or absolute magnitude). One can also show the main sequence, lumino ...
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Lab - Introduction to Astronomy
... those motions to the Earth’s seasons, variation in day length, and climate and to the development of the calendar Learning objectives What you will learn as you master the competency: a. ...
... those motions to the Earth’s seasons, variation in day length, and climate and to the development of the calendar Learning objectives What you will learn as you master the competency: a. ...
Lecture 1 - X-ray and Observational Astronomy Group
... elements e.g. Ca and Fe. The corona displays a number of features including; streamers, plumes, coronal loops and holes. Coronal gas hot enough to emit low energy X-rays X-ray images show irregular gas distribution Large loop structures hot gas trapped in magnetic loops Dark regions (gas less hot ...
... elements e.g. Ca and Fe. The corona displays a number of features including; streamers, plumes, coronal loops and holes. Coronal gas hot enough to emit low energy X-rays X-ray images show irregular gas distribution Large loop structures hot gas trapped in magnetic loops Dark regions (gas less hot ...
Dust in Space - Max-Planck
... does cosmic dust come from? How is it distributed in galaxies? What does comet dust reveal about the emergence of our solar system? These are just some of the questions the scientists are trying to answer. This year, the conference took place in Germany for the first time. The organizers could not h ...
... does cosmic dust come from? How is it distributed in galaxies? What does comet dust reveal about the emergence of our solar system? These are just some of the questions the scientists are trying to answer. This year, the conference took place in Germany for the first time. The organizers could not h ...
astronomy
... stones that are thought to have been aligned to track the movements of the Sun and Moon and to measure eclipses. Around 1300 BC, Chinese astronomers embarked on a long, precise study of eclipses, recording 900 solar eclipses and 600 lunar eclipses over the next 2600 years. In about 700 BC, the Babyl ...
... stones that are thought to have been aligned to track the movements of the Sun and Moon and to measure eclipses. Around 1300 BC, Chinese astronomers embarked on a long, precise study of eclipses, recording 900 solar eclipses and 600 lunar eclipses over the next 2600 years. In about 700 BC, the Babyl ...
Question 1 The rings of Saturn are seen by Answer 1. reflected and
... . We have seen that electron degeneracy occurs when the carbon core of a white dwarf becomes dense enough. We have also seen that neutron degeneracy occurs when a neutron star becomes dense enough. Why do you suppose we do not find “proton degeneracy” in some density range between electron and ne ...
... . We have seen that electron degeneracy occurs when the carbon core of a white dwarf becomes dense enough. We have also seen that neutron degeneracy occurs when a neutron star becomes dense enough. Why do you suppose we do not find “proton degeneracy” in some density range between electron and ne ...
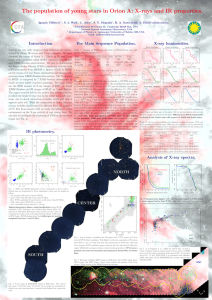
The population of young stars in Orion A: X-rays and... Ignazio Pillitteri , S. J. Wolk , L. Allen
... Through Spitzer and XMM-Newton we identify ∼ 702 PMS stars that emit in X-rays out of 1060 X-ray sources. By assuming the same fraction of X-ray detection of WTT stars and CTT stars we estimate a population of ∼ 1850 PMS stars, for an overall detection efficiency of ∼ 38% among PMS stars and a mean ...
... Through Spitzer and XMM-Newton we identify ∼ 702 PMS stars that emit in X-rays out of 1060 X-ray sources. By assuming the same fraction of X-ray detection of WTT stars and CTT stars we estimate a population of ∼ 1850 PMS stars, for an overall detection efficiency of ∼ 38% among PMS stars and a mean ...
Measuring Distance in the Universe
... that you can probably make those calculations yourself. I guess the difficulty comes in the precision of the distance, right? The measurements. Pamela: you have to know very precisely how far apart you and your friend are. And then you need to make very careful measurements of the distance to the st ...
... that you can probably make those calculations yourself. I guess the difficulty comes in the precision of the distance, right? The measurements. Pamela: you have to know very precisely how far apart you and your friend are. And then you need to make very careful measurements of the distance to the st ...